This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(December 2025) |
County of Apulia and Calabria | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1043–1130 | |||||||||||||||||
| Motto: Servire Nescit (Latin) | |||||||||||||||||
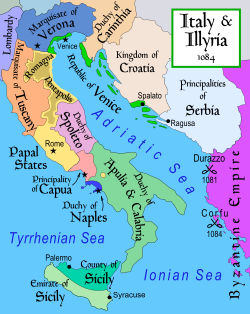 The Duchy (in green) in the political context of Italy and the Balkans in 1084. | |||||||||||||||||
| Status | Vassal state of the Papacy | ||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Melfi (1043–1077) Salerno (1077–1130) | ||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | |||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism Greek Orthodoxy | ||||||||||||||||
| Demonyms | Normans (generally), Lombards, Apulians, Calabrians | ||||||||||||||||
| Government | Feudal monarchy | ||||||||||||||||
| Count/Duke | |||||||||||||||||
• 1043–1046 | William I | ||||||||||||||||
• 1059–1085 | Robert I | ||||||||||||||||
• 1085–1111 | Roger Borsa | ||||||||||||||||
• 1111–1127 | William II | ||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||||||||||
| 1043 | |||||||||||||||||
• Emperor Henry III recognizes the County | 1047 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1053 | |||||||||||||||||
• Treaty of Melfi; the County becomes a Duchy | 1059 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1076 | |||||||||||||||||
• Death of the childless William II | 1127 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1130 | |||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Follis (common) | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | Italy | ||||||||||||||||
The County of Apulia and Calabria (Latin : Comitatus Apuliae et Calabriae), later the Duchy of Apulia and Calabria (Latin: Ducatus Apuliae et Calabriae), was a Norman state founded by William of Hauteville in 1043, composed of the territories of Gargano, Capitanata, Apulia, Vulture, and most of Campania. It became a duchy when Robert Guiscard was raised to the rank of duke by Pope Nicholas II in 1059.
Contents
- Creation
- Duchy of Apulia and Calabria
- List of counts and dukes
- Azzo of Spoleto (Duke of Calabria)
- Melus of Bari (Duke of Apulia)
- Guaimar of Salerno (Duke of Apulia and Calabria)
- References
- External links
The duchy was disestablished in 1130, when the last duke of Apulia and Calabria, Roger II, became King of Sicily. The title of duke was thereafter used intermittently as a title for the heir apparent to the Kingdom of Sicily.


