Related Research Articles
In politics, soft power is the ability to co-opt rather than coerce. It involves shaping the preferences of others through appeal and attraction. Soft power is non-coercive, using culture, political values, and foreign policies to enact change. In 2012, Joseph Nye of Harvard University explained that with soft power, "the best propaganda is not propaganda", further explaining that during the Information Age, "credibility is the scarcest resource".

The National Endowment for Democracy (NED) is a quasi-autonomous non-governmental organization in the United States founded in 1983 with the stated aim of advancing democracy worldwide, by promoting political and economic institutions, such as political groups, trade unions, free markets, and business groups.
The term "illiberal democracy" describes a governing system that hides its "nondemocratic practices behind formally democratic institutions and procedures". There is a lack of consensus among experts about the exact definition of illiberal democracy or whether it even exists.

The National Democratic Institute (NDI) is a non-profit American non-governmental organization whose stated mission is to "support and strengthen democratic institutions worldwide through citizen participation, openness and accountability". It is funded primarily by the United States and other Western governments, by major corporations and by nonprofits like the Open Society Foundations.

Larry Jay Diamond is an American political sociologist and leading contemporary scholar in the field of democracy studies. Diamond is a senior fellow at the Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies, Stanford University's main center for research on international issues. At the Institute Diamond served as the director of the Center on Democracy, Development, and the Rule of Law from 2009-2016. He was succeeded in that role by Francis Fukuyama and then Kathryn Stoner.
A government-organized non-governmental organization (GONGO) is a non-governmental organization that was set up or sponsored by a government in order to further its political interests and mimic the civic groups and civil society at home, or promote its international or geopolitical interests abroad.
Guided democracy, also called directed democracy and managed democracy, is a formally democratic government that functions as a de facto authoritarian government or, in some cases, as an autocratic government. Such hybrid regimes are legitimized by elections, but do not change the state's policies, motives, and goals.

Liberal democracy, western-style democracy, or substantive democracy is a form of government that combines the organization of a democracy with ideas of liberal political philosophy.

The U.S.-Middle East Partnership Initiative (MEPI) is a United States State Department program that fosters meaningful and effective partnerships between citizens, civil society, the private sector, and governments in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region to resolve local challenges and promote shared interests in the areas of participatory governance and economic opportunity and reform.
State media are typically understood as media outlets that are owned, operated, or significantly influenced by the government. They are distinguished from public service media, which are designed to serve the public interest, operate independently of government control, and are financed through a combination of public funding, licensing fees, and sometimes advertising. The crucial difference lies in the level of independence from government influence and the commitment to serving a broad public interest rather than the interests of a specific political party or government agenda.
In international relations, the term smart power refers to the combination of hard power and soft power strategies. It is defined by the Center for Strategic and International Studies as "an approach that underscores the necessity of a strong military, but also invests heavily in alliances, partnerships, and institutions of all levels to expand one's influence and establish legitimacy of one's action."
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political status quo, and reductions in democracy, separation of powers, civil liberties, and the rule of law. Political scientists have created many typologies describing variations of authoritarian forms of government. Authoritarian regimes may be either autocratic or oligarchic and may be based upon the rule of a party or the military. States that have a blurred boundary between democracy and authoritarianism have some times been characterized as "hybrid democracies", "hybrid regimes" or "competitive authoritarian" states.

Democracy promotion by the United States aims to encourage governmental and non-governmental actors to pursue political reforms that will lead ultimately to democratic governance.
A hybrid regime is a type of political system often created as a result of an incomplete democratic transition from an authoritarian regime to a democratic one. Hybrid regimes are categorized as having a combination of autocratic features with democratic ones and can simultaneously hold political repressions and regular elections. Hybrid regimes are commonly found in developing countries with abundant natural resources such as petro-states. Although these regimes experience civil unrest, they may be relatively stable and tenacious for decades at a time. There has been a rise in hybrid regimes since the end of the Cold War.
The International Forum for Democratic Studies (IFDS) is an analytical initiative of the National Endowment for Democracy (NED). Established in April 1994, its programs include the Journal of Democracy, the Network of Democracy Research Institutes, and fellowship programs such as the Reagan–Fascell Democracy Fellowship.

Political warfare is the use of hostile political means to compel an opponent to do one's will. The term political describes the calculated interaction between a government and a target audience, including another state's government, military, and/or general population. Governments use a variety of techniques to coerce certain actions, thereby gaining relative advantage over an opponent. The techniques include propaganda and psychological operations ("PsyOps"), which service national and military objectives respectively. Propaganda has many aspects and a hostile and coercive political purpose. Psychological operations are for strategic and tactical military objectives and may be intended for hostile military and civilian populations.
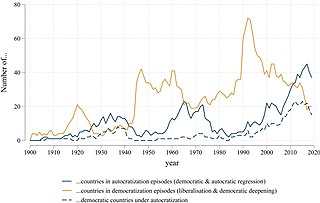
Democratic backsliding is a process of regime change toward autocracy in which the exercise of political power becomes more arbitrary and repressive. The process typically restricts the space for public contest and political participation in the process of government selection. Democratic decline involves the weakening of democratic institutions, such as the peaceful transition of power or free and fair elections, or the violation of individual rights that underpin democracies, especially freedom of expression. Democratic backsliding is the opposite of democratization.
Authoritarian capitalism, or illiberal capitalism, is an economic system in which a capitalist market economy exists alongside an authoritarian government. Related to and overlapping with state capitalism, a system in which the state undertakes commercial activity, authoritarian capitalism combines private property and the functioning of market forces with repression of dissent, restrictions on freedom of speech and either a lack of elections or an electoral system with a single dominant political party.
The G7 Rapid Response Mechanism (RRM) is an initiative introduced in the "Charlevoix Commitment on Defending Democracy from Foreign Threats", issued by the leaders of the Group of Seven (G7) countries—United States, Canada, Japan, United Kingdom, France, Germany and Italy—on June 9, 2018, during their summit in Charlevoix, Quebec. The RRM's mandate is to strengthen the coordination of G7 member countries, as well as
"to identify and respond to diverse and evolving threats to our democracies, including through sharing information and analysis, and identifying opportunities for coordinated response"

Shanthi Kalathil is an American foreign policy analyst and former journalist, currently serving as a Washington D.C.-based senior fellow at the University of Southern California's Center on Communication Leadership and Policy and a visiting senior fellow at the German Marshall Fund's Alliance for Securing Democracy, where her work focuses on strengthening global democratic resilience in countering authoritarian influence. She is also a board member of the National Democratic Institute and Radio Free Asia.
References
- ↑ Walker, Christopher; Ludwig, Jessica (16 November 2017). "The Meaning of Sharp Power". Foreign Affairs.
- ↑ "What is "Sharp Power"?".
- ↑ Historical frequency of use of the phrase
- ↑ Christopher Walker and Jessica Ludwig (November 16, 2017). "The Meaning of Sharp Power: How Authoritarian States Project Influence". Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on September 12, 2018. Retrieved July 11, 2018.
{{cite magazine}}: Cite magazine requires|magazine=(help) - 1 2 3 4 Walker, Christopher (2018). "What Is 'Sharp Power'?". Journal of Democracy. 29 (3): 9–23. doi:10.1353/jod.2018.0041. ISSN 1086-3214. S2CID 158305285.
- ↑ "Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference spokesman addresses Western charges of China using 'sharp power'". China Global Television Network. March 2, 2018. Archived from the original on July 1, 2019. Retrieved July 11, 2018.
- ↑ Wyeth, Grant. "Australia Aims to Combat Disinformation". thediplomat.com. The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 22 June 2020. Retrieved 23 June 2020.