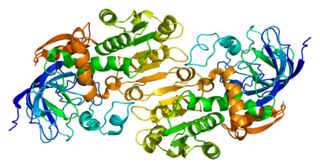
Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) (EC 1.1.1.1) are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to NADH. In humans and many other animals, they serve to break down alcohols that otherwise are toxic, and they also participate in generation of useful aldehyde, ketone, or alcohol groups during biosynthesis of various metabolites. In yeast, plants, and many bacteria, some alcohol dehydrogenases catalyze the opposite reaction as part of fermentation to ensure a constant supply of NAD+.

Acetaldehyde dehydrogenases are dehydrogenase enzymes which catalyze the conversion of acetaldehyde into acetic acid. The oxidation of acetaldehyde to acetate can be summarized as follows:

Methanofurans are a family of chemical compounds found in methanogenic archaea. These species feature a 2-aminomethylfuran linked to phenoxy group. At least three different end groups are recognized: R = tricarboxyheptanoyl (methanofuran), glutamyl-glutamyl, tricarboxy-2-hydroxyheptanoyl.
17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases, also 17-ketosteroid reductases (17-KSR), are a group of alcohol oxidoreductases which catalyze the reduction of 17-ketosteroids and the dehydrogenation of 17β-hydroxysteroids in steroidogenesis and steroid metabolism. This includes interconversion of DHEA and androstenediol, androstenedione and testosterone, and estrone and estradiol.
In enzymology, a cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.195) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a homoserine dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.157) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.3.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alcohol dehydrogenase (acceptor) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a guanylate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Collagen alpha-1(VI) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL6A1 gene.

17-β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase X (HSD10) also known as 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase type-2 is a mitochondrial enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HSD17B10 gene. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified, but the full-length nature of only two transcript variants has been determined. Human HSD10 cDNA was cloned from brain (NM_004493), and the resulting protein, a homotetramer, was first characterized as a short chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SCHAD). Active sites of this enzyme can accommodate different substrates; 17β-HSD10 is involved in the oxidation of isoleucine, branched-chain fatty acids, and xenobiotics as well as the metabolism of sex hormones and neuroactive steroids.

Alcohol dehydrogenase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADH4 gene.

Sorbitol dehydrogenase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SORD gene.

3-keto-steroid reductase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HSD17B7 gene.

Dehydrogenase/reductase SDR family member 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DHRS2 gene.

Carbonyl reductase [NADPH] 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CBR3 gene.
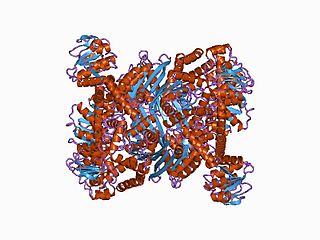
In molecular biology, the ELFV dehydrogenase family of enzymes include glutamate, leucine, phenylalanine and valine dehydrogenases. These enzymes are structurally and functionally related. They contain a Gly-rich region containing a conserved Lys residue, which has been implicated in the catalytic activity, in each case a reversible oxidative deamination reaction.

In molecular biology, group IV pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylases are a family of enzymes comprising ornithine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.17, lysine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.18, arginine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.19 and diaminopimelate decarboxylaseEC 4.1.1.20. It is also known as the Orn/Lys/Arg decarboxylase class-II family.
Alcohol dehydrogenase (nicotinoprotein) is an enzyme with systematic name ethanol:acceptor oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
















