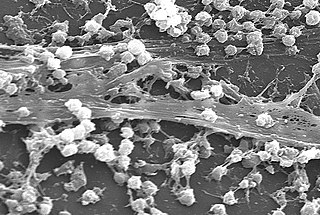
A biofilm is a syntrophic community of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric combination of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have a three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes".

Pseudomonas is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae in the class Gammaproteobacteria. The 313 members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a wide range of niches. Their ease of culture in vitro and availability of an increasing number of Pseudomonas strain genome sequences has made the genus an excellent focus for scientific research; the best studied species include P. aeruginosa in its role as an opportunistic human pathogen, the plant pathogen P. syringae, the soil bacterium P. putida, and the plant growth-promoting P. fluorescens, P. lini, P. migulae, and P. graminis.

Pseudomonas fluorescens is a common Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. It belongs to the Pseudomonas genus; 16S rRNA analysis as well as phylogenomic analysis has placed P. fluorescens in the P. fluorescens group within the genus, to which it lends its name.

Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common encapsulated, Gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, P. aeruginosa is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. P. aeruginosa is able to selectively inhibit various antibiotics from penetrating its outer membrane - and has high resistance to several antibiotics. According to the World Health Organization P. aeruginosa poses one of the greatest threats to humans in terms of antibiotic resistance.

Burkholderia cenocepacia is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in soil and water environments and may also be associated with plants and animals, particularly as a human pathogen. It is one of over 20 species in the Burkholderia cepacia complex (Bcc) and is notable due to its virulence factors and inherent antibiotic resistance that render it a prominent opportunistic pathogen responsible for life-threatening, nosocomial infections in immunocompromised patients, such as those with cystic fibrosis or chronic granulomatous disease. The quorum sensing systems CepIR and CciIR regulate the formation of biofilms and the expression of virulence factors such as siderophores and proteases. Burkholderia cenocepacia may also cause disease in plants, such as in onions and bananas. Additionally, some strains serve as plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria.

Pseudomonas syringae is a rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacterium with polar flagella. As a plant pathogen, it can infect a wide range of species, and exists as over 50 different pathovars, all of which are available to researchers from international culture collections such as the NCPPB, ICMP, and others.
In enzymology, a ferric-chelate reductase (EC 1.16.1.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In biology, an autoinducer is a signaling molecule that enables detection and response to changes in the population density of bacterial cells. Synthesized when a bacterium reproduces, autoinducers pass outside the bacterium and into the surrounding medium. They are a key component of the phenomenon of quorum sensing: as the density of quorum-sensing bacterial cells increases, so does the concentration of the autoinducer. A bacterium’s detection of an autoinducer above some minimum threshold triggers altered gene expression.

Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of these pathogenic species in humans is estimated to be fewer than a hundred. By contrast, several thousand species are part of the gut flora present in the digestive tract.

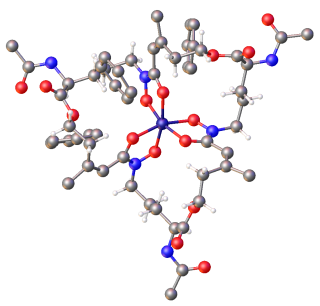
Ferrichrome is a cyclic hexa-peptide that forms a complex with iron atoms. It is a siderophore composed of three glycine and three modified ornithine residues with hydroxamate groups [-N(OH)C(=O)C-]. The 6 oxygen atoms from the three hydroxamate groups bind Fe(III) in near perfect octahedral coordination.

Pyoverdines are fluorescent siderophores produced by certain pseudomonads. Pyoverdines are important virulence factors, and are required for pathogenesis in many biological models of infection. Their contributions to bacterial pathogenesis include providing a crucial nutrient, regulation of other virulence factors, supporting the formation of biofilms, and are increasingly recognized for having toxicity themselves.
Microorganisms engage in a wide variety of social interactions, including cooperation. A cooperative behavior is one that benefits an individual other than the one performing the behavior. This article outlines the various forms of cooperative interactions seen in microbial systems, as well as the benefits that might have driven the evolution of these complex behaviors.

2,6-Pyridinedicarbothioic acid (PDTC) is an organosulfur compound that is produced by some bacteria. It functions as a, a low molecular weight compound that scavenges iron. Siderophores solubilize compounds by forming strong complexes. PDTC is secreted by the soil bacteria Pseudomonas stutzeri and Pseudomonas putida.
Many bacteria secrete small iron-binding molecules called siderophores, which bind strongly to ferric ions. FepA is an integral bacterial outer membrane porin protein that belongs to outer membrane receptor family and provides the active transport of iron bound by the siderophore enterobactin from the extracellular space, into the periplasm of Gram-negative bacteria. FepA has also been shown to transport vitamin B12, and colicins B and D as well. This protein belongs to family of ligand-gated protein channels.
Membrane vesicle trafficking in eukaryotic animal cells involves movement of biochemical signal molecules from synthesis-and-packaging locations in the Golgi body to specific release locations on the inside of the plasma membrane of the secretory cell. It takes place in the form of Golgi membrane-bound micro-sized vesicles, termed membrane vesicles (MVs).
Siderocalin(Scn), lipocalin-2, NGAL, 24p3 is a mammalian lipocalin-type protein that can prevent iron acquisition by pathogenic bacteria by binding siderophores, which are iron-binding chelators made by microorganisms. Iron serves as a key nutrient in host-pathogen interactions, and pathogens can acquire iron from the host organism via synthesis and release siderophores such as enterobactin. Siderocalin is a part of the mammalian defence mechanism and acts as an antibacterial agent. Crystallographic studies of Scn demonstrated that it includes a calyx, a ligand-binding domain that is lined with polar cationic groups. Central to the siderophore/siderocalin recognition mechanism are hybrid electrostatic/cation-pi interactions. To evade the host defences, pathogens evolved to produce structurally varied siderophores that would not be recognized by siderocalin, allowing the bacteria to acquire iron.

The type VI secretion system (T6SS) is one of the bacterial secretion systems, membrane protein complexes, used by a wide range of gram-negative bacteria to transport effectors. Effectors are moved from the interior of a bacterial cell, across the membrane into an adjacent target cell. While often reported that the T6SS was discovered in 2006 by researchers studying the causative agent of cholera, Vibrio cholerae, the first study demonstrating that T6SS genes encode a protein export apparatus was actually published in 2004, in a study of protein secretion by the fish pathogen Edwardsiella tarda.

Caenorhabditis elegans- microbe interactions are defined as any interaction that encompasses the association with microbes that temporarily or permanently live in or on the nematode C. elegans. The microbes can engage in a commensal, mutualistic or pathogenic interaction with the host. These include bacterial, viral, unicellular eukaryotic, and fungal interactions. In nature C. elegans harbours a diverse set of microbes. In contrast, C. elegans strains that are cultivated in laboratories for research purposes have lost the natural associated microbial communities and are commonly maintained on a single bacterial strain, Escherichia coli OP50. However, E. coli OP50 does not allow for reverse genetic screens because RNAi libraries have only been generated in strain HT115. This limits the ability to study bacterial effects on host phenotypes. The host microbe interactions of C. elegans are closely studied because of their orthologs in humans. Therefore, the better we understand the host interactions of C. elegans the better we can understand the host interactions within the human body.
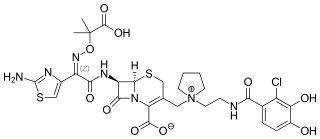
Cefiderocol, sold under the brand name Fetroja among others, is an antibiotic used to treat complicated urinary tract infections when no other options are available. It is indicated for the treatment of multi-drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It is given by injection into a vein.

Elisa Teresa Granato is a molecular microbiologist in the Departments of Zoology and Biochemistry at the University of Oxford, where she researches bacterial interactions and how they evolved, including the significance of features of bacteria that contribute to disease, also known as virulence factors.