In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.

In geometry, the snub dodecahedron, or snub icosidodecahedron, is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.

In particle physics, Fermi's interaction is an explanation of the beta decay, proposed by Enrico Fermi in 1933. The theory posits four fermions directly interacting with one another. This interaction explains beta decay of a neutron by direct coupling of a neutron with an electron, a neutrino and a proton.

In geometry, a deltoidal hexecontahedron is a Catalan solid which is the dual polyhedron of the rhombicosidodecahedron, an Archimedean solid. It is one of six Catalan solids to not have a Hamiltonian path among its vertices.

In geometry, a pentagonal hexecontahedron is a Catalan solid, dual of the snub dodecahedron. It has two distinct forms, which are mirror images of each other. It has 92 vertices that span 60 pentagonal faces. It is the Catalan solid with the most vertices. Among the Catalan and Archimedean solids, it has the second largest number of vertices, after the truncated icosidodecahedron, which has 120 vertices.

In geometry, Euler's rotation theorem states that, in three-dimensional space, any displacement of a rigid body such that a point on the rigid body remains fixed, is equivalent to a single rotation about some axis that runs through the fixed point. It also means that the composition of two rotations is also a rotation. Therefore the set of rotations has a group structure, known as a rotation group.

In mathematics, the plastic ratio is a geometrical proportion close to 53/40. Its true value is the real solution of the equation x3 = x + 1.

In geometry, the great snub icosidodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U57. It has 92 faces (80 triangles and 12 pentagrams), 150 edges, and 60 vertices. It can be represented by a Schläfli symbol sr{5⁄2,3}, and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram .

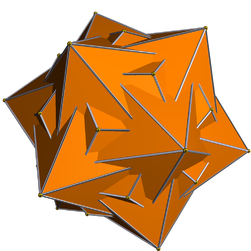
In geometry, the small snub icosicosidodecahedron or snub disicosidodecahedron is a uniform star polyhedron, indexed as U32. It has 112 faces (100 triangles and 12 pentagrams), 180 edges, and 60 vertices. Its stellation core is a truncated pentakis dodecahedron. It also called a holosnub icosahedron, ß{3,5}.

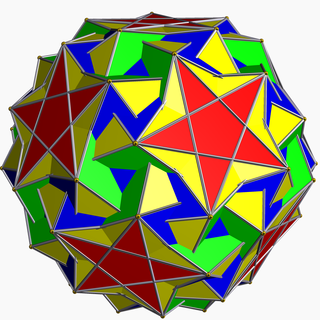
In geometry, the snub dodecadodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U40. It has 84 faces (60 triangles, 12 pentagons, and 12 pentagrams), 150 edges, and 60 vertices. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{5⁄2,5}, as a snub great dodecahedron.
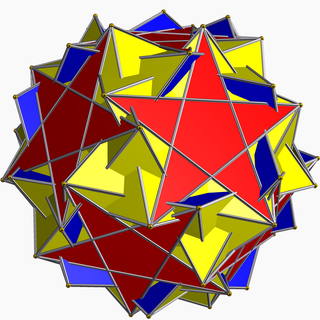
In geometry, the inverted snub dodecadodecahedron (or vertisnub dodecadodecahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U60. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{5/3,5}.
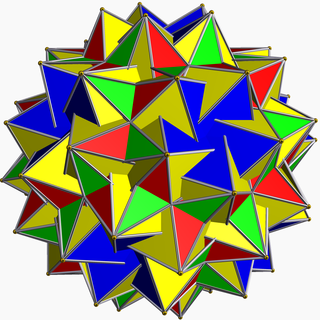
In geometry, the great snub dodecicosidodecahedron (or great snub dodekicosidodecahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U64. It has 104 faces (80 triangles and 24 pentagrams), 180 edges, and 60 vertices. It has Coxeter diagram . It has the unusual feature that its 24 pentagram faces occur in 12 coplanar pairs.

In geometry, the great inverted snub icosidodecahedron (or great vertisnub icosidodecahedron) is a uniform star polyhedron, indexed as U69. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{5⁄3,3}, and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram . In the book Polyhedron Models by Magnus Wenninger, the polyhedron is misnamed great snub icosidodecahedron, and vice versa.
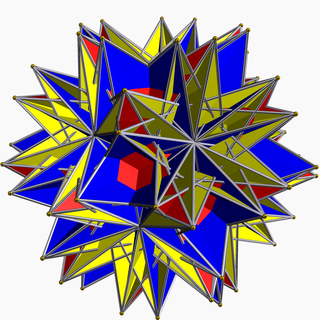
In geometry, the small retrosnub icosicosidodecahedron (also known as a retrosnub disicosidodecahedron, small inverted retrosnub icosicosidodecahedron, or retroholosnub icosahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U72. It has 112 faces (100 triangles and 12 pentagrams), 180 edges, and 60 vertices. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{⁵/₃,³/₂}.
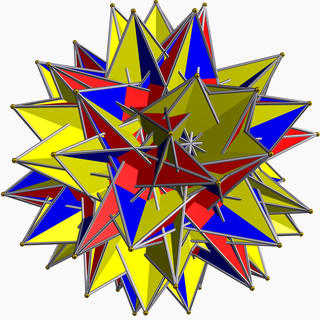
In geometry, the great retrosnub icosidodecahedron or great inverted retrosnub icosidodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U74. It has 92 faces (80 triangles and 12 pentagrams), 150 edges, and 60 vertices. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{3⁄2,5⁄3}.
A hydrogen-like atom (or hydrogenic atom) is any atom or ion with a single valence electron. These atoms are isoelectronic with hydrogen. Examples of hydrogen-like atoms include, but are not limited to, hydrogen itself, all alkali metals such as Rb and Cs, singly ionized alkaline earth metals such as Ca+ and Sr+ and other ions such as He+, Li2+, and Be3+ and isotopes of any of the above. A hydrogen-like atom includes a positively charged core consisting of the atomic nucleus and any core electrons as well as a single valence electron. Because helium is common in the universe, the spectroscopy of singly ionized helium is important in EUV astronomy, for example, of DO white dwarf stars.

In geometry, the medial pentagonal hexecontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the snub dodecadodecahedron. It has 60 intersecting irregular pentagonal faces.

In geometry, the great hexagonal hexecontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the uniform great snub dodecicosidodecahedron. It is partially degenerate, having coincident vertices, as its dual has coplanar pentagrammic faces.
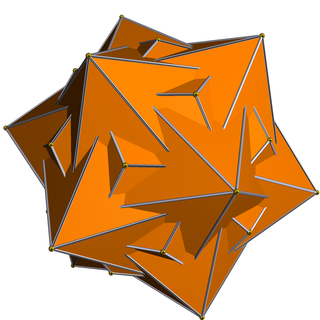
In geometry, the medial hexagonal hexecontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the uniform snub icosidodecadodecahedron.