
Hopanoids are a diverse subclass of triterpenoids with the same hydrocarbon skeleton as the compound hopane. This group of pentacyclic molecules therefore refers to simple hopenes, hopanols and hopanes, but also to extensively functionalized derivatives such as bacteriohopanepolyols (BHPs) and hopanoids covalently attached to lipid A.
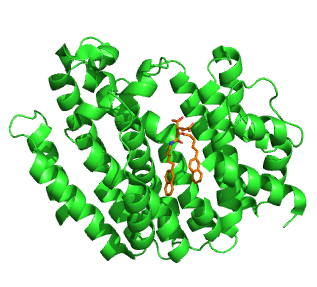
Squalene synthase (SQS) or farnesyl-diphosphate:farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyl transferase is an enzyme localized to the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. SQS participates in the isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway, catalyzing a two-step reaction in which two identical molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) are converted into squalene, with the consumption of NADPH. Catalysis by SQS is the first committed step in sterol synthesis, since the squalene produced is converted exclusively into various sterols, such as cholesterol, via a complex, multi-step pathway. SQS belongs to squalene/phytoene synthase family of proteins.
(S)-2,3-Oxidosqualene ((S)-2,3-epoxysqualene) is an intermediate in the synthesis of the cell membrane sterol precursors lanosterol and cycloartenol, as well as saponins. It is formed when squalene is oxidized by the enzyme squalene monooxygenase. 2,3-Oxidosqualene is the substrate of various oxidosqualene cyclases, including lanosterol synthase, which produces lanosterol, a precursor to cholesterol.

Lanosterol synthase is an oxidosqualene cyclase (OSC) enzyme that converts (S)-2,3-oxidosqualene to a protosterol cation and finally to lanosterol. Lanosterol is a key four-ringed intermediate in cholesterol biosynthesis. In humans, lanosterol synthase is encoded by the LSS gene.

Prenyltransferases (PTs) are a class of enzymes that transfer allylic prenyl groups to acceptor molecules. Prenyl transferases commonly refer to isoprenyl diphosphate syntheses (IPPSs). Prenyltransferases are a functional category and include several enzyme groups that are evolutionarily independent.
In enzymology, a cycloartenol synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Vetispiradiene synthase is an enzyme from Egyptian henbane that catalyzes the following chemical reaction:
Botryococcus squalene synthase (EC 1.3.1.96, SSL-2 (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name squalene:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dammarenediol II synthase (EC 4.2.1.125, dammarenediol synthase, 2,3-oxidosqualene (20S)-dammarenediol cyclase, DDS, (S)-squalene-2,3-epoxide hydro-lyase (dammarenediol-II forming)) is an enzyme with systematic name (3S)-2,3-epoxy-2,3-dihydrosqualene hydro-lyase (dammarenediol-II forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Squalene—hopanol cyclase (EC 4.2.1.129, squalene—hopene cyclase) is an enzyme with systematic name hopan-22-ol hydro-lyase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Sporulenol synthase (EC 4.2.1.137, sqhC (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name tetraprenyl-β-curcumene—sporulenol cyclase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
γ-Terpinene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name geranyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(–)-β-Pinene synthase (EC 4.2.3.120, β-geraniolene synthase, (–)-(1S,5S)-pinene synthase, geranyldiphosphate diphosphate lyase (pinene forming)) is an enzyme with systematic name geranyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase [cyclizing, (–)-β-pinene-forming]. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Squalene-hopene cyclase (SHC) (EC 5.4.99.17) or hopan-22-ol hydro-lyase is an enzyme in the terpene cyclase/mutase family. It catalyzes the interconversion of squalene into a pentacyclic triterpenes, hopene and hopanol. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reactions.
Dammaradiene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name squalene mutase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction: squalene dammara-20,24-diene
β-amyrin synthase is an enzyme with systematic name (3S)-2,3-epoxy-2,3-dihydrosqualene mutase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Lupeol synthase is an enzyme with systematic name (3S)-2,3-epoxy-2,3-dihydrosqualene mutase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Terpentedienyl-diphosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name terpentedienyl-diphosphate lyase (decyclizing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Oxidosqualene cyclases (OSC) are enzymes involved in cyclization reactions of 2,3-oxidosqualene to form sterols or triterpenes.

Tetrahymanol is a gammacerane-type membrane lipid first found in the marine ciliate Tetrahymena pyriformis. It was later found in other ciliates, fungi, ferns, and bacteria. After being deposited in sediments that compress into sedimentary rocks over millions of years, tetrahymanol is dehydroxylated into gammacerane. Gammacerane has been interpreted as a proxy for ancient water column stratification.







