Related Research Articles
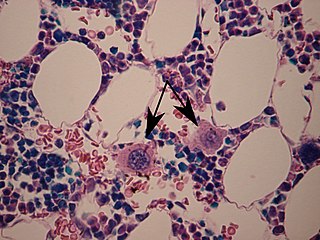
A megakaryocyte is a large bone marrow cell with a lobated nucleus responsible for the production of blood thrombocytes (platelets), which are necessary for normal blood clotting. In humans, megakaryocytes usually account for 1 out of 10,000 bone marrow cells, but can increase in number nearly 10-fold during the course of certain diseases. Owing to variations in combining forms and spelling, synonyms include megalokaryocyte and megacaryocyte.

Thrombopoietin (THPO) also known as megakaryocyte growth and development factor (MGDF) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the THPO gene.

Exenatide, sold under the brand name Byetta and Bydureon among others, is a medication used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2. It is used together with diet, exercise, and potentially other antidiabetic medication. It is a treatment option after metformin and sulfonylureas. It is given by injection under the skin within an hour before the first and last meal of the day. A once-weekly injection version is also available.

Mangafodipir is a contrast agent delivered intravenously to enhance contrast in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the liver, and has potential to serve as an adjunct for various chemotherapeutic agents and during coronary intervention. It has two parts, a paramagnetic manganese(II) ion and the fodipir chelating agent. When freed from the organic ligand, the manganese shortens the longitudinal relaxation time (T1) in an MRI scan. Normal liver tissue absorbs the manganese more than abnormal or cancerous tissue, which makes the normal tissue appear brighter in MRIs. This enhanced contrast allows lesions to be more easily identified.
Thrombopoietic agents are drugs that induce the growth and maturation of megakaryocytes. Some of them are currently in clinical use: romiplostim, eltrombopag, oprelvekin and thrombopoietin. Several others are under clinical investigation such as lusutrombopag and avatrombopag.

Eltrombopag, sold under the brand name Promacta among others, is a medication used to treat thrombocytopenia and severe aplastic anemia. Promacta (eltrombopag) is known as Revolade® outside the U.S. and is marketed worldwide by Novartis.

The thrombopoietin receptor also known as the myeloproliferative leukemia protein or CD110 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MPL oncogene.

Liraglutide, sold under the brand name Victoza among others, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes, obesity, and chronic weight management. In diabetes it is a less preferred agent compared to metformin. Its effects on long-term health outcomes like heart disease and life expectancy are unclear. It is given by injection under the skin.

Romiplostim, sold under the brand name Nplate among others, is a fusion protein analog of thrombopoietin, a hormone that regulates platelet production.
Albiglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist drug marketed by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) for treatment of type 2 diabetes. As of 2017 it is unclear if it affects a person's risk of death. GSK has announced that it intends to withdraw the drug from the worldwide market by July 2018 for economic reasons.
Taspoglutide is a pharmaceutical drug, a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist, under investigation for treatment of type 2 diabetes being codeveloped by Ipsen and Roche.
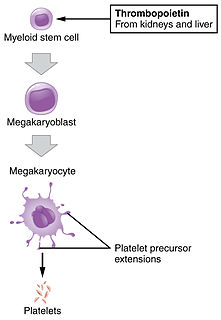
Thrombopoiesis is the formation of platelets in the Bone marrow. Thrombopoietin is the main regulator of thrombopoiesis. Thrombopoietin affects most aspects of the production of platelets. This includes self-renewal and expansion of hematopoietic stem cells, stimulating the increase of megakaryocyte progenitor cells, and supporting these cells so they mature to become platelet-producing cells. The process of Thrombopoiesis is caused by the breakdown of proplatelets. During the process almost all of the membranes, organelles, granules, and soluble macromolecules in the cytoplasm are being consumed. Apoptosis also plays a role in the final stages of thrombopoiesis by letting proplatelet processes to occur from the cytoskeleton of actin.
Fresolimumab (GC1008) is a human monoclonal antibody and an immunomodulator. It is intended for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and cancer.
Antibody mimetics are organic compounds that, like antibodies, can specifically bind antigens, but that are not structurally related to antibodies. They are usually artificial peptides or proteins with a molar mass of about 3 to 20 kDa.
Brilacidin, an investigational new drug (IND), is a polymer-based antibiotic currently in human clinical trials, and represents a new class of antibiotics called host defense protein mimetics, or HDP-mimetics, which are non-peptide synthetic small molecules modeled after host defense peptides (HDPs). HDPs, also called antimicrobial peptides, some of which are defensins, are part of the innate immune response and are common to most higher forms of life. As brilacidin is modeled after a defensin, it is also called a defensin mimetic.
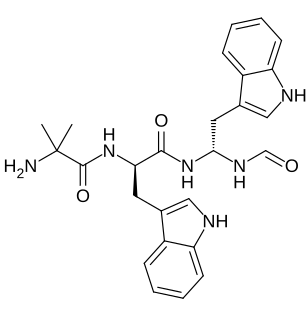
Macimorelin (INN) – or Macrilen – is a drug that was developed by Æterna Zentaris for use in the diagnosis of adult growth hormone deficiency. Macimorelin acetate, the salt formulation, is a synthetic growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist. It is a growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist causing release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland.Macimorelin acetate is described chemically as D-Tryptophanamide, 2-methylalanyl-N-[(1R)-1-(formylamino)-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]-acetate.
A protein mimetic is a molecule such as a peptide, a modified peptide or any other molecule that biologically mimics the action or activity of some other protein. Protein mimetics are commonly used in drug design and discovery.
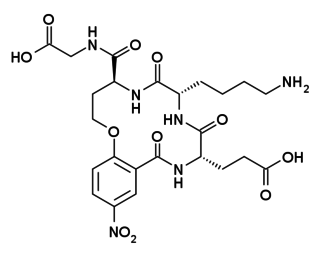
Tavilermide (INN) is a selective, cyclic peptide partial agonist of TrkA. Tavilermide was first synthesized by Burgess and co-workers at Texas A&M University with the intention of producing TrkA agonists. It is under development by Mimetogen Pharmaceuticals as an ophthalmic solution for the treatment of dry eyes, and is in phase III clinical trials for this indication. Tavilermide is currently being evaluated in two multi-center phase III clinical studies in the United States for the treatment of dry eye disease. Tavilermide is also in phase I clinical trials for the treatment of glaucoma; studies are ongoing.
Emicizumab is a humanized bispecific antibody for the treatment of haemophilia A, developed by Genentech and Chugai. A Phase I clinical trial found that it was well tolerated by healthy subjects.

Avatrombopag, sold under the brand name Doptelet, is a medication that used for certain conditions that lead to thrombocytopenia such as thrombocytopenia associated with chronic liver disease in adults who are to undergo a planned medical or dental procedure. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 2018, and in the European Union in 2019.
References
- ↑ "JPAC - Transfusion Guidelines".
- ↑ Ronald Hoffman; Edward J. Benz, Jr.; Leslie E. Silberstein; Helen Heslop; Jeffrey Weitz; John Anastasi (2013). Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 2135.