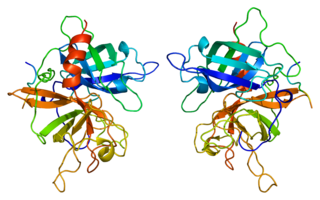A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that transfects a specific antigen-coding DNA sequence into the cells of an organism as a mechanism to induce an immune response.

Spider silk is a protein fibre spun by spiders. Spiders use their silk to make webs or other structures, which function as sticky nets to catch other animals, or as nests or cocoons to protect their offspring, or to wrap up prey. They can also use their silk to suspend themselves, to float through the air, or to glide away from predators. Most spiders vary the thickness and stickiness of their silk for different uses.

Erythropoietin, also known as erythropoetin, haematopoietin, or haemopoietin, is a glycoprotein cytokine secreted mainly by the kidneys in response to cellular hypoxia; it stimulates red blood cell production (erythropoiesis) in the bone marrow. Low levels of EPO are constantly secreted in sufficient quantities to compensate for normal red blood cell turnover. Common causes of cellular hypoxia resulting in elevated levels of EPO include any anemia, and hypoxemia due to chronic lung disease.

Thrombin is a serine protease, an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the F2 gene. Prothrombin is proteolytically cleaved to form thrombin in the clotting process. Thrombin in turn acts as a serine protease that converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble strands of fibrin, as well as catalyzing many other coagulation-related reactions.

Antithrombin (AT) is a small glycoprotein that inactivates several enzymes of the coagulation system. It is a 432-amino-acid protein produced by the liver. It contains three disulfide bonds and a total of four possible glycosylation sites. α-Antithrombin is the dominant form of antithrombin found in blood plasma and has an oligosaccharide occupying each of its four glycosylation sites. A single glycosylation site remains consistently un-occupied in the minor form of antithrombin, β-antithrombin. Its activity is increased manyfold by the anticoagulant drug heparin, which enhances the binding of antithrombin to factor IIa (thrombin) and factor Xa.
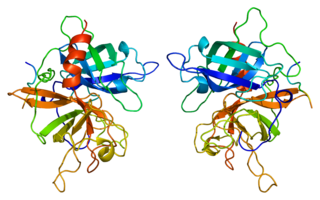
Tissue plasminogen activator is a protein involved in the breakdown of blood clots. It is a serine protease found on endothelial cells, the cells that line the blood vessels. As an enzyme, it catalyzes the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, the major enzyme responsible for clot breakdown. Human tPA has a molecular weight of ~70 kDa in the single-chain form.

Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, also known as colony-stimulating factor 3, is a glycoprotein that stimulates the bone marrow to produce granulocytes and stem cells and release them into the bloodstream.

Interleukin 10 (IL-10), also known as human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is an anti-inflammatory cytokine. In humans, interleukin 10 is encoded by the IL10 gene. IL-10 signals through a receptor complex consisting of two IL-10 receptor-1 and two IL-10 receptor-2 proteins. Consequently, the functional receptor consists of four IL-10 receptor molecules. IL-10 binding induces STAT3 signalling via the phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic tails of IL-10 receptor 1 + IL-10 receptor 2 by JAK1 and Tyk2 respectively.

Coagulation factor VII is one of the proteins that causes blood to clot in the coagulation cascade, and in humans is coded for by the gene F7. It is an enzyme of the serine protease class. Once bound to tissue factor released from damaged tissues, it is converted to factor VIIa, which in turn activates factor IX and factor X.
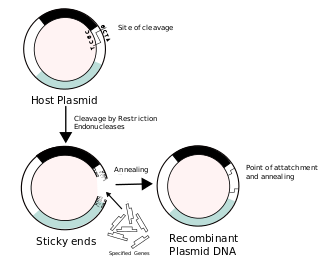
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome.

C1-inhibitor is a protease inhibitor belonging to the serpin superfamily. Its main function is the inhibition of the complement system to prevent spontaneous activation but also as the major regulator of the contact system. C1-inhibitor is an acute-phase protein that circulates in blood at levels of around 0.25 g/L. The levels rise ~2-fold during inflammation. C1-inhibitor irreversibly binds to and inactivates C1r and C1s proteases in the C1 complex of classical pathway of complement. MASP-1 and MASP-2 proteases in MBL complexes of the lectin pathway are also inactivated. This way, C1-inhibitor prevents the proteolytic cleavage of later complement components C4 and C2 by C1 and MBL. Although named after its complement inhibitory activity, C1-inhibitor also inhibits proteases of the fibrinolytic, clotting, and kinin pathways. Note that C1-inhibitor is the most important physiological inhibitor of plasma kallikrein, fXIa, and fXIIa.

Leukemia inhibitory factor, or LIF, is an interleukin 6 class cytokine that affects cell growth by inhibiting differentiation. When LIF levels drop, the cells differentiate.

α-Galactosidase is a glycoside hydrolase enzyme that catalyses the following reaction:

Interleukin 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL11 gene.

Proto-oncogene c-KIT is the gene encoding the receptor tyrosine kinase protein known as tyrosine-protein kinase KIT, CD117 or mast/stem cell growth factor receptor (SCFR). Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. KIT was first described by the German biochemist Axel Ullrich in 1987 as the cellular homolog of the feline sarcoma viral oncogene v-kit.
CD64 is a type of integral membrane glycoprotein known as an Fc receptor that binds monomeric IgG-type antibodies with high affinity. It is more commonly known as Fc-gamma receptor 1 (FcγRI). After binding IgG, CD64 interacts with an accessory chain known as the common γ chain, which possesses an ITAM motif that is necessary for triggering cellular activation.
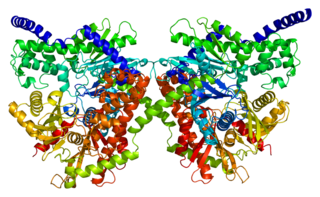
Hexokinase-1 (HK1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HK1 gene on chromosome 10. Hexokinases phosphorylate glucose to produce glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), the first step in most glucose metabolism pathways. This gene encodes a ubiquitous form of hexokinase which localizes to the outer membrane of mitochondria. Mutations in this gene have been associated with hemolytic anemia due to hexokinase deficiency. Alternative splicing of this gene results in five transcript variants which encode different isoforms, some of which are tissue-specific. Each isoform has a distinct N-terminus; the remainder of the protein is identical among all the isoforms. A sixth transcript variant has been described, but due to the presence of several stop codons, it is not thought to encode a protein. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]

Interleukin 5 receptor, alpha (IL5RA) also known as CD125 is a subunit of the Interleukin-5 receptor. IL5RA also denotes its human gene.

Interferon alpha-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA7 gene.
A subunit vaccine is a vaccine that contains purified parts of the pathogen that are antigenic, or necessary to elicit a protective immune response. Subunit vaccine can be made from dissembled viral particles in cell culture or recombinant DNA expression, in which case it is a recombinant subunit vaccine.