A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions.

Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are the families of protein kinases first discovered for their role in regulating the cell cycle. They are also involved in regulating transcription, mRNA processing, and the differentiation of nerve cells. They are present in all known eukaryotes, and their regulatory function in the cell cycle has been evolutionarily conserved. In fact, yeast cells can proliferate normally when their CDK gene has been replaced with the homologous human gene. CDKs are relatively small proteins, with molecular weights ranging from 34 to 40 kDa, and contain little more than the kinase domain. By definition, a CDK binds a regulatory protein called a cyclin. Without cyclin, CDK has little kinase activity; only the cyclin-CDK complex is an active kinase but its activity can be typically further modulated by phosphorylation and other binding proteins, like p27. CDKs phosphorylate their substrates on serines and threonines, so they are serine-threonine kinases. The consensus sequence for the phosphorylation site in the amino acid sequence of a CDK substrate is [S/T*]PX[K/R], where S/T* is the phosphorylated serine or threonine, P is proline, X is any amino acid, K is lysine, and R is arginine.
Wortmannin, a steroid metabolite of the fungi Penicillium funiculosum, Talaromyces wortmannii, is a non-specific, covalent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks). It has an in vitro inhibitory concentration (IC50) of around 5 nM, making it a more potent inhibitor than LY294002, another commonly used PI3K inhibitor. It displays a similar potency in vitro for the class I, II, and III PI3K members although it can also inhibit other PI3K-related enzymes such as mTOR, DNA-PKcs, some phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases, myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) at high concentrations Wortmannin has also been reported to inhibit members of the polo-like kinase family with IC50 in the same range as for PI3K. The half-life of wortmannin in tissue culture is about 10 minutes due to the presence of the highly reactive C20 carbon that is also responsible for its ability to covalently inactivate PI3K. Wortmannin is a commonly used cell biology reagent that has been used previously in research to inhibit DNA repair, receptor-mediated endocytosis and cell proliferation.
Gemcitabine, with brand names including Gemzar, is a chemotherapy medication. It treats cancers including testicular cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and bladder cancer. It is administered by intravenous infusion. It acts against neoplastic growth, and it inhibits the replication of Orthohepevirus A, the causative agent of Hepatitis E, through upregulation of interferon signaling.

Protein kinase B (PKB), also known as Akt, is the collective name of a set of three serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that play key roles in multiple cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, transcription, and cell migration.
Quinazoline is an organic compound with the formula C8H6N2. It is an aromatic heterocycle with a bicyclic structure consisting of two fused six-membered aromatic rings, a benzene ring and a pyrimidine ring. It is a light yellow crystalline solid that is soluble in water. Also known as 1,3-diazanaphthalene, quinazoline received its name from being an aza derivative of quinoline. Though the parent quinazoline molecule is rarely mentioned by itself in technical literature, substituted derivatives have been synthesized for medicinal purposes such as antimalarial and anticancer agents. Quinazoline is a planar molecule. It is isomeric with the other diazanaphthalenes of the benzodiazine subgroup: cinnoline, quinoxaline, and phthalazine. Over 200 biologically active quinazoline and quinoline alkaloids are identified.

Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment (pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks the growth of cancer cells by interfering with specific targeted molecules needed for carcinogenesis and tumor growth, rather than by simply interfering with all rapidly dividing cells. Because most agents for targeted therapy are biopharmaceuticals, the term biologic therapy is sometimes synonymous with targeted therapy when used in the context of cancer therapy. However, the modalities can be combined; antibody-drug conjugates combine biologic and cytotoxic mechanisms into one targeted therapy.

Lapatinib (INN), used in the form of lapatinib ditosylate (USAN) is an orally active drug for breast cancer and other solid tumours. It is a dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor which interrupts the HER2/neu and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathways. It is used in combination therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer. It is used for the treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer whose tumors overexpress HER2 (ErbB2).

Vernalis Research develops and applies fragment and structure-based methods to drug discovery, and has generated cell active lead compounds and development candidates against biological targets in oncology, neurodegeneration, anti-infectives and inflammation.

Bruton's tyrosine kinase, also known as tyrosine-protein kinase BTK, is a tyrosine kinase that is encoded by the BTK gene in humans. BTK plays a crucial role in B cell development.
A protein kinase inhibitor is a type of enzyme inhibitor that blocks the action of one or more protein kinases. Protein kinases are enzymes that phosphorylate (add a phosphate, or PO4, group) to a protein and can modulate its function.

Bexlosteride is a potent and noncompetitive inhibitor of the enzyme 5α-reductase related to finasteride and dutasteride. It is selective for the type I isoform of the enzyme. It advanced to Phase III clinical trials, but development was halted at that stage, and it was never marketed.

A tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) is a pharmaceutical drug that inhibits tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine kinases are enzymes responsible for the activation of many proteins by signal transduction cascades. The proteins are activated by adding a phosphate group to the protein (phosphorylation), a step that TKIs inhibit. TKIs are typically used as anticancer drugs. For example, they have substantially improved outcomes in chronic myelogenous leukemia. They have also been used to treat other diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKI) are the first-line therapy for most patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). More than 90% of CML cases are caused by a chromosomal abnormality that results in the formation of a so-called Philadelphia chromosome. This abnormality was discovered by Peter Nowell in 1960 and is a consequence of fusion between the Abelson (Abl) tyrosine kinase gene at chromosome 9 and the break point cluster (Bcr) gene at chromosome 22, resulting in a chimeric oncogene (Bcr-Abl) and a constitutively active Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase that has been implicated in the pathogenesis of CML. Compounds have been developed to selectively inhibit the tyrosine kinase.

mTOR inhibitors are a class of drugs that inhibit the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), which is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that belongs to the family of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) related kinases (PIKKs). mTOR regulates cellular metabolism, growth, and proliferation by forming and signaling through two protein complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2. The most established mTOR inhibitors are so-called rapalogs, which have shown tumor responses in clinical trials against various tumor types.
A MEK inhibitor is a chemical or drug that inhibits the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase enzymes MEK1 and/or MEK2. They can be used to affect the MAPK/ERK pathway which is often overactive in some cancers.
Triciribine is a cancer drug which was first synthesized in the 1970s and studied clinically in the 1980s and 1990s without success. Following the discovery in the early 2000s that the drug would be effective against tumours with hyperactivated Akt, it is now again under consideration in a variety of cancers. As PTX-200, the drug is currently in two early stage clinical trials in breast cancer and ovarian cancer being conducted by the small molecule drug development company Prescient Therapeutics.

Endoxifen, also known as 4-hydroxy-N-desmethyltamoxifen, is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group as well as a protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor. It is under development for the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer and for the treatment of mania in bipolar disorder. It is taken by mouth.
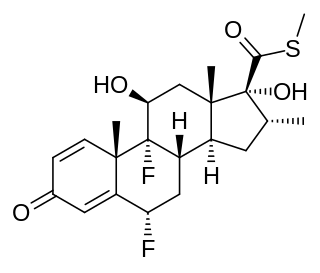
Ticabesone is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid which was never marketed.

Aigialomycin D is a macrolide antibiotic which is produced by the fungi Aigialus parvus. Aigialomycin D is a resorcylic acid lactone and has the molecular formula C18H22O6. Preliminary studies found that aigialomycin D is a protein kinase inhibitor with anti-tumor activity. Aigialomycin D has antimalarial activity.
















