Anatumomab mafenatox is a mouse monoclonal antibody studied for the treatment non-small cell lung cancer, which acts as a tumor-targeted superantigen.

Litoxetine (developmental code names SL 81-0385, IXA-001) is an antidepressant which was under clinical development for the treatment of depression in the early 1990s but was never marketed. It acts as a potent serotonin reuptake inhibitor (Ki for SERT = 7 nM) and modest 5-HT3 receptor antagonist (Ki = 315 nM). It has antiemetic activity, and unlike the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), appears to have a negligible incidence of nausea and vomiting. The drug is structurally related to indalpine. Development of litoxetine for depression was apparently ceased in the late 1990s. However, as of March 2017, development of litoxetine has been reinitiated and the drug is now in the phase II stage for the treatment of urinary incontinence.
Teprotumumab (RG-1507) is an experimental human monoclonal antibody developed by Genmab and Roche. It binds to IGF-1R.
Dusigitumab is a human monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer. It binds to IGLF2. It was developed by MedImmune, which was acquired by AstraZeneca, using Xenomouse technology licensed from Abgenix.
Tovetumab is an anti-PDGFRa monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer. It was developed by MedImmune, and trialed for use in glioblastoma and non-small cell lung cancer. Development was discontinued in 2013.

AZD-5423 is a nonsteroidal glucocorticoid and phase II experimental drug being developed by AstraZeneca and disclosed at the spring 2013 American Chemical Society meeting in New Orleans to treat respiratory diseases and in particular chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Ontuxizumab is a humanized rabbit monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer. It binds to endosialin.

Apricoxib is an experimental anticancer drug. It is a COX-2 inhibitor which is intended to improve standard therapy response in molecularly defined models of pancreatic cancer. Development was abandoned in 2015 due to poor clinical trial results.

Remeglurant is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist of the mGlu5 receptor. It is under development by Merz Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of drug-induced dyskinesia but no development has been reported since at least 2016.

ICI-164384, also known as N-n-butyl-N-methyl-11-(3,17β-dihydroxyestra-1,3,5 -trien-7α-yl)undecanamide, is a steroidal antiestrogen and a synthetic derivative of estradiol which is closely related to fulvestrant and was never marketed. It is a silent antagonist of the estrogen receptor (ER) with no intrinsic estrogenic activity and hence is a pure antiestrogen, unlike selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) like tamoxifen. The drug was under development by AstraZeneca for the treatment of breast cancer but was discontinued in favor of fulvestrant, which is very similar to ICI-164384 but is more potent in comparison.

Fispemifene is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was developed for the treatment of male hypogonadism but was abandoned and never marketed. It reached phase II clinical trials for this indication before development was terminated in March 2016. The drug failed to achieve statistical significance on key effectiveness endpoints in clinical trials and was discontinued by its developer for strategic reasons.
Cimlanod or CXL-1427 is an experimental drug for the treatment of acute decompensated heart failure. It was created by Cardioxyl Pharmaceuticals, which was acquired by Bristol-Myers Squibb. It is a nitric oxide donor.

Savolitinib is an experimental small molecule inhibitor of c-Met. It is being investigated for the treatment of cancer by AstraZeneca. It is in phase II clinical trials for adenocarcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma.
Aripiprazole/sertraline is a combination formulation of sertraline (Zoloft), a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), and aripiprazole (Abilify), an atypical antipsychotic, which is under development by Otsuka Pharmaceutical for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). The drug combines serotonin reuptake inhibition and modulation of dopamine and serotonin receptors. As of July 2017, it is in preregistration in Japan for the treatment of MDD.

Nivacortol is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid which was never marketed.
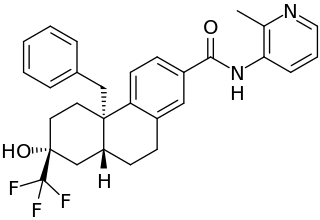
Dagrocorat is a nonsteroidal but steroid-like selective glucocorticoid receptor modulator (SGRM) which was under development for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis but was never marketed. It is described as a partial agonist and "dissociable" agonist of the glucocorticoid receptor. The drug reached phase I clinical trials prior to the discontinuation of its development. The C2α dihydrogen phosphate ester of dagrocorat, fosdagrocorat, was also under investigation, but its development was terminated as well.
Testosterone/dutasteride is a combination formulation of testosterone, an androgen, and dutasteride, a 5α-reductase inhibitor, which was under development by GlaxoSmithKline for the treatment of hypogonadism in men in the 2000s. It reached phase II clinical trials prior to the discontinuation of its development.
AGN-241751 is an orally active small-molecule NMDA receptor modulator which is under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). It was originated by Naurex and was acquired by Allergan from Aptinyx in May 2018. Allergan is also developing the NMDA receptor modulators rapastinel and apimostinel for the treatment of MDD. Like apimostinel, AGN-241751 is intended as an oral follow-up compound to rapastinel. As of May 2018, the drug is in phase I clinical trials.

Nemorexant (developmental code name ACT-541468) is a dual orexin receptor antagonist (DORA) which was originated by Actelion Pharmaceuticals and is under development by Idorsia Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of insomnia. It acts as a selective dual antagonist of the orexin receptors OX1 and OX2. As of June 2018, nemorexant is in phase III clinical trials for the treatment of insomnia.