
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, anemia, kidney dysfunction, and infections may occur. Complications may include hypercalcemia and amyloidosis.
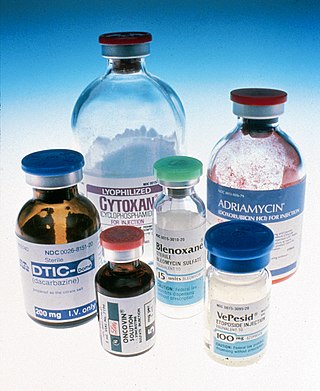
The era of cancer chemotherapy began in the 1940s with the first use of nitrogen mustards and folic acid antagonist drugs. The targeted therapy revolution has arrived, but many of the principles and limitations of chemotherapy discovered by the early researchers still apply.

Cluster of differentiation 40, CD40 is a type I transmembrane protein found on antigen-presenting cells and is required for their activation. The binding of CD154 (CD40L) on TH cells to CD40 activates antigen presenting cells and induces a variety of downstream effects.
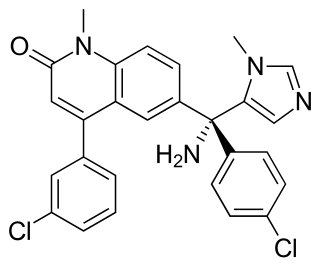
Tipifarnib is a farnesyltransferase inhibitor. Farnesyltransferase inhibitors block the activity of the farnesyltransferase enzyme by inhibiting prenylation of the CAAX tail motif, which ultimately prevents Ras from binding to the membrane, rendering it inactive.
Mapatumumab (HGS-ETR1) is an experimental human monoclonal antibody undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of cancer. It targets TRAIL-R1, also known as DR4, which is expressed on the surface of many tumor cell types.
CD70 is a protein that in humans is encoded by CD70 gene. CD70 is also known as a ligand for CD27.

B-cell maturation antigen, also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 17 (TNFRSF17), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF17 gene.
Oblimersen is an antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotide being studied as a possible treatment for several types of cancer, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, and breast cancer. It may kill cancer cells by blocking the production of Bcl-2—a protein that makes cancer cells live longer—and by making them more sensitive to chemotherapy.
Milatuzumab is an anti-CD74 humanized monoclonal antibody for the treatment of multiple myeloma non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Siltuximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody. It binds to interleukin-6. Siltuximab has been investigated for the treatment of neoplastic diseases: metastatic renal cell cancer, prostate cancer, other types of cancer, and for Castleman's disease.
Mogamulizumab, sold under the brand name Poteligeo, is a humanized, afucosylated monoclonal antibody targeting CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved it in August 2018 for treatment of relapsed or refractory mycosis fungoides and Sézary disease. It was approved in Japan in 2012, for the treatment of relapsed or refractory CCR4+ adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATCLL) and in 2014, for relapsed or refractory CCR4+ cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL). The latter approval was based on study with 28 subjects.
Urelumab is a fully human, non‐ligand binding, CD137 agonist immunoglobulin‐γ 4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody. It was developed utilizing Medarex's UltiMAb(R) technology by Bristol-Myers Squibb for the treatment of cancer and solid tumors. Urelumab promotes anti-tumor immunity, or an immune response against tumor cells, via CD137 activation. The application of Urelumab has been limited due to the fact that it can cause severe liver toxicity.

Daratumumab, sold under the brand name Darzalex, is an anti-cancer monoclonal antibody medication. It binds to CD38, which is overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells. Daratumumab was originally developed by Genmab, but it is now being jointly developed by Genmab along with the Johnson & Johnson subsidiary Janssen Biotech, which acquired worldwide commercialization rights to the drug from Genmab.
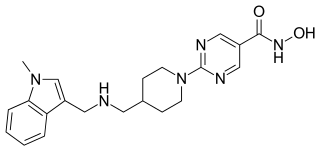
Quisinostat is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of cancer. It is a "second generation" histone deacetylase inhibitor with antineoplastic activity. It is highly potent against class I and II HDACs.
Seagen Inc. is an American biotechnology company focused on developing and commercializing innovative, empowered monoclonal antibody-based therapies for the treatment of cancer. The company, headquartered in Bothell, Washington, is the industry leader in antibody-drug conjugates or ADCs, a technology designed to harness the targeting ability of monoclonal antibodies to deliver cell-killing agents directly to cancer cells. Antibody-drug conjugates are intended to spare non-targeted cells and thus reduce many of the toxic effects of traditional chemotherapy, while potentially enhancing antitumor activity.
ImmunoGen, Inc. is a biotechnology company focused on the development of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) therapeutics for the treatment of cancer. ImmunoGen was founded in 1981 and is headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts.

Isatuximab, sold under the brand name Sarclisa, is a monoclonal antibody (mAb) medication for the treatment of multiple myeloma.

Selinexor sold under the brand name Xpovio among others, is a selective inhibitor of nuclear export used as an anti-cancer medication. It works by blocking the action of exportin 1 and thus blocking the transport of several proteins involved in cancer-cell growth from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm, which ultimately arrests the cell cycle and leads to apoptosis. It is the first drug with this mechanism of action.
Belantamab mafodotin, sold under the brand name Blenrep, is a medication for the treatment of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma.
Passive antibody therapy, also called serum therapy, is a subtype of passive immunotherapy that administers antibodies to target and kill pathogens or cancer cells. It is designed to draw support from foreign antibodies that are donated from a person, extracted from animals, or made in the laboratory to elicit an immune response instead of relying on the innate immune system to fight disease. It has a long history from the 18th century for treating infectious diseases and is now a common cancer treatment. The mechanism of actions include: antagonistic and agonistic reaction, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).








