Related Research Articles
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is a form of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) that can be triggered by a variety of factors such as infections and certain drugs. It refers to cytokine storm syndromes (CSS) and occurs when large numbers of white blood cells are activated and release inflammatory cytokines, which in turn activate yet more white blood cells. CRS is also an adverse effect of some monoclonal antibody medications, as well as adoptive T-cell therapies. When occurring as a result of a medication, it is also known as an infusion reaction.
Chimeric antigen receptor T cells are T cells that have been genetically engineered to produce an artificial T-cell receptor for use in immunotherapy.
The nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies is a naming scheme for assigning generic, or nonproprietary, names to monoclonal antibodies. An antibody is a protein that is produced in B cells and used by the immune system of humans and other vertebrate animals to identify a specific foreign object like a bacterium or a virus. Monoclonal antibodies are those that were produced in identical cells, often artificially, and so share the same target object. They have a wide range of applications including medical uses.
Inotuzumab ozogamicin is an antibody-drug conjugate used to treat relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).

CD33 or Siglec-3 is a transmembrane receptor expressed on cells of myeloid lineage. It is usually considered myeloid-specific, but it can also be found on some lymphoid cells.

Cluster of differentiation antigen 135 (CD135) also known as fms like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT-3), receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3, or fetal liver kinase-2 (Flk2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FLT3 gene. FLT3 is a cytokine receptor which belongs to the receptor tyrosine kinase class III. CD135 is the receptor for the cytokine Flt3 ligand (FLT3L).

CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha is a protein encoded by the CEBPA gene in humans. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha is a transcription factor involved in the differentiation of certain blood cells. For details on the CCAAT structural motif in gene enhancers and on CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Proteins see the specific page.
A bispecific monoclonal antibody is an artificial protein that can simultaneously bind to two different types of antigen. BsMabs can be manufactured in several structural formats, and current applications have been explored for cancer immunotherapy and drug delivery.

C-type lectin domain family 12 member A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLEC12A gene.
Blinatumomab is a biopharmaceutical drug used as a second-line treatment for Philadelphia chromosome-negative relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. It belongs to a class of constructed monoclonal antibodies, bi-specific T-cell engagers (BiTEs), that exert action selectively and direct the human immune system to act against tumor cells. Blinatumomab specifically targets the CD19 antigen present on B cells. In December 2014, it was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration under the accelerated approval program; marketing authorization depended on the outcome of clinical trials that were ongoing at the time of approval.
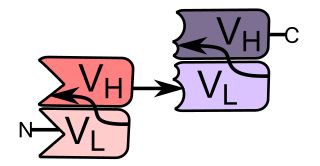
Bi-specific T-cell engagers (BiTEs) are a class of artificial bispecific monoclonal antibodies that are investigated for the use as anti-cancer drugs. They direct a host's immune system, more specifically the T cells' cytotoxic activity, against cancer cells. BiTE is a registered trademark of Micromet AG.
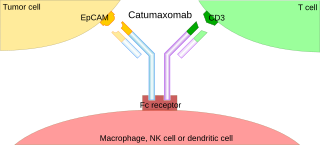
A trifunctional antibody is a monoclonal antibody with binding sites for two different antigens, typically CD3 and a tumor antigen, making it a type of bispecific monoclonal antibody. In addition, its intact Fc-part can bind to an Fc receptor on accessory cells like conventional monospecific antibodies. The net effect is that this type of drug links T cells and monocytes/macrophages, natural killer cells, dendritic cells or other Fc receptor expressing cells to the tumor cells, leading to their destruction.
Quilizumab (INN) is a humanized monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of asthma. It binds to IGHE.
Lirilumab (INN) is a human monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer. It binds to KIR2DL1/2L3.
Denintuzumab mafodotin is a humanized monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate designed for the treatment of CD19-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia and B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It consists of an anti-CD19 mAb linked to monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF), a cytotoxic agent. This drug was developed by Seattle Genetics.
Lenzilumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets colony stimulating factor 2 (CSF2)/granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF).
Loncastuximab tesirine or ADCT-402 is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) composed of a humanized antibody targeting the protein CD19, which is expressed in a wide range of B cell hematological tumors. The experimental drug, developed by ADC Therapeutics is being tested in clinical trials for the treatment of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Camidanlumab tesirine is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) composed of a human antibody that binds to the protein CD25, conjugated to a pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer toxin. The experimental drug, developed by ADC Therapeutics is being tested in clinical trials for the treatment of B-cell Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), and for the treatment of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Ravulizumab, sold under the brand name Ultomiris, is a humanized monoclonal antibody complement inhibitor medication designed for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. It is designed to bind to and prevent the activation of Complement component 5 (C5).
References
- ↑ World Health Organization (2017). "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Proposed INN: List 118" (PDF). WHO Drug Information. 31 (4).
- ↑ Guy DG, Uy GL (October 2018). "Bispecific Antibodies for the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia". Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 13 (6): 417–425. doi:10.1007/s11899-018-0472-8. PMC 6295344 . PMID 30280288.
- ↑ Campagne O, Delmas A, Fouliard S, Chenel M, Chichili GR, Li H, Alderson R, Scherrmann JM, Mager DE (June 2018). "Integrated Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Model of a Bispecific CD3xCD123 DART Molecule in Nonhuman Primates: Evaluation of Activity and Impact of Immunogenicity". Clin. Cancer Res. 24 (11): 2631–2641. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2265 . PMID 29463552..
- ↑ Assi R, Kantarjian H, Ravandi F, Daver N (March 2018). "Immune therapies in acute myeloid leukemia: a focus on monoclonal antibodies and immune checkpoint inhibitors". Curr. Opin. Hematol. 25 (2): 136–145. doi:10.1097/MOH.0000000000000401. PMID 29206680. S2CID 23901088.
- ↑ Statement On A Nonproprietary Name Adopted By The USAN Council - Flotetuzumab, American Medical Association.
| This monoclonal antibody–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |