
Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues or tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues are tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph, and lymphatic system. Because these tissues are all intimately connected through both the circulatory system and the immune system, a disease affecting one will often affect the others as well, making aplasia, myeloproliferation and lymphoproliferation closely related and often overlapping problems. While uncommon in solid tumors, chromosomal translocations are a common cause of these diseases. This commonly leads to a different approach in diagnosis and treatment of hematological malignancies. Hematological malignancies are malignant neoplasms ("cancer"), and they are generally treated by specialists in hematology and/or oncology. In some centers "hematology/oncology" is a single subspecialty of internal medicine while in others they are considered separate divisions. Not all hematological disorders are malignant ("cancerous"); these other blood conditions may also be managed by a hematologist.

Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, pemphigus vulgaris, myasthenia gravis and Epstein–Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcers. It is given by slow intravenous infusion. Biosimilars of Rituxan include Blitzima, Riabni, Ritemvia, Rituenza, Rixathon, Ruxience, and Truxima.

Ibritumomab tiuxetan, sold under the trade name Zevalin, is a monoclonal antibody radioimmunotherapy treatment for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The drug uses the monoclonal mouse IgG1 antibody ibritumomab in conjunction with the chelator tiuxetan, to which a radioactive isotope is added. Tiuxetan is a modified version of DTPA whose carbon backbone contains an isothiocyanatobenzyl and a methyl group.

Cluster of differentiation 40, CD40 is a type I transmembrane protein found on antigen-presenting cells and is required for their activation. The binding of CD154 (CD40L) on TH cells to CD40 activates antigen presenting cells and induces a variety of downstream effects.

Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have varied therapeutic uses. It is possible to create a mAb that binds specifically to almost any extracellular target, such as cell surface proteins and cytokines. They can be used to render their target ineffective, to induce a specific cell signal, to cause the immune system to attack specific cells, or to bring a drug to a specific cell type.
Apolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody intended for use in hematologic cancers. Development was abandoned in 2005, because of toxic effects and lack of efficacy in humans. The observed dose limiting toxic effects were aseptic meningitis and hemolytic uremia.
Toralizumab was a humanized monoclonal antibody and an immunosuppressive drug. Possible indications included treatment of antibody-mediated disorders, T-cell-mediated diseases, and B-cell malignancies such as CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma, follicular cell lymphoma grade I or II, marginal zone lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, MALT lymphoma, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, monocytoid B-cell lymphoma; relapsed/refractory Hodgkin's disease).
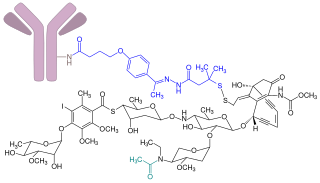
Inotuzumab ozogamicin, sold under the brand name Besponsa, is an antibody-drug conjugate medication used to treat relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Lucatumumab is a human monoclonal antibody against CD40 development of which was discontinued by Novartis in 2013 after it was investigated for the treatment of various types of cancer like multiple myeloma and follicular lymphoma.
Milatuzumab is an anti-CD74 humanized monoclonal antibody for the treatment of multiple myeloma non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Veltuzumab is a monoclonal antibody which is being investigated for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. As of December 2011, it is undergoing Phase I/II clinical trials. When used with milatuzumab it showed activity.
Siltuximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody. It binds to interleukin-6. Siltuximab has been investigated for the treatment of neoplastic diseases: metastatic renal cell cancer, prostate cancer, other types of cancer, and for Castleman's disease.
Mogamulizumab, sold under the brand name Poteligeo, is a humanized, afucosylated monoclonal antibody targeting CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved it in August 2018 for treatment of relapsed or refractory mycosis fungoides and Sézary disease. It was approved in Japan in 2012, for the treatment of relapsed or refractory CCR4+ adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATCLL) and in 2014, for relapsed or refractory CCR4+ cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL). The latter approval was based on study with 28 subjects.
Radretumab is an antineoplastic. Philogen, a pharmaceutical company specializing in antibody-drug conjugates, is developing it as a conjugate of Iodine-131 to an antibody which binds to fibronectin extra domain-B for treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma.
Otlertuzumab (TRU‐016) is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets CD37 designed for the treatment of cancer.
Seagen Inc. is an American biotechnology company focused on developing and commercializing innovative, empowered monoclonal antibody-based therapies for the treatment of cancer. The company, headquartered in Bothell, Washington, is the industry leader in antibody-drug conjugates or ADCs, a technology designed to harness the targeting ability of monoclonal antibodies to deliver cell-killing agents directly to cancer cells. Antibody-drug conjugates are intended to spare non-targeted cells and thus reduce many of the toxic effects of traditional chemotherapy, while potentially enhancing antitumor activity.

PD-1 inhibitors and PD-L1 inhibitors are a group of checkpoint inhibitor anticancer drugs that block the activity of PD-1 and PDL1 immune checkpoint proteins present on the surface of cells. Immune checkpoint inhibitors are emerging as a front-line treatment for several types of cancer.
Denintuzumab mafodotin is a humanized monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate designed for the treatment of CD19-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia and B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It consists of an anti-CD19 mAb linked to monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF), a cytotoxic agent. This drug was developed by Seattle Genetics.
Camidanlumab tesirine is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) composed of a human antibody that binds to the protein CD25, conjugated to a pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer toxin. The experimental drug, developed by ADC Therapeutics is being tested in clinical trials for the treatment of B-cell Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), and for the treatment of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Passive antibody therapy, also called serum therapy, is a subtype of passive immunotherapy that administers antibodies to target and kill pathogens or cancer cells. It is designed to draw support from foreign antibodies that are donated from a person, extracted from animals, or made in the laboratory to elicit an immune response instead of relying on the innate immune system to fight disease. It has a long history from the 18th century for treating infectious diseases and is now a common cancer treatment. The mechanism of actions include: antagonistic and agonistic reaction, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).






