
Cetuximab, sold under the brand name Erbitux, is an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor medication used for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer and head and neck cancer. Cetuximab is a chimeric (mouse/human) monoclonal antibody given by intravenous infusion.

Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment (pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks the growth of cancer cells by interfering with specific targeted molecules needed for carcinogenesis and tumor growth, rather than by simply interfering with all rapidly dividing cells. Because most agents for targeted therapy are biopharmaceuticals, the term biologic therapy is sometimes synonymous with targeted therapy when used in the context of cancer therapy. However, the modalities can be combined; antibody-drug conjugates combine biologic and cytotoxic mechanisms into one targeted therapy.

Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) uses an antibody labeled with a radionuclide to deliver cytotoxic radiation to a target cell. It is a form of unsealed source radiotherapy. In cancer therapy, an antibody with specificity for a tumor-associated antigen is used to deliver a lethal dose of radiation to the tumor cells. The ability for the antibody to specifically bind to a tumor-associated antigen increases the dose delivered to the tumor cells while decreasing the dose to normal tissues. By its nature, RIT requires a tumor cell to express an antigen that is unique to the neoplasm or is not accessible in normal cells.

Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have varied therapeutic uses. It is possible to create a mAb that binds specifically to almost any extracellular target, such as cell surface proteins and cytokines. They can be used to render their target ineffective, to induce a specific cell signal, to cause the immune system to attack specific cells, or to bring a drug to a specific cell type.
Panitumumab, sold under the brand name Vectibix, is a fully human monoclonal antibody specific to the epidermal growth factor receptor.
Edrecolomab is a mouse-derived monoclonal antibody targeting the cell-surface glycoprotein EpCAM (17-1A), which is expressed on epithelial tissues and on various carcinomas.

Pertuzumab, sold under the brand name Perjeta, is a monoclonal antibody used in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel for the treatment of metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer; it also used in the same combination as a neoadjuvant in early HER2-positive breast cancer.
Adecatumumab (MT201) is a recombinant human IgG1 monoclonal antibody which is used to target tumor cells. It binds to the epithelial cell adhesion molecule, with the intent to trigger antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. It was developed by Micromet Inc, which was acquired by Amgen.

KRAS is a gene that provides instructions for making a protein called K-Ras, a part of the RAS/MAPK pathway. The protein relays signals from outside the cell to the cell's nucleus. These signals instruct the cell to grow and divide (proliferate) or to mature and take on specialized functions (differentiate). It is called KRAS because it was first identified as a viral oncogene in the KirstenRAt Sarcoma virus. The oncogene identified was derived from a cellular genome, so KRAS, when found in a cellular genome, is called a proto-oncogene.
Ipilimumab, sold under the brand name Yervoy, is a monoclonal antibody medication that works to activate the immune system by targeting CTLA-4, a protein receptor that downregulates the immune system.
Matuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody for the treatment of cancer. It binds to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) with high affinity. The mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb425) from which matuzumab was developed at the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Minretumomab (CC49) is a mouse monoclonal antibody that was designed for the treatment of cancers that express the TAG-72 antigen. This includes breast, colon, lung, and pancreatic cancers. Apparently, it never got past Phase I clinical trials for this purpose.
Etaracizumab, also known as MEDI-522, trade name Abegrin, is a humanized monoclonal antibody which is being investigated for the treatment of metastatic melanoma, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer and various other types of cancer. It is manufactured by MedImmune.
Ramucirumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody (IgG1) developed for the treatment of solid tumors. This drug was developed by ImClone Systems Inc. It was isolated from a native phage display library from Dyax.
Tigatuzumab (CS-1008) is a monoclonal antibody for the treatment of cancer. As of October 2009, a clinical trial for the treatment of pancreatic cancer, Phase II trials for colorectal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and ovarian cancer have been completed.
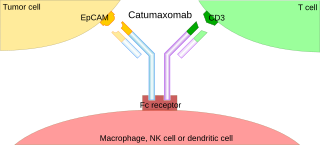
A trifunctional antibody is a monoclonal antibody with binding sites for two different antigens, typically CD3 and a tumor antigen, making it a type of bispecific monoclonal antibody. In addition, its intact Fc-part can bind to an Fc receptor on accessory cells like conventional monospecific antibodies. The net effect is that this type of drug links T cells and monocytes/macrophages, natural killer cells, dendritic cells or other Fc receptor expressing cells to the tumor cells, leading to their destruction.
Carlumab is a discontinued human recombinant monoclonal antibody that targets human CC chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2)/monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP1). Carlumab was under development for use in the treatment of oncology and immune indications and was studied for application in systemic sclerosis, atherosclerosis, diabetic nephropathy, liver fibrosis and type 2 diabetes.
Urelumab is a fully human, non‐ligand binding, CD137 agonist immunoglobulin‐γ 4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody. It was developed utilizing Medarex's UltiMAb(R) technology by Bristol-Myers Squibb for the treatment of cancer and solid tumors. Urelumab promotes anti-tumor immunity, or an immune response against tumor cells, via CD137 activation. The application of Urelumab has been limited due to the fact that it can cause severe liver toxicity.
Indusatumab vedotin (MLN-0264) is an antibody-drug conjugate that is under development for the treatment of pancreatic cancer and other gastrointestinal cancers. It consists of a monoclonal antibody (indusatumab) that targets the enzyme guanylate cyclase 2C which is present in some cancers, linked to an average of three to four molecules of the chemotherapeutic agent monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE).
Abituzumab is a humanized IgG2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeted at CD51 currently in development by Merck KGaA Darmstadt, Germany in an attempt to prevent bone lesion metastases in castration-resistant prostate cancer.







