
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, organization of the intracellular cytoskeleton, and movement of new receptors to the cell membrane. The presence of integrins allows rapid and flexible responses to events at the cell surface.

Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix, a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Cell adhesion is also essential for infectious organisms, such as bacteria or viruses, to cause diseases.
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are a subset of cell surface proteins that are involved in the binding of cells with other cells or with the extracellular matrix (ECM), in a process called cell adhesion. In essence, CAMs help cells stick to each other and to their surroundings. CAMs are crucial components in maintaining tissue structure and function. In fully developed animals, these molecules play an integral role in generating force and movement and consequently ensuring that organs are able to execute their functions normally. In addition to serving as "molecular glue", CAMs play important roles in the cellular mechanisms of growth, contact inhibition, and apoptosis. Aberrant expression of CAMs may result in a wide range of pathologies, ranging from frostbite to cancer.

Integrin alpha M (ITGAM) is one protein subunit that forms heterodimeric integrin alpha-M beta-2 (αMβ2) molecule, also known as macrophage-1 antigen (Mac-1) or complement receptor 3 (CR3). ITGAM is also known as CR3A, and cluster of differentiation molecule 11B (CD11B). The second chain of αMβ2 is the common integrin β2 subunit known as CD18, and integrin αMβ2 thus belongs to the β2 subfamily integrins.

Biological therapy, the use of medications called biopharmaceuticals or biologics that are tailored to specifically target an immune or genetic mediator of disease, plays a major role in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Even for diseases of unknown cause, molecules that are involved in the disease process have been identified, and can be targeted for biological therapy. Many of these molecules, which are mainly cytokines, are directly involved in the immune system. Biological therapy has found a niche in the management of cancer, autoimmune diseases, and diseases of unknown cause that result in symptoms due to immune related mechanisms.
Volociximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody jointly developed by PDL BioPharma and Biogen Idec for treatment of a variety of advanced solid tumors. It binds to and inhibits the functional activity of α5β1 integrin.

Sanford Burnham Prebys is a 501(c)(3) non-profit medical research institute focusing on basic and translational research, with major research programs in cancer, neurodegeneration, diabetes, infectious, inflammatory, and childhood diseases. The institute also specializes in stem cell research and drug discovery technologies.

Cilengitide is a molecule designed and synthesized at the Technical University Munich in collaboration with Merck KGaA in Darmstadt. It is based on the cyclic peptide cyclo(-RGDfV-), which is selective for αv integrins, which are important in angiogenesis, and other aspects of tumor biology. Hence, it is under investigation for the treatment of glioblastoma, where it may act by inhibiting angiogenesis, and influencing tumor invasion and proliferation.

Cell division control protein 42 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the Cdc42 gene. Cdc42 is involved in regulation of the cell cycle. It was originally identified in S. cerevisiae (yeast) as a mediator of cell division, and is now known to influence a variety of signaling events and cellular processes in a variety of organisms from yeast to mammals.
Etaracizumab, also known as MEDI-522, trade name Abegrin, is a humanized monoclonal antibody which is being investigated for the treatment of metastatic melanoma, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer and various other types of cancer. It is manufactured by MedImmune.

72 kDa type IV collagenase also known as matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and gelatinase A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMP2 gene. The MMP2 gene is located on chromosome 16 at position 12.2.

Integrin alpha-V is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITGAV gene.

CD47 also known as integrin associated protein (IAP) is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the CD47 gene. CD47 belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and partners with membrane integrins and also binds the ligands thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) and signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα). CD-47 acts as a don't eat me signal to macrophages of the immune system which has made it a potential therapeutic target in some cancers, and more recently, for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis.
αVβ3 is a type of integrin that is a receptor for vitronectin. It consists of two components, integrin alpha V and integrin beta 3 (CD61), and is expressed by platelets. Furthermore, it is a receptor for phagocytosis on macrophages or dendritic cells.
α5β1, also known as the fibronectin receptor, is an integrin that binds to matrix macromolecules and proteinases and thereby stimulates angiogenesis. It is composed of α5 (ITGA5/CD49e) and β1 (ITGB1/CD29) subunits. It is the primary receptor for fibronectin. The interaction of VLA-5 with fibronectin plays an important role in regulating inflammatory cytokine production by human articular chondrocytes.
Vitaxin (MEDI-523) is a humanized monoclonal antibody against the vascular integrin alpha-v beta-3. It is shown to be a promising angiogenesis inhibitor used in the treatment of some forms of cancer. Vitaxin was in 2002 being studied for rheumatoid arthritis. It is the developmental precursor of Etaracizumab (MEDI-522). Both are derived from the mouse antibody LM609.
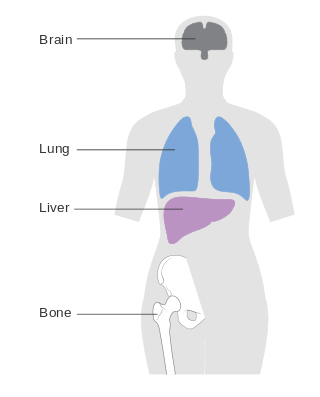
Metastatic breast cancer, also referred to as metastases, advanced breast cancer, secondary tumors, secondaries or stage IV breast cancer, is a stage of breast cancer where the breast cancer cells have spread to distant sites beyond the axillary lymph nodes. There is no cure for metastatic breast cancer; there is no stage after IV.

Arginylglycylaspartic acid (RGD) is the most common peptide motif responsible for cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM), found in species ranging from Drosophila to humans. Cell adhesion proteins called integrins recognize and bind to this sequence, which is found within many matrix proteins, including fibronectin, fibrinogen, vitronectin, osteopontin, and several other adhesive extracellular matrix proteins. The discovery of RGD and elucidation of how RGD binds to integrins has led to the development of a number of drugs and diagnostics, while the peptide itself is used ubiquitously in bioengineering. Depending on the application and the integrin targeted, RGD can be chemically modified or replaced by a similar peptide which promotes cell adhesion.
Abituzumab is a humanized IgG2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeted at CD51 currently in development by Merck KGaA Darmstadt, Germany in an attempt to prevent bone lesion metastases in castration-resistant prostate cancer.

Kairbaan Hodivala-Dilke, FMedSci is an English cell biologist who has made significant contributions to the understanding of the cellular and molecular biology of the tumour microenvironment and in particular angiogenesis. She is Professor of Angiogenesis and the Tumour Microenvironment and Deputy Institute Director of Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary University of London. In 2015 she was awarded the Hooke medal from the British Society for Cell Biology and EMBO membership.











