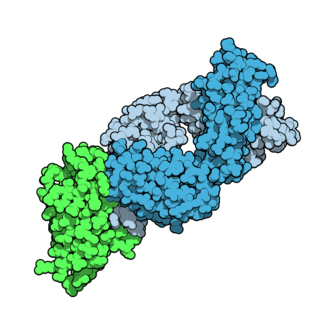
Tremelimumab, sold under the brand name Imjudo, is a fully human monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Tremelimumab is designed to attach to and block CTLA-4, a protein that controls the activity of T cells, which are part of the immune system.
Mapatumumab (HGS-ETR1) is an experimental human monoclonal antibody undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of cancer. It targets TRAIL-R1, also known as DR4, which is expressed on the surface of many tumor cell types.
Cixutumumab (IMC-A12) is a human monoclonal antibody for the treatment of solid tumors.
Figitumumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor that was investigated for the treatment of various types of cancer, for example adrenocortical carcinoma and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

Iniparib was a drug candidate for cancer treatment. It was originally believed to act as an irreversible inhibitor of PARP1 and possibly other enzymes through covalent modification, but its effects against PARP were later disproven. It underwent clinical trials for treatment of some types of breast cancer, but was discontinued after disappointing phase III clinical trials.

Trastuzumab emtansine, sold under the brand name Kadcyla, is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of the humanized monoclonal antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin) covalently linked to the cytotoxic agent DM1. Trastuzumab alone stops growth of cancer cells by binding to the HER2 receptor, whereas trastuzumab emtansine undergoes receptor-mediated internalization into cells, is catabolized in lysosomes where DM1-containing catabolites are released and subsequently bind tubulin to cause mitotic arrest and cell death. Trastuzumab binding to HER2 prevents homodimerization or heterodimerization (HER2/HER3) of the receptor, ultimately inhibiting the activation of MAPK and PI3K/AKT cellular signalling pathways. Because the monoclonal antibody targets HER2, and HER2 is only over-expressed in cancer cells, the conjugate delivers the cytotoxic agent DM1 specifically to tumor cells. The conjugate is abbreviated T-DM1.
Girentuximab is a chimeric IgG1 monoclonal antibody to carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX). CAIX is expressed on the surface of most renal cancer cells and is hypothesized to be on the surface of other tumor cells. It is investigational agent in clinical trials for renal cell carcinoma. Its development was suspended as a "naked" or unconjugated antibody during phase III trials due to efficacy.
Yttrium (90Y) clivatuzumab tetraxetan is a humanized monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate designed for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. The antibody part, clivatuzumab, is conjugated with tetraxetan, a chelator for yttrium-90, a radioisotope which destroys the tumour cells.
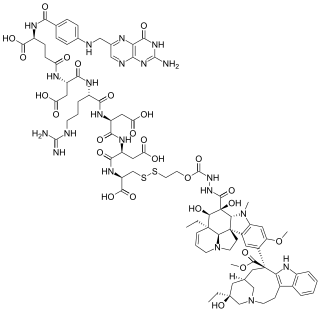
Vintafolide is an investigational targeted cancer therapeutic currently under development by Endocyte and Merck & Co. It is a small molecule drug conjugate consisting of a small molecule targeting the folate receptor, which is overexpressed on certain cancers, such as ovarian cancer, and a potent chemotherapy drug, vinblastine.
Vorsetuzumab mafodotin (SGN-75) is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) directed to the protein CD70 designed for the treatment of cancer. It is a humanized monoclonal antibody, vorsetuzumab, conjugated with noncleavable monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF), a cytotoxic agent.
Seagen Inc. is an American biotechnology company focused on developing and commercializing innovative, empowered monoclonal antibody-based therapies for the treatment of cancer. The company, headquartered in Bothell, Washington, is the industry leader in antibody-drug conjugates or ADCs, a technology designed to harness the targeting ability of monoclonal antibodies to deliver cell-killing agents directly to cancer cells. Antibody-drug conjugates are intended to spare non-targeted cells and thus reduce many of the toxic effects of traditional chemotherapy, while potentially enhancing antitumor activity.
ImmunoGen, Inc. was a biotechnology company focused on the development of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) therapeutics for the treatment of cancer. ImmunoGen was founded in 1981 and was headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts.
Sofituzumab vedotin is a monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Enfortumab vedotin, sold under the brand name Padcev, is an antibody-drug conjugate used for the treatment of urothelial cancer. It is a nectin-4-directed antibody and microtubule inhibitor conjugate. Enfortumab refers to the monoclonal antibody part, and vedotin refers to the payload drug (MMAE) and the linker.
Denintuzumab mafodotin is a humanized monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate designed for the treatment of CD19-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia and B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It consists of an anti-CD19 mAb linked to monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF), a cytotoxic agent. This drug was developed by Seattle Genetics.
Depatuxizumab mafodotin is an antibody-drug conjugate designed for the treatment of cancer. It is composed of an EGFR IGg1 monoclonal antibody (depatuxizumab) conjugated to the tubulin inhibitor monomethyl auristatin F via a stable maleimidocaproyl link.

Tislelizumab, sold under the brand name Tevimbra among others, is a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against programmed death receptor-1. It is being developed by BeiGene.
Cofetuzumab pelidotin is an experimental antibody-drug conjugate in development for the treatment of cancer. It was created by Stemcentrx and is being developed by Pfizer. The drug is an anti-PTK7 monoclonal antibody linked to auristatin-0101, an auristatin microtubule inhibitor.
Relatlimab is a monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of melanoma. It is used in combination with nivolumab to treat melanoma.
Tisotumab vedotin, sold under the brand name Tivdak, is an antibody-drug conjugate used to treat cervical cancer. It is a combination of tisotumab, a monoclonal antibody against tissue factor, and monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), a potent inhibitor of cell division. It is administered by infusion into a vein.





