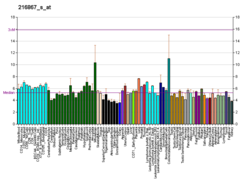
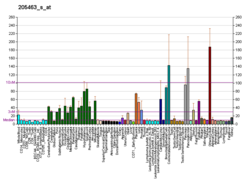
Platelet-derived growth factor subunit A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDGFA gene. [5] [6]
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor family. The four members of this family are mitogenic factors for cells of mesenchymal origin and are characterized by a motif of eight cysteines. This gene product can exist either as a homodimer or as a heterodimer with the platelet-derived growth factor beta polypeptide, where the dimers are connected by disulfide bonds. Studies using knockout mice have shown cellular defects in oligodendrocytes, alveolar smooth muscle cells, and Leydig cells in the testis; knockout mice die either as embryos or shortly after birth. Two splice variants have been identified for this gene. [7]