
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), or abrineurin, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the BDNF gene. BDNF is a member of the neurotrophin family of growth factors, which are related to the canonical nerve growth factor (NGF), a family which also includes NT-3 and NT-4/NT-5. Neurotrophic factors are found in the brain and the periphery. BDNF was first isolated from a pig brain in 1982 by Yves-Alain Barde and Hans Thoenen.

Neurotrophins are a family of proteins that induce the survival, development, and function of neurons.

Nerve growth factor (NGF) is a neurotrophic factor and neuropeptide primarily involved in the regulation of growth, maintenance, proliferation, and survival of certain target neurons. It is perhaps the prototypical growth factor, in that it was one of the first to be described. Since it was first isolated by Nobel Laureates Rita Levi-Montalcini and Stanley Cohen in 1956, numerous biological processes involving NGF have been identified, two of them being the survival of pancreatic beta cells and the regulation of the immune system.

The metabotropic glutamate receptors, or mGluRs, are a type of glutamate receptor that are active through an indirect metabotropic process. They are members of the group C family of G-protein-coupled receptors, or GPCRs. Like all glutamate receptors, mGluRs bind with glutamate, an amino acid that functions as an excitatory neurotransmitter.

Tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA), also known as high affinity nerve growth factor receptor, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 1, or TRK1-transforming tyrosine kinase protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTRK1 gene.

Tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), also known as tyrosine receptor kinase B, or BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor or neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTRK2 gene. TrkB is a receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Standard pronunciation is "track bee".
Tropomyosin receptor kinase C (TrkC), also known as NT-3 growth factor receptor, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 3, or TrkC tyrosine kinase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTRK3 gene.

Neurotrophin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTF3 gene.

N-Acetylserotonin (NAS), also known as normelatonin, is a naturally occurring chemical intermediate in the endogenous production of melatonin from serotonin. It also has biological activity in its own right, including acting as a melatonin receptor agonist, an agonist of the TrkB, and having antioxidant effects.
Trk receptors are a family of tyrosine kinases that regulates synaptic strength and plasticity in the mammalian nervous system. Trk receptors affect neuronal survival and differentiation through several signaling cascades. However, the activation of these receptors also has significant effects on functional properties of neurons.

25CN-NBOH is a compound indirectly derived from the phenethylamine series of hallucinogens, which was discovered in 2014 at the University of Copenhagen. This compound is notable as one of the most selective agonist ligands for the 5-HT2A receptor yet discovered, with a pKi of 8.88 at the human 5-HT2A receptor and with 100x selectivity for 5-HT2A over 5-HT2C, and 46x selectivity for 5-HT2A over 5-HT2B. A tritiated version of 25CN-NBOH has also been accessed and used for more detailed investigations of the binding to 5-HT2 receptors and autoradiography.
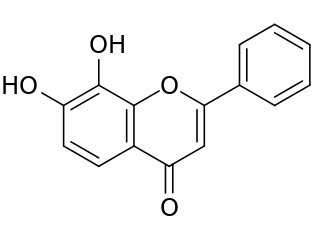
Tropoflavin, also known as 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, is a naturally occurring flavone found in Godmania aesculifolia, Tridax procumbens, and primula tree leaves. It has been found to act as a potent and selective small-molecule agonist of the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), the main signaling receptor of the neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Tropoflavin is both orally bioavailable and able to penetrate the blood–brain barrier. A prodrug of tropoflavin with greatly improved potency and pharmacokinetics, R13, is under development for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.

Deoxygedunin, or 14,15-deoxygedunin, is a tetranortriterpenoid isolated from the Indian neem tree a plant that has been in traditional Indian medicine since ancient times as a remedy for various ailments.
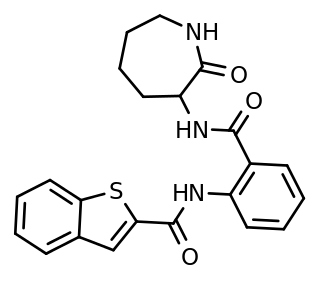
ANA-12 is a selective, small-molecule non-competitive antagonist of TrkB, the main receptor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). The compound crosses the blood-brain-barrier and exerts central TrkB blockade, producing effects as early as 30 minutes and as long as 6 hours following intraperitoneal injection in mice. It blocks the neurotrophic actions of BDNF without compromising neuron survival.

LM22A-4 is a synthetic, selective small-molecule partial agonist of TrkB (EC50 for TrkB activation = 200–500 pM; IC50 for inhibition of BDNF binding to TrkB = 47 nM; IA = ~85%), the main receptor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. It has been found to possess poor blood-brain-barrier penetration when administered systemically, so LM22A-4 has been given to animals instead via intranasal administration, with central nervous system TrkB activation observed. The compound produces neurogenic and neuroprotective effects in animals, and shows beneficial effects on respiration in animal models of Rett syndrome.

R7 is a small-molecule flavonoid and orally active, potent, and selective agonist of the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) – the main signaling receptor for the neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) – which is under development for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It is a structural modification and prodrug of tropoflavin (7,8-DHF) with improved potency and pharmacokinetics, namely oral bioavailability and duration.

7,8,3′-Trihydroxyflavone (7,8,3'-THF) is a flavone and small-molecule agonist of TrkB, the main receptor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), that was derived from tropoflavin (7,8-DHF). Relative to tropoflavin, 7,8,3'-THF is 2–3-fold more potent in vitro as a TrkB agonist. 7,3’-Dihydroxyflavone (7,3'-DHF) is also more potent than tropoflavin in vitro, indicating that a 3'-hydroxy group on the B-ring enhances TrkB agonistic activity. 7,8,3'-THF has been tested in vivo and was found to produce TrkB-dependent neuroprotective effects in mice similarly to tropoflavin.

Eutropoflavin (4'-Dimethylamino-7,8-dihydroxyflavone) is a synthetic flavone and selective small-molecule agonist of TrkB, the main receptor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which was derived from structural modification of tropoflavin (7,8-DHF). Relative to tropoflavin, eutropoflavin possesses higher agonistic activity at TrkB, is significantly more potent than tropoflavin both in vitro and in vivo, and has a longer duration of action. The compound has been found to produce neuroprotective and neurogenic effects in the brain and spinal cord as well as antidepressant-like effects in animals.
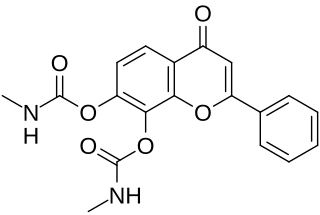
R13 is a small-molecule flavonoid and orally active, potent, and selective agonist of the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) – the main signaling receptor for the neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) – which is under development for the potential treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It is a structural modification and prodrug of tropoflavin (7,8-DHF) with improved potency and pharmacokinetics, namely oral bioavailability and duration. The compound is a replacement for the earlier tropoflavin prodrug R7 and has similar properties to it. It was developed because while R7 displayed a good drug profile in animal studies, it showed almost no conversion into tropoflavin in human liver microsomes. In contrast to R7, R13 is readily hydrolyzed into tropoflavin in human liver microsomes.
Neurotrophin mimetics are small molecules or peptide like molecules that can modulate the action of the neurotrophin receptor. One of the main causes of neurodegeneration involves changes in the expression of neurotrophins (NTs) and/or their receptors. Indeed, these imbalances or changes in their activity, lead to neuronal damage resulting in neurological and neurodegenerative conditions. The therapeutic properties of neurotrophins attracted the focus of many researchers during the years, but the poor pharmacokinetic properties, such as reduced bioavailability and low metabolic stability, the hyperalgesia, the inability to penetrate the blood–brain barrier and the short half-lives render the large neurotrophin proteins not suitable to be implemented as drugs.


















