
Camptotheca is a genus of medium-sized deciduous trees growing to 20 metres (66 ft) tall, native to southern China and Tibet. The genus is usually included in the tupelo family Nyssaceae, but sometimes included in the dogwood family Cornaceae.
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used together with other chemotherapy agents. Doxorubicin is given by injection into a vein.

Anthracyclines are a class of drugs used in cancer chemotherapy that are extracted from Streptomyces bacterium. These compounds are used to treat many cancers, including leukemias, lymphomas, breast, stomach, uterine, ovarian, bladder cancer, and lung cancers. The first anthracycline discovered was daunorubicin, which is produced naturally by Streptomyces peucetius, a species of Actinomycetota. Clinically the most important anthracyclines are doxorubicin, daunorubicin, epirubicin and idarubicin.

Topotecan, sold under the brand name Hycamtin among others, is a chemotherapeutic agent medication that is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It is a synthetic, water-soluble analog of the natural chemical compound camptothecin. It is used in the form of its hydrochloride salt to treat ovarian cancer, lung cancer and other cancer types.

Epothilones are a class of potential cancer drugs. Like taxanes, they prevent cancer cells from dividing by interfering with tubulin, but in early trials, epothilones have better efficacy and milder adverse effects than taxanes.
Topoisomerase inhibitors are chemical compounds that block the action of topoisomerases, which are broken into two broad subtypes: type I topoisomerases (TopI) and type II topoisomerases (TopII). Topoisomerase plays important roles in cellular reproduction and DNA organization, as they mediate the cleavage of single and double stranded DNA to relax supercoils, untangle catenanes, and condense chromosomes in eukaryotic cells. Topoisomerase inhibitors influence these essential cellular processes. Some topoisomerase inhibitors prevent topoisomerases from performing DNA strand breaks while others, deemed topoisomerase poisons, associate with topoisomerase-DNA complexes and prevent the re-ligation step of the topoisomerase mechanism. These topoisomerase-DNA-inhibitor complexes are cytotoxic agents, as the un-repaired single- and double stranded DNA breaks they cause can lead to apoptosis and cell death. Because of this ability to induce apoptosis, topoisomerase inhibitors have gained interest as therapeutics against infectious and cancerous cells.

Tubulin beta-3 chain, Class III β-tubulin, βIII-tubulin (β3-tubulin) or β-tubulin III, is a microtubule element of the tubulin family found almost exclusively in neurons, and in testis cells. In humans, it is encoded by the TUBB3 gene.

Camptothecin (CPT) is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It was discovered in 1966 by M. E. Wall and M. C. Wani in systematic screening of natural products for anticancer drugs. It was isolated from the bark and stem of Camptotheca acuminata, a tree native to China used in traditional Chinese medicine. It has been used clinically in China for the treatment of gastrointestinal tumors. CPT showed anticancer activity in preliminary clinical trials, especially against breast, ovarian, colon, lung, and stomach cancers. However, it has low solubility and adverse effects have been reported when used therapeutically, so synthetic and medicinal chemists have developed numerous syntheses of camptothecin and various derivatives to increase the benefits of the chemical, with good results. Four CPT analogues have been approved and are used in cancer chemotherapy today: topotecan, irinotecan, belotecan, and trastuzumab deruxtecan. Camptothecin has also been found in other plants including Chonemorpha fragrans.

Uroplakin-2 (UP2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPK2 gene.
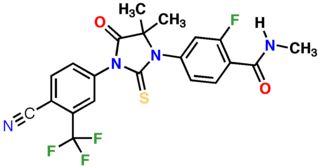
Enzalutamide, sold under the brand name Xtandi, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is indicated for use in conjunction with castration in the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, and metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (mCSPC). It is taken by mouth.
Thymidylate synthase inhibitors are chemical agents which inhibit the enzyme thymidylate synthase and have potential as an anticancer chemotherapy. This inhibition prevents the methylation of C5 of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) thereby inhibiting the synthesis of deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). The downstream effect is promotion of cell death because cells would not be able to properly undergo DNA synthesis if they are lacking dTMP, a necessary precursor to dTTP. Five agents were in clinical trials in 2002: raltitrexed, pemetrexed, nolatrexed, Plevitrexed( ZD9331/BGC9331), and GS7904L.

Veliparib (ABT-888) is a potential anti-cancer drug acting as a PARP inhibitor. It kills cancer cells by blocking a protein called PARP, thereby preventing the repair of DNA or genetic damage in cancer cells and possibly making them more susceptible to anticancer treatments. Veliparib may make whole brain radiation treatment work more effectively against brain metastases from NSCLC. It has been shown to potentiate the effects of many chemotherapeutics, and as such has been part of many combination clinical trials.

Plant sources of anti-cancer agents are plants, the derivatives of which have been shown to be usable for the treatment or prevention of cancer in humans.

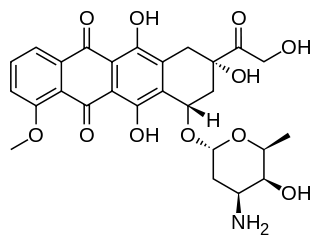
Zoptarelin doxorubicin consists of doxorubicin linked to a small peptide agonist to the luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) receptor. It has been developed as a potential treatment for a number of human cancers. The LHRH receptor is aberrantly present on the cell surface of approximately 80% of endometrial and ovarian cancers, 86% of prostate cancers and about 50% of breast cancers. Whereas in normal tissues, expression of this receptor is mainly confined to the pituitary gland, reproductive organs and hematopoietic stem cells. To a lesser extent the LHRH receptor is also found on the surface of bladder, colorectal, and pancreatic cancers, sarcomas, lymphomas, melanomas, and renal cell carcinomas.

Motesanib is an experimental drug candidate originally developed by Amgen but later investigated by the Takeda Pharmaceutical Company. It is an orally administered small molecule belonging to angiokinase inhibitor class which acts as an antagonist of VEGF receptors, platelet-derived growth factor receptors, and stem cell factor receptors. It is used as the phosphate salt motesanib diphosphate. After clinical trials in thyroid cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, gastrointestinal stromal cancer, colorectal cancer, and breast cancer, the drug was not found to show sufficient efficacy for further development, and development was abandoned by Takeda.
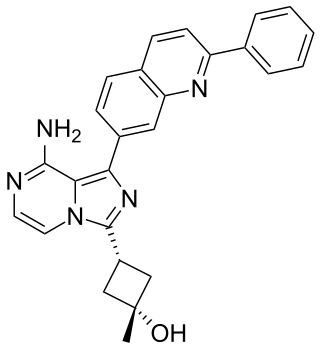
Linsitinib is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of various types of cancer. It is an inhibitor of the insulin receptor and of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R). This prevents tumor cell proliferation and induces tumor cell apoptosis.

Mirvetuximab soravtansine, sold under the brand name Elahere, is a medication used as a treatment for epithelial ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer, or primary peritoneal cancer. Mirvetuximab soravtansine is a folate receptor alpha directed antibody and microtubule inhibitor conjugate.
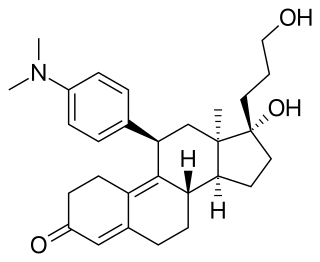
Onapristone is a synthetic and steroidal antiprogestogen with additional antiglucocorticoid activity which was developed by Schering and described in 1984 but was never marketed. It is a silent antagonist of the progesterone receptor (PR), in contrast to the related antiprogestogen mifepristone. Moreover, compared to mifepristone, onapristone has reduced antiglucocorticoid activity, shows little antiandrogenic activity, and has 10- to 30-fold greater potency as an antiprogestogen. The medication was under development for clinical use, for instance in the treatment of breast cancer and as an endometrial contraceptive, but was discontinued during phase III clinical trials in 1995 due to findings that liver function abnormalities developed in a majority patients.
Bradley J. Monk is an American gynecologic oncologist, academician and researcher. He is a professor on the Clinical Scholar Track in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the University of Arizona College of Medicine in Phoenix, Arizona, as well as at the Creighton University School of Medicine in Omaha, Nebraska. He also serves as Director of the Division of Gynecologic Oncology at the St. Joseph's Hospital and Medical Center in Phoenix.

Enloplatin is a water-soluble cancer medication. It is a platinum-based antineoplastic investigated for treatment of platinum-refractory ovarian cancer, in which it was demonstrated to have minimal activity. This cancer is suspected to be at least partially cross-resistant with another third-generation platinum analog, zeniplatin, which also shows minimal antitumor activity in this type of cancer. It was found to be cross-resistant with carboplatin.


















