Related Research Articles
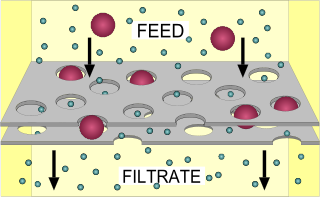
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as oversize and the fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles. Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms.

Settling is the process by which particulates move towards the bottom of a liquid and form a sediment. Particles that experience a force, either due to gravity or due to centrifugal motion will tend to move in a uniform manner in the direction exerted by that force. For gravity settling, this means that the particles will tend to fall to the bottom of the vessel, forming sludge or slurry at the vessel base.

Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of both water clarity and water quality.

A nephelometer or aerosol photometer is an instrument for measuring the concentration of suspended particulates in a liquid or gas colloid. A nephelometer measures suspended particulates by employing a light beam and a light detector set to one side of the source beam. Particle density is then a function of the light reflected into the detector from the particles. To some extent, how much light reflects for a given density of particles is dependent upon properties of the particles such as their shape, color, and reflectivity. Nephelometers are calibrated to a known particulate, then use environmental factors (k-factors) to compensate lighter or darker colored dusts accordingly. K-factor is determined by the user by running the nephelometer next to an air sampling pump and comparing results. There are a wide variety of research-grade nephelometers on the market as well as open source varieties.

Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through treatment of the water, can be assessed. The most common standards used to monitor and assess water quality convey the health of ecosystems, safety of human contact, extent of water pollution and condition of drinking water. Water quality has a significant impact on water supply and oftentimes determines supply options.

A settling basin, settling pond or decant pond is an earthen or concrete structure using sedimentation to remove settleable matter and turbidity from wastewater. The basins are used to control water pollution in diverse industries such as agriculture, aquaculture, and mining. Turbidity is an optical property of water caused by scattering of light by material suspended in that water. Although turbidity often varies directly with weight or volumetric measurements of settleable matter, correlation is complicated by variations in size, shape, refractive index, and specific gravity of suspended matter. Settling ponds may be ineffective at reducing turbidity caused by small particles with specific gravity low enough to be suspended by Brownian motion.

Sand filters are used as a step in the water treatment process of water purification.

Total organic carbon (TOC) is an analytical parameter representing the concentration of organic carbon in a sample. TOC determinations are made in a variety of application areas. For example, TOC may be used as a non-specific indicator of water quality, or TOC of source rock may be used as one factor in evaluating a petroleum play. For marine surface sediments average TOC content is 0.5% in the deep ocean, and 2% along the eastern margins.

Wastewater quality indicators are laboratory test methodologies to assess suitability of wastewater for disposal, treatment or reuse. The main parameters in sewage that are measured to assess the sewage strength or quality as well as treatment options include: solids, indicators of organic matter, nitrogen, phosphorus, indicators of fecal contamination. Tests selected vary with the intended use or discharge location. Tests can measure physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the wastewater. Physical characteristics include temperature and solids. Chemical characteristics include pH value, dissolved oxygen concentrations, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD), nitrogen, phosphorus, chlorine. Biological characteristics are determined with bioassays and aquatic toxicology tests.
A particle counter is used for monitoring and diagnosing particle contamination within specific clean media, including air, water and chemicals. Particle counters are used in a variety of applications in support of clean manufacturing practices, industries include: electronic components and assemblies, pharmaceutical drug products and medical devices, and industrial technologies such as oil and gas.
Sedimentation is a physical water treatment process using gravity to remove suspended solids from water. Solid particles entrained by the turbulence of moving water may be removed naturally by sedimentation in the still water of lakes and oceans. Settling basins are ponds constructed for the purpose of removing entrained solids by sedimentation. Clarifiers are tanks built with mechanical means for continuous removal of solids being deposited by sedimentation. Clarification does not remove dissolved species. Sedimentation is the act of depositing sediment.

Siltation is water pollution caused by particulate terrestrial clastic material, with a particle size dominated by silt or clay. It refers both to the increased concentration of suspended sediments and to the increased accumulation of fine sediments on bottoms where they are undesirable. Siltation is most often caused by soil erosion or sediment spill.

Total dissolved solids (TDS) is a measure of the dissolved combined content of all inorganic and organic substances present in a liquid in molecular, ionized, or micro-granular suspended form. TDS concentrations are often reported in parts per million (ppm). Water TDS concentrations can be determined using a digital meter.
Suspended solids refers to small solid particles which remain in suspension in water as a colloid or due to motion of the water. Suspended solids can be removed by sedimentation if their size or density is comparatively large, or by filtration. It is used as one indicator of water quality and of the strength of sewage, or wastewater in general. It is an important design parameter for sewage treatment processes.
A lamella clarifier or inclined plate settler (IPS) is a type of clarifier designed to remove particulates from liquids.
Depth filters are the variety of filters that use a porous filtration medium to retain particles throughout the medium, rather than just on the surface of the medium. These filters are commonly used when the fluid to be filtered contains a high load of particles because, relative to other types of filters, they can retain a large mass of particles before becoming clogged.
Raw water is water found in the environment that has not been treated and does not have any of its minerals, ions, particles, bacteria, or parasites removed. Raw water includes rainwater, ground water, water from infiltration wells, and water from bodies like lakes and rivers.
Ultrapure water (UPW), high-purity water or highly purified water (HPW) is water that has been purified to uncommonly stringent specifications. Ultrapure water is a term commonly used in manufacturing to emphasize the fact that the water is treated to the highest levels of purity for all contaminant types, including: organic and inorganic compounds; dissolved and particulate matter; volatile and non-volatile; reactive, and inert; hydrophilic and hydrophobic; and dissolved gases.
Mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) is the concentration of suspended solids, in an aeration tank during the activated sludge process, which occurs during the treatment of waste water. The units MLSS is primarily measured in milligram per litre (mg/L), but for activated sludge its mostly measured in gram per litre [g/L] which is equal to kilogram per cubic metre [kg/m3]. Mixed liquor is a combination of raw or unsettled wastewater or pre-settled wastewater and activated sludge within an aeration tank. MLSS consists mostly of microorganisms and non-biodegradable suspended matter. MLSS is an important part of the activated sludge process to ensure that there is a sufficient quantity of active biomass available to consume the applied quantity of organic pollutant at any time. This is known as the food to microorganism ratio, more commonly notated as the F/M ratio. By maintaining this ratio at the appropriate level the biomass will consume high percentages of the food. This minimizes the loss of residual food in the treated effluent. In simple terms, the more the biomass consumes the lower the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) will be in the discharge. It is important that MLSS removes COD and BOD in order to purify water for clean surface waters, and subsequently clean drinking water and hygiene. Raw sewage enters in the water treatment process with a concentration of sometimes several hundred mg/L of BOD. Upon being treated by screening, pre-settling, activated sludge processes or other methods of treatment, the concentration of BOD in water can be lowered to less than 2 mg/L, which is considered to be clean, safe to discharge to surface waters or to reuse water.

Water clarity is a descriptive term for how deeply visible light penetrates through water. In addition to light penetration, the term water clarity is also often used to describe underwater visibility. Water clarity is one way that humans measure water quality, along with oxygen concentration and the presence or absence of pollutants and algal blooms.
References
- ↑ United States. Clean Water Act, sec. 304(a)(4), .
- ↑ Michaud, Joy P. (1994). "Measuring Total Suspended Solids and Turbidity in lakes and streams." Archived 2010-07-30 at the Wayback Machine A Citizen's Guide to Understanding and Monitoring Lakes and Streams. State of Washington, Department of Ecology.
- Moran, Joseph M.; Morgan, Michael D., & Wiersma, James H. (1980). Introduction to Environmental Science (2nd ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.
- Eaton, Andrew D.; Greenberg, Arnold E.; Rice, Eugene W.; Clesceri, Lenore S.; Franson, Mary Ann H., eds. (2005). Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater (21 ed.). American Public Health Association. ISBN 978-0-87553-047-5. Also available on CD-ROM and online by subscription.
- Ramsey, Justin. 2001. Design of septic tanks design summary series.
- National Association of Wastewater Transporters. Scandia, MN (1998). Introduction to Proper Onsite Sewage Treatment.