
Interferons are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses.

A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. After invading a host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome, the reverse of the usual pattern, thus retro (backwards). The new DNA is then incorporated into the host cell genome by an integrase enzyme, at which point the retroviral DNA is referred to as a provirus. The host cell then treats the viral DNA as part of its own genome, transcribing and translating the viral genes along with the cell's own genes, producing the proteins required to assemble new copies of the virus. Many retroviruses cause serious diseases in humans, other mammals, and birds.
Gene silencing is the regulation of gene expression in a cell to prevent the expression of a certain gene. Gene silencing can occur during either transcription or translation and is often used in research. In particular, methods used to silence genes are being increasingly used to produce therapeutics to combat cancer and other diseases, such as infectious diseases and neurodegenerative disorders.

Hepadnaviridae is a family of viruses. Humans, apes, and birds serve as natural hosts. There are currently 18 species in this family, divided among 5 genera. Its best-known member is hepatitis B virus. Diseases associated with this family include: liver infections, such as hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinomas, and cirrhosis. It is the sole accepted family in the order Blubervirales.
Papillomaviridae is a family of non-enveloped DNA viruses whose members are known as papillomaviruses. Several hundred species of papillomaviruses, traditionally referred to as "types", have been identified infecting all carefully inspected mammals, but also other vertebrates such as birds, snakes, turtles and fish. Infection by most papillomavirus types, depending on the type, is either asymptomatic or causes small benign tumors, known as papillomas or warts. Papillomas caused by some types, however, such as human papillomaviruses 16 and 18, carry a risk of becoming cancerous.
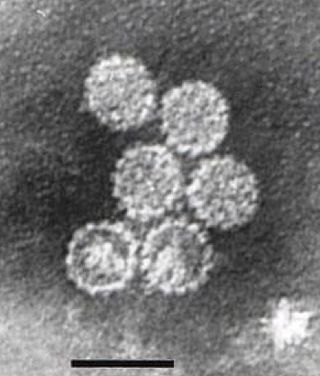
Polyomaviridae is a family of viruses whose natural hosts are primarily mammals and birds. As of 2024, there are eight recognized genera. 14 species are known to infect humans, while others, such as Simian Virus 40, have been identified in humans to a lesser extent. Most of these viruses are very common and typically asymptomatic in most human populations studied. BK virus is associated with nephropathy in renal transplant and non-renal solid organ transplant patients, JC virus with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, and Merkel cell virus with Merkel cell cancer.

SV40 is an abbreviation for simian vacuolating virus 40 or simian virus 40, a polyomavirus that is found in both monkeys and humans. Like other polyomaviruses, SV40 is a DNA virus that sometimes causes tumors in animals, but most often persists as a latent infection. SV40 has been widely studied as a model eukaryotic virus, leading to many early discoveries in eukaryotic DNA replication and transcription.
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, when the term "oncornaviruses" was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the letters "RNA" removed, it now refers to any virus with a DNA or RNA genome causing cancer and is synonymous with "tumor virus" or "cancer virus". The vast majority of human and animal viruses do not cause cancer, probably because of longstanding co-evolution between the virus and its host. Oncoviruses have been important not only in epidemiology, but also in investigations of cell cycle control mechanisms such as the retinoblastoma protein.
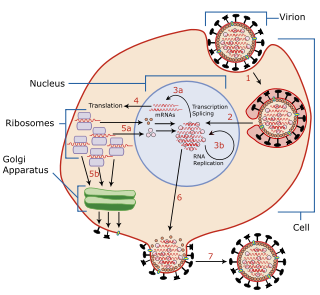
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome and packaging these copies, the virus continues infecting new hosts. Replication between viruses is greatly varied and depends on the type of genes involved in them. Most DNA viruses assemble in the nucleus while most RNA viruses develop solely in cytoplasm.
SV40 large T antigen is a hexamer protein that is a dominant-acting oncoprotein derived from the polyomavirus SV40. TAg is capable of inducing malignant transformation of a variety of cell types. The transforming activity of TAg is due in large part to its perturbation of the retinoblastoma (pRb) and p53 tumor suppressor proteins. In addition, TAg binds to several other cellular factors, including the transcriptional co-activators p300 and CBP, which may contribute to its transformation function. Similar proteins from related viruses are known as large tumor antigen in general.
Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) is a retrovirus and is the first oncovirus to have been described. It causes sarcoma in chickens.
The murine leukemia viruses are retroviruses named for their ability to cause cancer in murine (mouse) hosts. Some MLVs may infect other vertebrates. MLVs include both exogenous and endogenous viruses. Replicating MLVs have a positive sense, single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) genome that replicates through a DNA intermediate via the process of reverse transcription.

Viral vectors are tools commonly used by molecular biologists to deliver genetic material into cells. This process can be performed inside a living organism or in cell culture. Viruses have evolved specialized molecular mechanisms to efficiently transport their genomes inside the cells they infect. Delivery of genes or other genetic material by a vector is termed transduction and the infected cells are described as transduced. Molecular biologists first harnessed this machinery in the 1970s. Paul Berg used a modified SV40 virus containing DNA from the bacteriophage λ to infect monkey kidney cell maintained in culture.

Murine respirovirus, formerly Sendai virus (SeV) and previously also known as murine parainfluenza virus type 1 or hemagglutinating virus of Japan (HVJ), is an enveloped, 150-200 nm–diameter, negative sense, single-stranded RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It typically infects rodents and it is not pathogenic for humans or domestic animals.
The gag-onc fusion protein is a general term for a fusion protein formed from a group-specific antigen ('gag') gene and that of an oncogene ('onc'), a gene that plays a role in the development of a cancer. The name is also written as Gag-v-Onc, with "v" indicating that the Onc sequence resides in a viral genome. Onc is a generic placeholder for a given specific oncogene, such as C-jun..
Merkel cell polyomavirus was first described in January 2008 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was the first example of a human viral pathogen discovered using unbiased metagenomic next-generation sequencing with a technique called digital transcriptome subtraction. MCV is one of seven currently known human oncoviruses. It is suspected to cause the majority of cases of Merkel cell carcinoma, a rare but aggressive form of skin cancer. Approximately 80% of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) tumors have been found to be infected with MCV. MCV appears to be a common—if not universal—infection of older children and adults. It is found in respiratory secretions, suggesting that it might be transmitted via a respiratory route. However, it has also been found elsewhere, such as in shedded healthy skin and gastrointestinal tract tissues, thus its precise mode of transmission remains unknown. In addition, recent studies suggest that this virus may latently infect the human sera and peripheral blood mononuclear cells.

A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 11,000 of the millions of virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology.

HBx is a hepatitis B viral protein. It is 154 amino acids long and interferes with transcription, signal transduction, cell cycle progress, protein degradation, apoptosis and chromosomal stability in the host. It forms a heterodimeric complex with its cellular target protein, and this interaction dysregulates centrosome dynamics and mitotic spindle formation. It interacts with DDB1 redirecting the ubiquitin ligase activity of the CUL4-DDB1 E3 complexes, which are intimately involved in the intracellular regulation of DNA replication and repair, transcription and signal transduction.

The large tumor antigen is a protein encoded in the genomes of polyomaviruses, which are small double-stranded DNA viruses. LTag is expressed early in the infectious cycle and is essential for viral proliferation. Containing four well-conserved protein domains as well as several intrinsically disordered regions, LTag is a fairly large multifunctional protein; in most polyomaviruses, it ranges from around 600-800 amino acids in length. LTag has two primary functions, both related to replication of the viral genome: it unwinds the virus's DNA to prepare it for replication, and it interacts with proteins in the host cell to dysregulate the cell cycle so that the host's DNA replication machinery can be used to replicate the virus's genome. Some polyomavirus LTag proteins - most notably the well-studied SV40 large tumor antigen from the SV40 virus - are oncoproteins that can induce neoplastic transformation in the host cell.
HSV epigenetics is the epigenetic modification of herpes simplex virus (HSV) genetic code.

















