Related Research Articles

An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy. Heat engines convert heat into work via various thermodynamic processes. The internal combustion engine is perhaps the most common example of a heat engine, in which heat from the combustion of a fuel causes rapid pressurisation of the gaseous combustion products in the combustion chamber, causing them to expand and drive a piston, which turns a crankshaft. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, pneumatic motors use compressed air, and clockwork motors in wind-up toys use elastic energy. In biological systems, molecular motors, like myosins in muscles, use chemical energy to create forces and ultimately motion.

A multihull is a ship or boat with more than one hull, whereas a vessel with a single hull is a monohull.

A yacht is a sail or power vessel used for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, so the term applies to such vessels that have a cabin with amenities that accommodate overnight use. To be termed a yacht, as opposed to a boat, such a pleasure vessel is likely to be at least 33 feet (10 m) in length and may have been judged to have good aesthetic qualities.

Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.
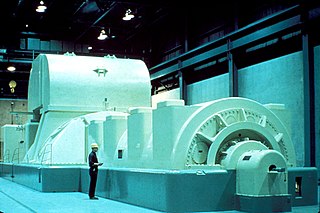
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power into electrical power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all of the power for electric power grids.

A catamaran is a multi-hulled watercraft featuring two parallel hulls of equal size. It is a geometry-stabilized craft, deriving its stability from its wide beam, rather than from a ballasted keel as with a monohull boat. Catamarans typically have less hull volume, smaller displacement, and shallower draft (draught) than monohulls of comparable length. The two hulls combined also often have a smaller hydrodynamic resistance than comparable monohulls, requiring less propulsive power from either sails or motors. The catamaran's wider stance on the water can reduce both heeling and wave-induced motion, as compared with a monohull, and can give reduced wakes.

A railcar, is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coach, with a driver's cab at one or both ends. Some railway companies, such as the Great Western, termed such vehicles "railmotors".

A power inverter, or inverter, is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of “converters” which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC.

Tidal power or tidal energy is harnessed by converting energy from tides into useful forms of power, mainly electricity using various methods.

An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters, and provide safe waterways for other boats and ships. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels, such as the icebreaking boats that were once used on the canals of the United Kingdom.

Wave power is the capture of energy of wind waves to do useful work – for example, electricity generation, water desalination, or pumping water. A machine that exploits wave power is a wave energy converter (WEC).

A motor torpedo boat is a fast torpedo boat, especially of the mid 20th century. The motor in the designation originally referred to their use of petrol engines, typically marinised aircraft engines or their derivatives, which distinguished them from other naval craft of the era, including other torpedo boats, that used steam turbines or reciprocating steam engines. Later, diesel-powered torpedo boats appeared, in turn or retroactively referred to as "motor torpedo boats" for their internal combustion engines, as distinct from steam powered reciprocating or turbine propulsion.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 80th United States Congress took place in 1946. These midterm elections occurred 19 months after President Harry S. Truman assumed office upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt.

Development started as early as the 17th century with the invention of the first steam-powered vehicle, which led to the creation of the first steam-powered automobile capable of human transportation, built by Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot in 1769. Inventors began to branch out at the start of the 19th century, creating the de Rivas engine, one of the first internal combustion engines, and an early electric motor. Samuel Brown later tested the first industrially applied internal combustion engine in 1826.

An ultrasonic motor is a type of electric motor powered by the ultrasonic vibration of a component, the stator, placed against another component, the rotor or slider depending on the scheme of operation. Ultrasonic motors differ from piezoelectric actuators in several ways, though both typically use some form of piezoelectric material, most often lead zirconate titanate and occasionally lithium niobate or other single-crystal materials. The most obvious difference is the use of resonance to amplify the vibration of the stator in contact with the rotor in ultrasonic motors. Ultrasonic motors also offer arbitrarily large rotation or sliding distances, while piezoelectric actuators are limited by the static strain that may be induced in the piezoelectric element.

Sindhudurg Fort is a historical fort that occupies an island in the Arabian Sea, just off the coast of Maharashtra in Western India. The fort was built by Shivaji. The fortress lies on the shore of Malvan town of Sindhudurg District in the Konkan region of Maharashtra, 450 kilometres (280 mi) south of Mumbai. It is a protected monument.

A tide mill is a water mill driven by tidal rise and fall. A dam with a sluice is created across a suitable tidal inlet, or a section of river estuary is made into a reservoir. As the tide comes in, it enters the mill pond through a one-way gate, and this gate closes automatically when the tide begins to fall. When the tide is low enough, the stored water can be released to turn a water wheel.
The Scottish east coast fishery has been in existence for more than a thousand years, spanning the Viking Age right up to the present day.

Merryweather & Sons of Clapham, later Greenwich, London, were builders of steam fire engines and steam tram engines.

A car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transportation. Most definitions of cars say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people rather than goods.
