
The Great Victoria Desert is a sparsely populated desert ecoregion and interim Australian bioregion in Western Australia and South Australia.

The Carnarvon xeric shrublands is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion of Western Australia. The ecoregion is coterminous with the Carnarvon Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) bioregion.

The Murchison is a loosely defined area of Western Australia located within the interior of the Mid West region. It was the subject of a major gold rush in the 1890s and remains a significant mining district. The Murchison is also included as an interim Australian bioregion. The bioregion is loosely related to the catchment area of the Murchison River and has an area of 281,205 square kilometres (108,574 sq mi).

Warren, also known as Karri Forest Region and the Jarrah-Karri forest and shrublands ecoregion, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located in the southwest corner of Western Australia between Cape Naturaliste and Albany, it is bordered to the north and east by the Jarrah Forest region. Its defining characteristic is an extensive tall forest of Eucalyptus diversicolor (karri). This occurs on dissected, hilly ground, with a moderately wet climate. Karri is a valuable timber and much of the karri forest has been logged over, but less than a third has been cleared for agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), and as a terrestrial ecoregion by the World Wide Fund for Nature, it was first defined by Ludwig Diels in 1906.

Esperance mallee is an ecoregion on the south coast of Western Australia, a coastal strip where the predominant vegetation consists of short eucalyptus trees and shrubs.
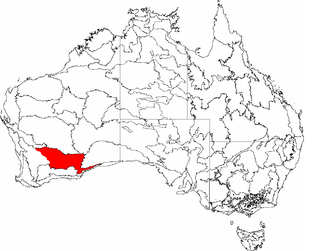
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of 129,122.09 square kilometres (49,854.32 sq mi). It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands.
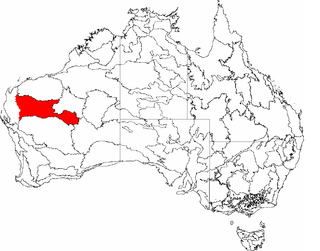
Gascoyne is an interim Australian bioregion located in Western Australia. It has an area of 180,752.57 square kilometres (69,788.96 sq mi). Together with Murchison bioregion to the south, it constitutes the Western Australian Mulga shrublands ecoregion, as assessed by the World Wildlife Fund.

Hampton is an interim Australian bioregion located in southeastern coastal Western Australia, with a small portion (4%) extending into adjacent South Australia. It has an area of 1,088,198 hectares. The Hampton bioregion is part of the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion.
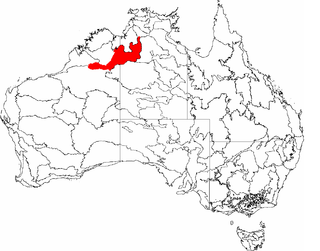
The Ord Victoria Plain, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the Northern Territory and Western Australia, comprising 12,540,703 hectares.

Yalgoo is an interim Australian bioregion located in Western Australia. It has an area of 5,087,577 hectares. The bioregion, together with the Avon Wheatbelt and Geraldton Sandplains bioregions, is part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion as classified by the World Wildlife Fund.

The Brigalow Belt is a wide band of acacia-wooded grassland that runs between tropical rainforest of the coast and the semi-arid interior of Queensland and northern New South Wales, Australia. The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) divides the Brigalow Belt into two IBRA regions, or bioregions, Brigalow Belt North (BBN) and Brigalow Belt South (BBS). The North and South Brigalow Belt are two of the 85 bioregions across Australia and the 15 bioregions in Queensland. Together they form most of the Brigalow tropical savanna ecoregion.

The Coolgardie woodlands is an ecoregion in southern Western Australia. The predominant vegetation is woodlands and mallee scrub. The ecoregion is a transitional zone between the Mediterranean-climate forests, woodlands, and shrublands of Southwest Australia and the deserts and dry scrublands of the Australian interior.

The Eyre Yorke Block, also known as the Eyre and Yorke mallee, is an interim Australian (IBRA) bioregion and a World Wildlife Fund ecoregion covering part of the Eyre Peninsula and all of Yorke Peninsula as well as land to its immediate east in South Australia.

The Southwest Australia savanna is an ecoregion in Western Australia.

The Central Ranges xeric scrub is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion of Australia.

The Great Sandy-Tanami desert is a ecoregion of Western Australia extending into the Northern Territory. It is designated as a World Wildlife Fund region.

The Tirari–Sturt stony desert is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in central Australia.

The Pilbara shrublands is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in Western Australia. It is coterminous with the Pilbara IBRA region. For other definitions and uses of "Pilbara region" see Pilbara.

Mulga is a type of habitat composed of woodland or open forest dominated by the mulga tree, Acacia aneura, or similar species of Acacia.






















