
Various Mongolian writing systems have been devised for the Mongolian language over the centuries, and from a variety of scripts. The oldest and native script, called simply the Mongolian script, has been the predominant script during most of Mongolian history, and is still in active use today in the Inner Mongolia region of China and has de facto use in Mongolia.
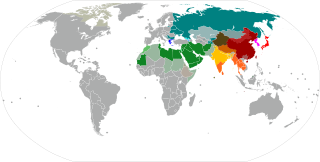
The Brahmic scripts, also known as Indic scripts, are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia and parts of East Asia. They are descended from the Brahmi script of ancient India and are used by various languages in several language families in South, East and Southeast Asia: Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Tibeto-Burman, Mongolic, Austroasiatic, Austronesian, and Tai. They were also the source of the dictionary order (gojūon) of Japanese kana.

Languages spoken in the Republic of India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians, both families together are sometimes known as Indic languages. Languages spoken by the remaining 2.31% of the population belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino–Tibetan, Tai–Kadai, and a few other minor language families and isolates. As per the People's Linguistic Survey of India, India has the second highest number of languages (780), after Papua New Guinea (840). Ethnologue lists a lower number of 456.

A sacred language, holy language or liturgical language is any language that is cultivated and used primarily for religious reasons by people who speak another, primary language in their daily lives.

Meitei, also known as Manipuri, is a Tibeto-Burman language of northeast India. It is the official language and the lingua franca of Manipur as well as one of the 22 official languages of the Indian Republic. Native to the Meitei people, it is spoken by around 1.8 million people, predominantly in the state of Manipur, but also by smaller communities in the rest of the country and in parts of neighbouring Myanmar and Bangladesh. It was used as a court language in the historic Manipur Kingdom.

Jewish languages are the various languages and dialects that developed in Jewish communities in the diaspora. The original Jewish language is Hebrew, supplanted as the primary vernacular by Aramaic following the Babylonian exile. Jewish languages feature a syncretism of Hebrew and Judeo-Aramaic with the languages of the local non-Jewish population.

An official script is a writing system that is specifically designated to be official in the constitutions or other applicable laws of countries, states, and other jurisdictions. Akin to an official language, an official script is much rarer. It is used primarily where an official language is in practice written with two or more scripts. As, in these languages, use of script often has cultural or political connotations, proclamation of an official script is sometimes criticized as having a goal of influencing culture or politics or both. Desired effects also may include easing education, communication and some other aspects of life.

The Assamese alphabet is a writing system of the Assamese language and is a part of the Bengali-Assamese script. This script was also used in Assam and nearby regions for Sanskrit as well as other languages such as Bodo, Khasi, Mising, Jaintia etc. It evolved from Kamarupi script. The current form of the script has seen continuous development from the 5th-century Umachal/Nagajari-Khanikargaon rock inscriptions written in an eastern variety of the Gupta script, adopting significant traits from the Siddhaṃ script in the 7th century. By the 17th century three styles of Assamese alphabets could be identified that converged to the standard script following typesetting required for printing. The present standard is identical to the Bengali alphabet except for two letters, ৰ (ro) and ৱ (vo); and the letter ক্ষ (khya) has evolved into an individual consonant by itself with its own phonetic quality whereas in the Bengali alphabet it is a conjunct of two letters.

Bishnupriya Manipuri, also known as Bishnupriya Meitei or simply as Bishnupriya, is an Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Bengali–Assamese linguistic sub-branch. It is a creole of Bengali language and Meitei language and it still retains its pre-Bengali features. It is spoken in parts of the Indian states of Assam, Tripura and Manipur as well as in the Sylhet Division of Bangladesh. It uses the Bengali-Assamese script as its writing system. Bishnupriya Manipuri, being a member of the Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, was evolved from Magadhi Prakrit. So, its origin is associated with Magadha realm. The Government of Tripura categorized Bishnnupriya Manipuri under the "Tribal Language Cell" of the State Council of Educational Research and Training. Its speakers are also given the "Other Backward Classes" status by the Assam Government and notably, there is no legal status of the Bishnupriyas in Manipur. In the 2020s, the Bishnupriya speaking people started demanding that the Assam Government should give them the status of “indigenous people” of Assam and treat the same like other indigenous communities of the state.

Since the Iron Age in India, the native languages of the Indian subcontinent are divided into various language families, of which the Indo-Aryan and the Dravidian are the most widely spoken. There are also many languages belonging to unrelated language families such as Munda and Tibeto-Burman, spoken by smaller groups.

The Meitei script, also known as the Meetei script, is an abugida used for the Meitei language, the official language of Manipur state and one of the 22 official languages of India. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. It is also popularly known as the Kanglei script and the Kok Sam Lai script. Its earliest known evidence of existence dates back to the 6th century AD coins, engraving the Meitei letters, as verified by the various publications of the National Sahitya Akademi. It was used until the 18th century, when it was replaced by the Bengali alphabet. A few manuscripts survive. In the 20th century, the script has experienced a resurgence, and is again being used. Starting from 2021, Meitei script was officially used by the Government of Manipur, along with the Bengali-Assamese script, to write the Meitei language, as per "The Manipur Official Language (Amendment) Act, 2021".

The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world, the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the third-most by number of users.
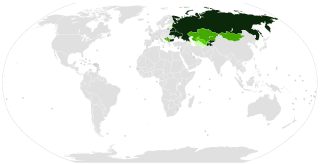
Numerous Cyrillic alphabets are based on the Cyrillic script. The early Cyrillic alphabet was developed in the 9th century AD and replaced the earlier Glagolitic script developed by the Byzantine theologians Cyril and Methodius. It is the basis of alphabets used in various languages, past and present, Slavic origin, and non-Slavic languages influenced by Russian. As of 2011, around 252 million people in Eurasia use it as the official alphabet for their national languages. About half of them are in Russia. Cyrillic is one of the most-used writing systems in the world. The creator is Saint Clement of Ohrid from the Preslav literary school in the First Bulgarian Empire.

The Bengali script or Bangla alphabet is the alphabet used to write the Bengali language based on the Bengali-Assamese script, and has historically been used to write Sanskrit within Bengal. It is one of the most widely adopted writing systems in the world . It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. It is used as the official script of Bengali language in Bangladesh and West Bengal as well as Meitei language in Manipur, two of the official languages of India.

The Bengali–Assamese script, also known as Eastern Nagari, is a modern eastern Indic script that emerged from the Brahmi script. Gaudi script is considered the ancestor of the script. It is known as Bengali script among Bengali speakers, as Assamese script among Assamese speakers, and Eastern-Nāgarī is used in academic discourse.
Bengali numerals are the units of the numeral system, originating from the Indian subcontinent, used officially in Bengali, Assamese and Meitei, 3 of the 22 official languages of the Indian Republic, as well as traditionally in Sylheti, Chittagonian, Bishnupriya, Chakma and Hajong languages. They are used by more than 350 million people around the world, and are a variety of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system.

The Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India lists the official languages of the Republic of India. At the time when the Constitution was enacted, inclusion in this list meant that the language was entitled to representation on the Official Languages Commission, and that the language would be one of the bases that would be drawn upon to enrich Hindi and English, the official languages of the Union. The list has since, however, acquired further significance. The Government of India is now under an obligation to take measures for the development of these languages, such that "they grow rapidly in richness and become effective means of communicating modern knowledge." In addition, candidates sitting for an examination conducted for public service are entitled to use any of these languages as a medium to answer the paper.

Meitei input methods are the methods that allow users of computers to input texts in the Meitei script, systematically for Meitei language.

The official scripts of the 22 official languages of the Indian Republic include abugidas (pseudo-alphabets), alphabetical writing systems and abjads.
















