Related Research Articles

Dementia is the general name for a decline in cognitive abilities that impacts a person's ability to perform everyday activities. This typically involves problems with memory, thinking, and behavior. Aside from memory impairment and a disruption in thought patterns, the most common symptoms include emotional problems, difficulties with language, and decreased motivation. The symptoms may be described as occurring in a continuum over several stages. Dementia ultimately has a significant effect on the individual, caregivers, and on social relationships in general. A diagnosis of dementia requires the observation of a change from a person's usual mental functioning and a greater cognitive decline than what is caused by normal aging.
Delirium is a specific state of acute confusion attributable to the direct physiological consequence of a medical condition, effects of a psychoactive substance, or multiple causes, which usually develops over the course of hours to days. As a syndrome, delirium presents with disturbances in attention, awareness, and higher-order cognition. People with delirium may experience other neuropsychiatric disturbances, including changes in psychomotor activity, disrupted sleep-wake cycle, emotional disturbances, disturbances of consciousness, or, altered state of consciousness, as well as perceptual disturbances, although these features are not required for diagnosis.
Vascular dementia (VaD) is dementia caused by problems in the blood supply to the brain, resulting from a cerebrovascular disease. Restricted blood supply (ischemia) leads to cell and tissue death in the affected region, known as an infarct. The three types of vascular dementia are subcortical vascular dementia, multi-infarct dementia, and stroke related dementia. Subcortical vascular dementia is brought about by damage to the small blood vessels in the brain. Multi-infarct dementia is brought about by a series of mini-strokes where many regions have been affected. The third type is stroke related where more serious damage may result. Such damage leads to varying levels of cognitive decline. When caused by mini-strokes, the decline in cognition is gradual. When due to a stroke, the cognitive decline can be traced back to the event.

Cerebral edema is excess accumulation of fluid (edema) in the intracellular or extracellular spaces of the brain. This typically causes impaired nerve function, increased pressure within the skull, and can eventually lead to direct compression of brain tissue and blood vessels. Symptoms vary based on the location and extent of edema and generally include headaches, nausea, vomiting, seizures, drowsiness, visual disturbances, dizziness, and in severe cases, death.
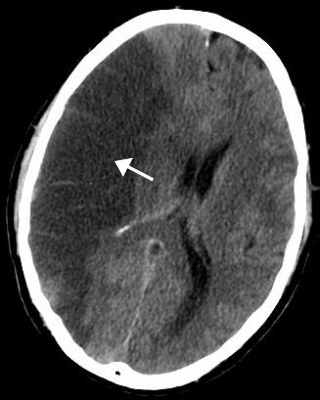
Stroke (also known as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) or brain attack) is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly.

Piracetam is a drug marketed as a treatment for myoclonus. It is also used as a cognitive enhancer to improve memory, attention, and learning. Evidence to support its use is unclear, with some studies showing modest benefits in specific populations and others showing minimal or no benefit. Piracetam is sold as a medication in many European countries. Sale of piracetam is not illegal in the United States, although it is not regulated nor approved by the FDA so it is legally sold for research use only.

Donepezil, sold under the brand name Aricept among others, is a medication used to treat dementia of the Alzheimer's type. It appears to result in a small benefit in mental function and ability to function. Use, however, has not been shown to change the progression of the disease. Treatment should be stopped if no benefit is seen. It is taken by mouth or via a transdermal patch.
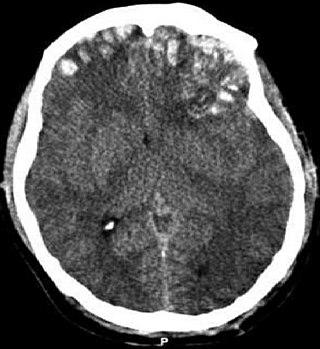
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumatic brain injury. TBI can also be characterized based on mechanism or other features. Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional and behavioral symptoms, and outcomes can range from complete recovery to permanent disability or death.
Cognitive disorders (CDs), also known as neurocognitive disorders (NCDs), are a category of mental health disorders that primarily affect cognitive abilities including learning, memory, perception, and problem-solving. Neurocognitive disorders include delirium, mild neurocognitive disorders, and major neurocognitive disorder. They are defined by deficits in cognitive ability that are acquired, typically represent decline, and may have an underlying brain pathology. The DSM-5 defines six key domains of cognitive function: executive function, learning and memory, perceptual-motor function, language, complex attention, and social cognition.
Psychomotor agitation is a symptom in various disorders and health conditions. It is characterized by unintentional and purposeless motions and restlessness, often but not always accompanied by emotional distress. Typical manifestations include pacing around, wringing of the hands, uncontrolled tongue movement, pulling off clothing and putting it back on, and other similar actions. In more severe cases, the motions may become harmful to the individual, and may involve things such as ripping, tearing, or chewing at the skin around one's fingernails, lips, or other body parts to the point of bleeding. Psychomotor agitation is typically found in various mental disorders, especially in psychotic and mood disorders. It can be a result of drug intoxication or withdrawal. It can also be caused by severe hyponatremia. The middle-aged and the elderly are more at risk to express it.
Cerebral atrophy is a common feature of many of the diseases that affect the brain. Atrophy of any tissue means a decrement in the size of the cell, which can be due to progressive loss of cytoplasmic proteins. In brain tissue, atrophy describes a loss of neurons and the connections between them. Brain atrophy can be classified into two main categories: generalized and focal atrophy. Generalized atrophy occurs across the entire brain whereas focal atrophy affects cells in a specific location. If the cerebral hemispheres are affected, conscious thought and voluntary processes may be impaired.
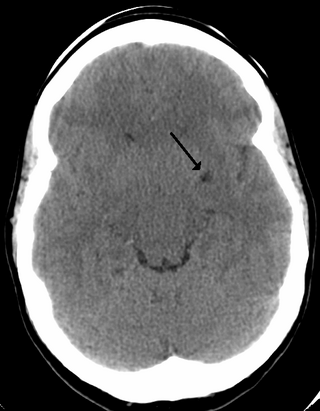
A perivascular space, also known as a Virchow–Robin space, is a fluid-filled space surrounding certain blood vessels in several organs, including the brain, potentially having an immunological function, but more broadly a dispersive role for neural and blood-derived messengers. The brain pia mater is reflected from the surface of the brain onto the surface of blood vessels in the subarachnoid space. In the brain, perivascular cuffs are regions of leukocyte aggregation in the perivascular spaces, usually found in patients with viral encephalitis.

Neuroprotection refers to the relative preservation of neuronal structure and/or function. In the case of an ongoing insult the relative preservation of neuronal integrity implies a reduction in the rate of neuronal loss over time, which can be expressed as a differential equation. It is a widely explored treatment option for many central nervous system (CNS) disorders including neurodegenerative diseases, stroke, traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, and acute management of neurotoxin consumption. Neuroprotection aims to prevent or slow disease progression and secondary injuries by halting or at least slowing the loss of neurons. Despite differences in symptoms or injuries associated with CNS disorders, many of the mechanisms behind neurodegeneration are the same. Common mechanisms of neuronal injury include decreased delivery of oxygen and glucose to the brain, energy failure, increased levels in oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, excitotoxicity, inflammatory changes, iron accumulation, and protein aggregation. Of these mechanisms, neuroprotective treatments often target oxidative stress and excitotoxicity—both of which are highly associated with CNS disorders. Not only can oxidative stress and excitotoxicity trigger neuron cell death but when combined they have synergistic effects that cause even more degradation than on their own. Thus limiting excitotoxicity and oxidative stress is a very important aspect of neuroprotection. Common neuroprotective treatments are glutamate antagonists and antioxidants, which aim to limit excitotoxicity and oxidative stress respectively.

Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), also known as hemorrhagic stroke, is a sudden bleeding into the tissues of the brain, into its ventricles, or into both. An ICH is a type of bleeding within the skull and one kind of stroke. Symptoms can vary dramatically depending on the severity, acuity, and location (anatomically) but can include headache, one-sided weakness, numbness, tingling, or paralysis, speech problems, vision or hearing problems, memory loss, attention problems, coordination problems, balance problems, dizziness or lightheadedness or vertigo, nausea/vomiting, seizures, decreased level of consciousness or total loss of consciousness, neck stiffness, and fever.
Cognitive impairment is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process or different areas of cognition. Cognition, also known as cognitive function, refers to the mental processes of how a person gains knowledge, uses existing knowledge, and understands things that are happening around them using their thoughts and senses. A cognitive impairment can be in different domains or aspects of a person's cognitive function including memory, attention span, planning, reasoning, decision-making, language, executive functioning, and visuospatial functioning. The term cognitive impairment covers many different diseases and conditions and may also be symptom or manifestation of a different underlying condition. Examples include impairments in overall intelligence ,specific and restricted impairments in cognitive abilities, neuropsychological impairments, or it may describe drug-induced impairment in cognition and memory. Cognitive impairments may be short-term, progressive or permanent.
The prevention of dementia involves reducing the number of risk factors for the development of dementia, and is a global health priority needing a global response. Initiatives include the establishment of the International Research Network on Dementia Prevention (IRNDP) which aims to link researchers in this field globally, and the establishment of the Global Dementia Observatory a web-based data knowledge and exchange platform, which will collate and disseminate key dementia data from members states. Although there is no cure for dementia, it is well established that modifiable risk factors influence both the likelihood of developing dementia and the age at which it is developed. Dementia can be prevented by reducing the risk factors for vascular disease such as diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, smoking, physical inactivity and depression. A study concluded that more than a third of dementia cases are theoretically preventable. Among older adults both an unfavorable lifestyle and high genetic risk are independently associated with higher dementia risk. A favorable lifestyle is associated with a lower dementia risk, regardless of genetic risk. In 2020, a study identified 12 modifiable lifestyle factors, and the early treatment of acquired hearing loss was estimated as the most significant of these factors, potentially preventing up to 9% of dementia cases.

Propentofylline is a xanthine derivative drug with purported neuroprotective effects.
Psychological therapies for dementia are starting to gain some momentum. Improved clinical assessment in early stages of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia, increased cognitive stimulation of the elderly, and the prescription of drugs to slow cognitive decline have resulted in increased detection in the early stages. Although the opinions of the medical community are still apprehensive to support cognitive therapies in dementia patients, recent international studies have started to create optimism.

Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens, and is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation, mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years.

The neurobiological effects of physical exercise involve possible interrelated effects on brain structure, brain function, and cognition. Research in humans has demonstrated that consistent aerobic exercise may induce improvements in certain cognitive functions, neuroplasticity and behavioral plasticity; some of these long-term effects may include increased neuron growth, increased neurological activity, improved stress coping, enhanced cognitive control of behavior, improved declarative, spatial, and working memory, and structural and functional improvements in brain structures and pathways associated with cognitive control and memory. The effects of exercise on cognition may affect academic performance in children and college students, improve adult productivity, preserve cognitive function in old age, preventing or treating certain neurological disorders, and improving overall quality of life.
References
- ↑ Windisch M, Gschanes A, Hutter-Paier B (1998). "Neurotrophic activities and therapeutic experience with a brain derived peptide preparation". Ageing and Dementia. Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementa. Vol. 53. pp. 289–98. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-6467-9_25. ISBN 978-3-211-83114-4. PMID 9700665.
- 1 2 3 Ziganshina LE, Abakumova T, Nurkhametova D, Ivanchenko K, et al. (Cochrane Stroke Group) (October 2023). "Cerebrolysin for acute ischaemic stroke". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2023 (10): CD007026. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007026.pub7. PMC 10565895. PMID 37818733.
- 1 2 Cui S, Chen N, Yang M, Guo J, Zhou M, Zhu C, He L (November 2019). "Cerebrolysin for vascular dementia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (11). doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008900.pub3. PMC 6844361 . PMID 31710397.
- ↑ Heiss WD, Brainin M, Bornstein NM, Tuomilehto J, Hong Z (March 2012). "Cerebrolysin in patients with acute ischemic stroke in Asia: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial". Stroke. 43 (3): 630–636. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.628537 . PMID 22282884. S2CID 26004422.
- ↑ Woo PY, Ho JW, Ko NM, Li RP, Jian L, Chu AC, et al. (November 2020). "Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, pilot trial to investigate safety and efficacy of Cerebrolysin in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage". BMC Neurology. 20 (1): 401. doi: 10.1186/s12883-020-01908-9 . PMC 7607674 . PMID 33143640.
- ↑ Fan F, Liu H, Shi X, Ai Y, Liu Q, Cheng Y (2022). "The Efficacy and Safety of Alzheimer's Disease Therapies: An Updated Umbrella Review". Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 85 (3): 1195–1204. doi:10.3233/JAD-215423. PMID 34924395. S2CID 245311001.
- ↑ Ghaffarpasand F, Torabi S, Rasti A, Niakan MH, Aghabaklou S, Pakzad F, et al. (2019). "Effects of cerebrolysin on functional outcome of patients with traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. 15: 127–135. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S186865 . PMC 6311329 . PMID 30643411.
- ↑ El Sayed I, Zaki A, Fayed AM, Shehata GM, Abdelmonem S (April 2018). "A meta-analysis of the effect of different neuroprotective drugs in management of patients with traumatic brain injury". Neurosurgical Review. 41 (2): 427–438. doi:10.1007/s10143-016-0775-y. PMID 27539610. S2CID 3980956.
- ↑ Xiao S, Xue H, Li G, Yuan C, Li X, Chen C, et al. (February 2012). "Therapeutic effects of cerebrolysin added to risperidone in patients with schizophrenia dominated by negative symptoms". The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 46 (2): 153–160. doi:10.1177/0004867411433213. PMID 22311531. S2CID 206397952.
- ↑ Khabirov FA, Khaybullin TI, Granatov EV, Shakirzianova SR (2016). "[Effect of cerebrolysin on remyelination processes in multiple sclerosis patients in stage of relapse regression]". Zhurnal Nevrologii I Psikhiatrii Imeni S.S. Korsakova. 116 (12): 48–53. doi: 10.17116/jnevro201611612148-53 . PMID 28139626.
- ↑ Nasiri J, Safavifar F (June 2017). "Effect of cerebrolysin on gross motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a clinical trial". Acta Neurologica Belgica. 117 (2): 501–505. doi:10.1007/s13760-016-0743-x. PMID 28074392. S2CID 3805375.
- ↑ Allam AF, Abotakia TA, Koptan W (July 2018). "Role of Cerebrolysin in cervical spondylotic myelopathy patients: a prospective randomized study". The Spine Journal. 18 (7): 1136–1142. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2017.11.002. PMID 29155000. S2CID 23283518.
- ↑ Menon PK, Muresanu DF, Sharma A, Mössler H, Sharma HS (February 2012). "Cerebrolysin, a mixture of neurotrophic factors induces marked neuroprotection in spinal cord injury following intoxication of engineered nanoparticles from metals". CNS & Neurological Disorders Drug Targets. 11 (1): 40–49. doi:10.2174/187152712799960781. PMID 22229324.
- ↑ Ziganshina LE, Abakumova T, Hoyle CH (July 2020). "Cerebrolysin for acute ischaemic stroke". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 7 (7): CD007026. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007026.pub6. PMC 7387239 . PMID 32662068.
- ↑ Plosker GL, Gauthier S (2009). "Cerebrolysin: a review of its use in dementia". Drugs & Aging. 26 (11): 893–915. doi:10.2165/11203320-000000000-00000. PMID 19848437.
- ↑ Masliah E, Díez-Tejedor E (April 2012). "The pharmacology of neurotrophic treatment with Cerebrolysin: brain protection and repair to counteract pathologies of acute and chronic neurological disorders". Drugs of Today. 48 (Suppl A): 3–24. doi:10.1358/dot.2012.48(Suppl.A).1739716. PMID 22514792. S2CID 23181962.
- ↑ Rogers S (29 October 2020). "Nicholasville compounding pharmacy, owner plead guilty to distribution". ABC 36 News.
- ↑ "Nicholasville Compounding Pharmacy and Its Owner Sentenced for Unlawful Distribution of Prescription Drugs Unlawful Distribution of Prescription Drugs". www.justice.gov. 24 February 2021.