
Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment (pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks the growth of cancer cells by interfering with specific targeted molecules needed for carcinogenesis and tumor growth, rather than by simply interfering with all rapidly dividing cells. Because most agents for targeted therapy are biopharmaceuticals, the term biologic therapy is sometimes synonymous with targeted therapy when used in the context of cancer therapy. However, the modalities can be combined; antibody-drug conjugates combine biologic and cytotoxic mechanisms into one targeted therapy.

Sorafenib, sold under the brand name Nexavar, is a kinase inhibitor drug approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer, advanced primary liver cancer, FLT3-ITD positive AML and radioactive iodine resistant advanced thyroid carcinoma.

Sunitinib, sold under the brand name Sutent, is an anti-cancer medication. It is a small-molecule, multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor that was approved by the FDA for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) in January 2006. Sunitinib was the first cancer drug simultaneously approved for two different indications.

Lapatinib (INN), used in the form of lapatinib ditosylate (USAN) is an orally active drug for breast cancer and other solid tumours. It is a dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor which interrupts the HER2/neu and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathways. It is used in combination therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer. It is used for the treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer whose tumors overexpress HER2 (ErbB2).

Dasatinib, sold under the brand name Sprycel among others, is a targeted therapy medication used to treat certain cases of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Specifically it is used to treat cases that are Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+). It is taken by mouth.

Cediranib is a potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor tyrosine kinases.
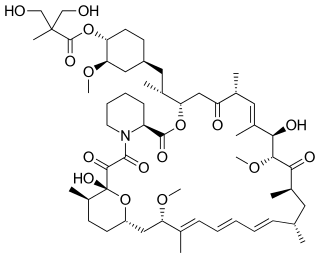
Temsirolimus, sold under the brand name Torisel, is an intravenous drug for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), developed by Wyeth Pharmaceuticals and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May 2007, and was also approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in November 2007. It is a derivative and prodrug of sirolimus.
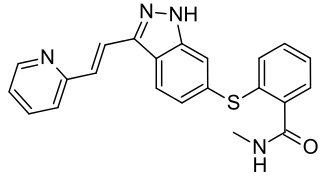
Axitinib, sold under the brand name Inlyta, is a small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor developed by Pfizer. It has been shown to significantly inhibit growth of breast cancer in animal (xenograft) models and has shown partial responses in clinical trials with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and several other tumour types.
Aflibercept, sold under the brand names Eylea and Zaltrap, is a medication used to treat wet macular degeneration and metastatic colorectal cancer. It was developed by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and is approved in the United States and the European Union.
Ramucirumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody (IgG1) developed for the treatment of solid tumors. This drug was developed by ImClone Systems Inc. It was isolated from a native phage display library from Dyax.

Vatalanib is a small molecule protein kinase inhibitor that inhibits angiogenesis. It is being studied as a possible treatment for several types of cancer, particularly cancer that is at an advanced stage or has not responded to chemotherapy. Vatalanib is orally active, that is, it is effective when taken by mouth.
SUGEN (Sugen) was a drug discovery company focused on development of protein kinase inhibitors. It was founded in 1991, and shut down in 2003, after pioneering protein kinases as therapeutic targets and developing the successful cancer therapy sunitinib (Sutent).

Toceranib is a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor and is used in the treatment of canine mast cell tumor also called mastocytoma. Together with masitinib, toceranib is the only dog-specific anti-cancer drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is sold under the brand name Palladia as its phosphate salt, toceranib phosphate (INN) by Pfizer. It was developed by SUGEN as SU11654, a sister compound to sunitinib, which was later approved for human therapies. Toceranib is likely to act mostly through inhibition of the kit tyrosine kinase, though it may also have an anti-angiogenic effect.

Lenvatinib, sold under the brand name Lenvima among others, is an anti-cancer medication for the treatment of certain kinds of thyroid cancer and for other cancers as well. It was developed by Eisai Co. and acts as a multiple kinase inhibitor against the VEGFR1, VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 kinases.
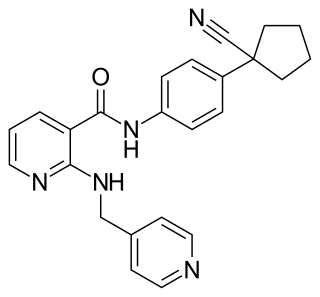
Apatinib, also known as rivoceranib, is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that selectively inhibits the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. It is an orally bioavailable, small molecule agent which is thought to inhibit angiogenesis in cancer cells; specifically, apatinib inhibits VEGF-mediated endothelial cell migration and proliferation thus blocking new blood vessel formation in tumor tissue. This agent also mildly inhibits c-Kit and c-SRC tyrosine kinases.

A tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) is a pharmaceutical drug that inhibits tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine kinases are enzymes responsible for the activation of many proteins by signal transduction cascades. The proteins are activated by adding a phosphate group to the protein (phosphorylation), a step that TKIs inhibit. TKIs are typically used as anticancer drugs. For example, they have substantially improved outcomes in chronic myelogenous leukemia. They have also been used to treat other diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.

Cabozantinib, sold under the brand names Cometriq and Cabometyx among others, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat medullary thyroid cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma. It is a small molecule inhibitor of the tyrosine kinases c-Met and VEGFR2, and also inhibits AXL and RET. It was discovered and developed by Exelixis Inc.
Foretinib is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of cancer. It was discovered by Exelixis and is under development by GlaxoSmithKline. About 10 Phase II clinical trials have been run. As of October 2015 it appears development has been discontinued.
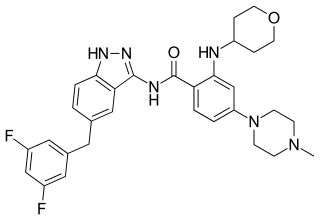
Entrectinib, sold under the brand name Rozlytrek, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat ROS1-positive non-small cell lung cancer and NTRK fusion-positive solid tumors. It is a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), of the tropomyosin receptor kinases (TRK) A, B and C, C-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK).
VEGFR-2 inhibitor, also known as kinase insert domain receptor(KDR) inhibitor, are tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitors that reduce angiogenesis or lymphangiogenesis, leading to anticancer activity. Generally they are small, synthesised molecules that bind competitively to the ATP-site of the tyrosine kinase domain. VEGFR-2 selective inhibitor can interrupt multiple signaling pathways involved in tumor, including proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis.















