Related Research Articles

The 2nd century BC started the first day of 200 BC and ended the last day of 101 BC. It is considered part of the Classical era, although depending on the region being studied, other terms may be more suitable. It is also considered to be the end of the Axial Age. In the context of the Eastern Mediterranean, it is the mid-point of the Hellenistic period.
Year 105 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Rufus and Maximus and the Sixth Year of Yuanfeng. The denomination 105 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 103 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marius and Orestes and the Second Year of Taichu. The denomination 103 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 102 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marius and Catulus and the Third Year of Taichu. The denomination 102 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 101 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marius and Aquillius and the Fourth Year of Taichu. The denomination 101 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 100 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the scholarship of Marius and Flaccus and the First Year of Tianhan. The denomination 100 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
This article concerns the period 69 BC – 60 BC.

This article concerns the period 109 BC – 100 BC.
This article concerns the period 119 BC – 110 BC.
This article concerns the period 139 BC – 130 BC.
This article concerns the period 149 BC – 140 BC.
This article concerns the period 159 BC – 150 BC.
Year 90 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Lupus and the Third Year of Zhenghe. The denomination 90 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 87 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Octavius and Cinna/Merula and the Second Year of Houyuan. The denomination 87 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 134 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aemilianus and Flaccus and the First Year of Yuanguang. The denomination 134 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 135 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Flaccus and Piso and the Sixth Year of Jianyuan. The denomination 135 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
108 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Galba and Hortensius/Scaurus and the Third Year of Yuanfeng. The denomination 108 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 111 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Serapio and Bestia and the Sixth Year of Yuanding. The denomination 111 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 30 BC was either a common year starting on Wednesday, Thursday or Friday or a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Octavian and Crassus. The denomination 30 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
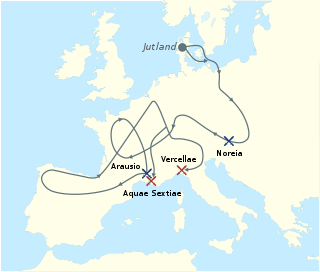
Year 113 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caprarius and Carbo and the Fourth Year of Yuanding. The denomination 113 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
References
- ↑ Hung, Hing Ming (2020). The Magnificent Emperor Wu: China's Han Dynasty. pp. 197–198. ISBN 978-1628944167.
- ↑ "Jugurtha". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved February 27, 2024.