
The Bronze Age was a historical period lasting from approximately 3300 to 1200 BC. It was characterized by the use of bronze, the use of writing in some areas, and other features of early urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, between the Stone and Iron Ages. Worldwide, the Bronze Age generally followed the Neolithic period, with the Chalcolithic serving as a transition.
The 6th century BC started on the first day of 600 BC and ended on the last day of 501 BC.
The 2nd millennium BC spanned the years 2000 BC to 1001 BC. In the Ancient Near East, it marks the transition from the Middle to the Late Bronze Age. The Ancient Near Eastern cultures are well within the historical era: The first half of the millennium is dominated by the Middle Kingdom of Egypt and Babylonia. The alphabet develops. At the center of the millennium, a new order emerges with Mycenaean Greek dominance of the Aegean and the rise of the Hittite Empire. The end of the millennium sees the Bronze Age collapse and the transition to the Iron Age.
The 12th century BC is the period from 1200 to 1101 BC. The Late Bronze Age collapse in the ancient Near East and eastern Mediterranean is often considered to begin in this century.
The 15th century BC was the century that lasted from 1500 BC to 1401 BC.

The 17th century BC was the century that lasted from 1700 BC to 1601 BC.
The 1600s BC was a decade lasting from January 1, 1609 BC to December 31, 1600 BC.
The 1550s BC was a decade lasting from January 1, 1559 BC to December 31, 1550 BC.
The 1500s BC was a decade lasting from January 1, 1509 BC to December 31, 1500 BC.

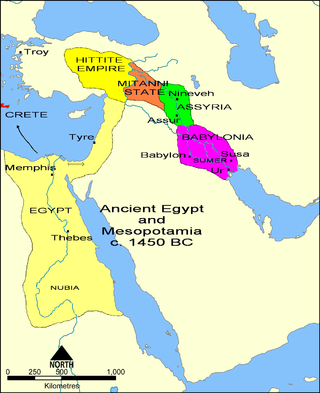
Babylonia was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia. It emerged as an Akkadian populated but Amorite-ruled state c. 1894 BC. During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was retrospectively called "the country of Akkad", a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older ethno-linguistically related state of Assyria in the north of Mesopotamia and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apart after the death of Hammurabi and reverted to a small kingdom centered around the city of Babylon.

The Kassites were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC.

Ancient art refers to the many types of art produced by the advanced cultures of ancient societies with different forms of writing, such as those of ancient China, India, Mesopotamia, Persia, Palestine, Egypt, Greece, and Rome. The art of pre-literate societies is normally referred to as prehistoric art and is not covered here. Although some pre-Columbian cultures developed writing during the centuries before the arrival of Europeans, on grounds of dating these are covered at pre-Columbian art and articles such as Maya art, Aztec art, and Olmec art.
Ahmose is an Ancient Egyptian name meaning "The Moon is born" or "Child of the Moon". It was a very popular name in the beginning of the eighteenth dynasty.
This timeline of ancient history lists historical events of the documented ancient past from the beginning of recorded history until the Early Middle Ages. Prior to this time period, prehistory civilizations were pre-literate and did not have written language.
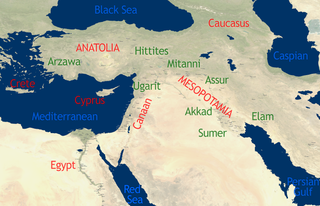
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Comparing many records pieces together a relative chronology relating dates in cities over a wide area.

The Middle Babylonian period, also known as the Kassite period, in southern Mesopotamia is dated from c. 1595 – c. 1155 BC and began after the Hittites sacked the city of Babylon. The Kassites, whose dynasty is synonymous with the period, eventually assumed political control over the region and consolidated their power by subjugating the Sealand dynasty c. 1475 BC. After the subjugation of the Sealand dynasty, the Kassites unified the region of Babylonia into a single political entity. At the height of the Middle Babylonian period, the Kassite kings were engaging in commerce, trade, and organising diplomatic marriages with the kings of Egypt and other regional powers. However, after a period of gradual decline, the Middle Babylonian period collapsed with the fall of the Kassite dynasty c. 1155 BC. The collapse came as a result of an Assyrian invasion, that temporarily displaced the Kassites from their rule over southern Mesopotamia. Finally, the Elamites conducted various raids and eventually invaded Babylonian c. 1158 BC, which brought the Kassite dynasty and Middle Babylonian period to an end.








