
The governor of South Dakota is the head of government of South Dakota. The governor is elected to a four-year term in even years when there is no presidential election. The current governor is Kristi Noem, a member of the Republican Party who took office on January 5, 2019.

The 1885 New York state election was held on November 3, 1885, to elect the governor, the lieutenant governor, the secretary state, the state comptroller, the attorney general, the state treasurer and the state engineer, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate.

Henry Loucks (1846–1928) was a newspaper editor and politician in the Dakota Territory, United States.
Lora Lyn Hubbel is an American politician; a former member of the South Dakota House of Representatives and a former chair of the Minnehaha County Republican Party and the former state chair of the Constitution Party of South Dakota.

The 1889 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on October 1, 1889, to elect the first Governor of South Dakota. Territorial Governor Arthur C. Mellette received the Republican nomination and faced former Territorial Commissioner of Immigration P. F. McClure, the Democratic nominee, in the general election. Mellette defeated McClure in a landslide.

The 1894 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 6, 1894. Incumbent Republican Governor Charles H. Sheldon ran for re-election to a second term. Despite facing a thread of defeat at the Republican convention, Sheldon was renominated unanimously. In the general election, he faced Populist nominee Isaac Howe, a Spink County Judge; James A. Ward, the former state chairman of the South Dakota Democratic Party; and Prohibition nominee M. D. Alexander. The election was largely a replay of the gubernatorial elections of 1890 and 1892, with the Farmers' Alliance candidate placing second and the Democratic nominee placing a distant third. This time, however, Sheldon won an outright majority and the Democratic Party's vote share shrunk to just 11%, its worst performance in state history.
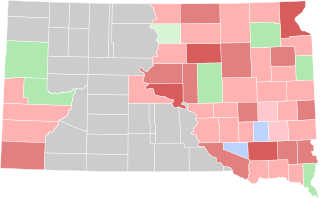
The 1892 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 1892. Incumbent Republican Governor Arthur C. Mellette declined to seek re-election to a third term. Former territorial legislator Charles H. Sheldon was nominated by the Republican Party as Mellette's replacement, and he faced former legislator Abraham Lincoln Van Osdel, a leader in the South Dakota Farmers' Alliance and the nominee of the Independent Party, along with Democratic nominee Peter Couchman, in the general election. The result was largely a replay of the 1890 election, with Sheldon winning by a large margin, but only a plurality, and Van Osdel taking second place over Couchman.

The 1896 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1896. Incumbent Republican Governor Charles H. Sheldon declined to run for re-election to a third term. Former Secretary of State Amund O. Ringsrud was nominated as Sheldon's replacement at the Republican convention. Ringrud's main opponent was businessman Andrew E. Lee, who was nominated by a makeshift coalition of Populists, Free Silver Republicans, and Democrats. In the general election, Lee narrowly defeated Ringsrud, the first defeat for the Republican Party in a gubernatorial election since statehood.

The 1898 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 1898. Incumbent governor Andrew E. Lee, elected in 1896 as a Populist, he ran for re-election as a Fusion candidate. He was challenged by Republican nominee Kirk G. Phillips, the state treasurer. Lee narrowly defeated Phillips to win his second term as governor, but most of his Fusion allies lost their elections, leaving him as the lone statewide officeholder.

The 1904 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 1904. Incumbent Republican Governor Charles N. Herreid declined to run for re-election to a third term. Clark County State's Attorney Samuel H. Elrod won the Republican nomination to run as Herreid's successor, and he faced Democratic nominee Louis N. Crill, the former president of the state Senate, and former U.S. Congressman Freeman Knowles, the Socialist nominee. For the first time since 1894, the Democratic and Populist Parties nominated separate candidates. Ultimately, the split in the two parties did not prove dispositive; Elrod defeated Crill and the other candidates in a landslide.

The 1906 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 6, 1906. Incumbent Republican Governor Samuel H. Elrod ran for re-election, but was defeated for renomination at the Republican convention by former Attorney General Coe I. Crawford. In the general election, Crawford was opposed by the Democratic nominee, former State Representative John A. Stransky of Brule County. Crawford had little difficulty defeating Stransky in a landslide, largely matching Elrod's margin of victory from two years earlier.

The 1942 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 3, 1942. Incumbent Democratic Senator William J. Bulow ran for re-election to a third term. During the primary, Bulow was attacked for being insufficiently supportive of President Franklin Roosevelt's foreign policy and war preparedness. Former Governor Tom Berry, Bulow's chief opponent, drew a contrast between Bulow's isolationism and his support for Roosevelt's policies. In the end, Berry defeated Bulow in a landslide, and advanced to the general election, where he faced Harlan J. Bushfield, the incumbent Republican Governor of South Dakota. As Republicans gained ground nationwide, Bushfield defeated Berry in a landslide to pick up the seat for the Republican Party. Bushfield did not serve his full term, however; shortly before the 1948 U.S. Senate election, he died.

The 1964 United States presidential election in South Dakota took place on November 3, 1964, as part of the 1964 United States presidential election. Voters chose four representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

John L. Pyle was an attorney and politician from the state of South Dakota. A Republican, he was notable for his service as State's Attorney of Hand County (1886-1888) and state Attorney General (1899-1902).

The 1890 Tennessee gubernatorial election was held on November 4, 1890. Incumbent Democratic Governor Robert Love Taylor did not seek re-election. Democratic nominee John P. Buchanan defeated Republican nominee Lewis T. Baxter and Prohibition nominee D. C. Kelley with 56.57% of the vote.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1889, in eleven states.
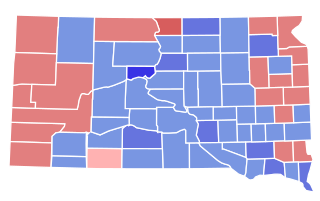
The 1928 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 6, 1928. Incumbent Democratic Governor William J. Bulow ran for re-election to a second term. In the general election, he faced Attorney General Buell F. Jones, the Republican nominee. Despite Republican presidential nominee Herbert Hoover overwhelmingly defeating Democratic nominee Al Smith overwhelmingly in South Dakota, Bulow defeated Jones by a decisive margin to retain the governorship. In so doing, he became the first Democratic candidate for Governor to receive a majority of the vote in the state's history.

The 1930 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 4, 1930. Incumbent Democratic Governor William J. Bulow declined to run for re-election to a third term, instead opting to successfully run for the U.S. Senate. The Republican nomination was hard-fought and the primary was crowded; because no candidate received 35% of the vote, state law required that the nomination be decided at a state party convention. There, former State Senator Warren Green, the last-place finisher in the primary, defeated Secretary of State Gladys Pyle, the plurality winner. In the general election, Green faced D. A. McCullough, the state's Rural Credits Commissioner and the Democratic nominee. Despite Bulow's success in the preceding two elections, Green defeated McCullough by a decisive margin—even as Bulow himself was elected to the U.S. Senate.

The 1936 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1936. Incumbent Democratic Governor Tom Berry ran for re-election to a third term, the first Governor of South Dakota to do so. Berry was challenged by Republican Leslie Jensen, the former Collector of Internal Revenue for the state of South Dakota. Both Berry and Jensen won their primaries uncontested and advanced to the general election. Some drama surrounded the potential candidacy of Democratic State Auditor George O'Neill as an independent candidate for Governor or, in the alternative, his cross-party endorsement of Jensen; after initially announcing his campaign and hedging, O'Neill dropped out of the race in September and endorsed the Democratic ticket in the state, including Berry.
The following is a list of events of the year 1889 in South Dakota.






















