
William Henry McMaster was an American politician who served as the tenth Governor of South Dakota from 1921 until 1925. A member of the Republican Party, he went on to serve as a member of the United States Senate from South Dakota from 1925 to 1931.

The 1948 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 2, 1948. Incumbent Republican Senator Harlan J. Bushfield, suffering from poor health, declined to run for re-election. On September 27, 1948, he died in office; his wife, Vera C. Bushfield, was appointed to succeed him. Congressman Karl E. Mundt easily won the Republican primary and advanced to the general election, where he was opposed by Democratic nominee John A. Engel, an attorney. Hundt defeated Engel in a landslide.

The 2014 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 4, 2014, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the state of South Dakota, concurrently with the election of the Governor of South Dakota, as well as other elections to the United States Senate in other states and elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections.

The 1956 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 6, 1956. Incumbent Republican Senator Francis H. Case ran for re-election to a second term. In the general election, Case was opposed by former State Representative Kenneth Holum, who was the 1954 Democratic nominee for the U.S. Senate. Owing in part to anger among the state's farmers, the race between Case and Holum was quite close, with Holum leading Case on election night and only falling behind the next day. Case ended up narrowly winning re-election, defeating Holum by just 4,620 votes.

The 1950 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 7, 1950. Incumbent Republican senator Chan Gurney ran for re-election to a third term. He was challenged in the Republican primary by Congressman Francis H. Case, who had represented the 2nd District since 1939. In the general election, Case faced John A. Engel, an attorney and the 1948 Democratic nominee for the U.S. Senate. As the Republican Party was making significant gains nationwide, Case defeated Engel in a landslide.

The 1918 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 5, 1918. Incumbent Republican Senator Thomas Sterling sought re-election in his first popular election. He defeated former Governor Frank M. Byrne in the Republican primary and then faced former State Representative Orville Rinehart, the 1916 Democratic nominee for Governor, in the general election. Sterling defeated Rinehart, along with independent candidate W. T. Rafferty, by a wide margin to win re-election.
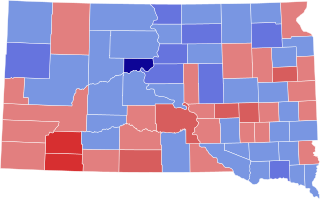
The 1930 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 4, 1930. Incumbent Republican Senator William H. McMaster ran for re-election to a second term. After beating back a challenge in the Republican primary from former State Senator George J. Danforth, McMaster faced Democratic nominee William J. Bulow, the incumbent Governor, in the general election. As the Democratic Party performed well nationwide, Bulow narrowly defeated McMaster.

The 1932 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 7, 1944. Incumbent Republican Senator Chan Gurney ran for re-election to a second term. He faced a strong challenge in the Republican primary from Lieutenant Governor A. C. Miller, who claimed that Gurney was too friendly to New Deal policies, but was defeated by Gurney by a wide margin. In the general election, Gurney faced former State Senator George M. Bradshaw, whom he defeated in a landslide as Thomas E. Dewey was decisively winning the state over President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the presidential election.

The 1960 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 8, 1960. Incumbent Republican Senator Karl E. Mundt ran for re-election to his third term. He was challenged by Congressman George McGovern. Both Mundt and McGovern won their respective primaries unopposed and the campaign between the two began. Despite the landslide victory for Vice-President Richard M. Nixon over John F. Kennedy, the race between Mundt and McGovern was quite close. Mundt narrowly won re-election, and McGovern ran for the U.S. Senate again in 1962. He served alongside Mundt for a decade.

The 1962 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 6, 1962. Incumbent Republican Senator Francis H. Case ran for re-election to a third term. He won the Republican primary against Attorney General A. C. Miller, but shortly after the primary, died. The Republican State Central Committee named Lieutenant Governor Joseph H. Bottum as Case's replacement on the ballot, and Governor Archie Gubbrud appointed Bottum to fill the vacancy caused by Case's death. In the general election, Bottum was opposed by Democratic nominee George McGovern, the Director of Food for Peace and the former U.S. Congressman from South Dakota's 1st congressional district. The contest between Bottum and McGovern was quite close, with McGovern narrowly defeating him for election by just 597 votes, making him the first Democrat to win a Senate election in South Dakota since William J. Bulow's win in 1936.

The 1966 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 8, 1966. Incumbent Republican Senator Karl E. Mundt ran for re-election to his fourth term. He was challenged in the Republican primary by a John Birch Society member, but easily turned away the challenge. In the general election, he faced State Representative Donn Wright, the Democratic nominee. Owing in large part to the Republican landslide taking place nationwide, Mundt defeated Wright by an unprecedented margin.

The 1968 United States Senate election in South Dakota took place on November 5, 1968. Incumbent Democratic Senator George McGovern ran for re-election to a second term. He was challenged by former Governor Archie M. Gubbrud, who was persuaded to enter the race by the South Dakota Republican establishment. McGovern defeated Gubbrud by a wide margin, even as Richard Nixon was defeating Hubert Humphrey in the state's presidential election in a landslide.

The 1914 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1914. Despite a close election in 1912, incumbent Republican Governor Frank M. Byrne defeated Democratic nominee James W. McCarter, an Edmunds County Judge, with 50.07% of the vote. Coincidently, Bryne's Democratic opponent in 1912, Edwin S. Johnson, was elected the same year to represent South Dakota in the United States Senate.
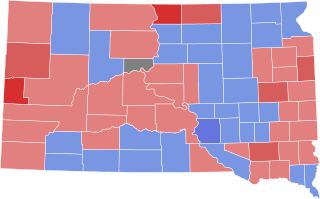
The 1938 United States Senate elections in South Dakota took place on November 8, 1938. Incumbent Republican Senator Peter Norbeck died in office on December 20, 1936. Herbert E. Hitchcock was appointed by Governor Tom Berry as Norbeck's replacement. Two elections for the same Senate seat were held on the same day; one as a special election to fill the remainder of Norbeck's six-year term, and another to select a Senator to serve the next six-year term.

The 1924 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 4, 1924. Incumbent Republican Governor William H. McMaster declined to run for re-election to a third term, instead opting to run for the U.S. Senate. Lieutenant Governor Carl Gunderson won the Republican primary unopposed. In the general election, he faced three prominent opponents: Democratic nominee William J. Bulow, a former State Senator and Mayor of Beresford; Farmer–Labor nominee A. L. Putnam; and perennial candidate Richard O. Richards. Gunderson. With the left-leaning vote split, Gunderson won the election in a landslide.
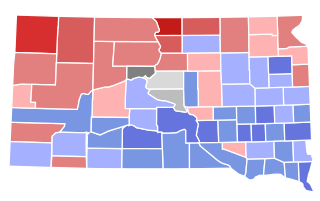
The 1926 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 2, 1926. Incumbent Republican Governor Carl Gunderson ran for re-election to a second term. The election was largely a rematch of the 1924 election, with Gunderson's chief opponent from two years prior, Democrat William J. Bulow, challenging him once again. Two other candidates—Farmer–Labor nominee Tom Ayres and Pierre Mayor John E. Hipple, an independent—also ran. Though the left-leaning vote was split, Bulow was still able to win a decisive victory over Gunderson, whose support from two years earlier had completely collapsed.

The 1930 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 4, 1930. Incumbent Democratic Governor William J. Bulow declined to run for re-election to a third term, instead opting to successfully run for the U.S. Senate. The Republican nomination was hard-fought and the primary was crowded; because no candidate received 35% of the vote, state law required that the nomination be decided at a state party convention. There, former State Senator Warren Green, the last-place finisher in the primary, defeated Secretary of State Gladys Pyle, the plurality winner. In the general election, Green faced D. A. McCullough, the state's Rural Credits Commissioner and the Democratic nominee. Despite Bulow's success in the preceding two elections, Green defeated McCullough by a decisive margin—even as Bulow himself was elected to the U.S. Senate.

The 1936 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1936. Incumbent Democratic Governor Tom Berry ran for re-election to a third term, the first Governor of South Dakota to do so. Berry was challenged by Republican Leslie Jensen, the former Collector of Internal Revenue for the state of South Dakota. Both Berry and Jensen won their primaries uncontested and advanced to the general election. Some drama surrounded the potential candidacy of Democratic State Auditor George O'Neill as an independent candidate for Governor or, in the alternative, his cross-party endorsement of Jensen; after initially announcing his campaign and hedging, O'Neill dropped out of the race in September and endorsed the Democratic ticket in the state, including Berry.

The 1940 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 5, 1940. Incumbent Republican Governor Harlan J. Bushfield sought re-election to a second term. After winning the Republican primary by a large margin, he faced Democrat Lewis W. Bicknell, former Day County State's Attorney, in the general election. Though Bushfield underperformed Republican presidential nominee Wendell Willkie, who won the state in a landslide, he nonetheless defeated Bicknell by a wide margin to easily win re-election.

The 1942 South Dakota gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1942. Incumbent Republican Governor Harlan J. Bushfield declined to seek re-election to a third term and instead successfully ran for the U.S. Senate. A crowded Republican primary developed to succeed him, and because no candidate received 35% of the vote, the nomination was decided at the state Republican convention, where former Attorney General Merrell Q. Sharpe, the second-place finisher in the primary, won the nomination. In the general election, Sharpe faced Democratic nominee Lewis W. Bicknell, the 1940 Democratic nominee for Governor. Aided by the national Republican landslide, Sharpe defeated Bicknell in a landslide.




















