Methanethiol is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula CH
3SH. It is a colorless gas with a distinctive putrid smell. It is a natural substance found in the blood, brain and feces of animals, as well as in plant tissues. It also occurs naturally in certain foods, such as some nuts and cheese. It is one of the chemical compounds responsible for bad breath and the smell of flatus. Methanethiol is the simplest thiol and is sometimes abbreviated as MeSH. It is very flammable.

Methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil) is an organic compound with the formula C8H8O3. It is the methyl ester of salicylic acid. It is a colorless, viscous liquid with a sweet, fruity odor reminiscent of root beer, but often associatively called "minty", as it is an ingredient in mint candies. It is produced by many species of plants, particularly wintergreens. It is also produced synthetically, used as a fragrance and as a flavoring agent.

5-Nitroimidazole is an organic compound with the formula O2NC3H2N2H. The nitro group at position 5 on the imidazole ring is the most common positional isomer. The term nitroimidazole also refers to a class of antibiotics that share similar chemical structures.
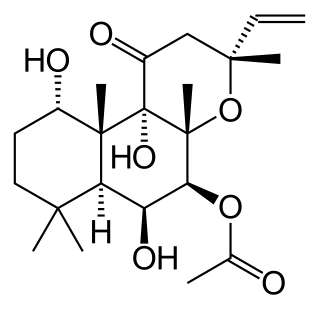
Forskolin (coleonol) is a labdane diterpene produced by the plant Coleus barbatus. Other names include pashanabhedi, Indian coleus, makandi, HL-362, mao hou qiao rui hua. As with other members of the large diterpene class of plant metabolites, forskolin is derived from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). Forskolin contains some unique functional elements, including the presence of a tetrahydropyran-derived heterocyclic ring. Forskolin is commonly used in laboratory research to increase levels of cyclic AMP by stimulation of adenylate cyclase.
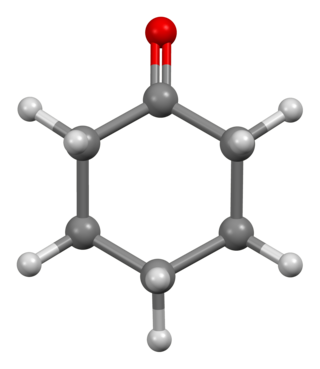
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has an odor reminiscent of acetone. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Billions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon.
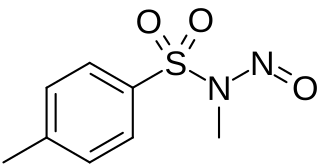
Diazald (N-methyl-N-nitroso-p-toluenesulfonamide) is used as a relatively safe and easily handled precursor to diazomethane, which is toxic and unstable. Diazald has become the favored commercially available precursor for the synthesis of diazomethane, compared to reagents like N-methyl-N-nitrosourea and N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine, which are less thermally stable and more toxic and mutagenic, respectively.
Sigma-Aldrich is an American chemical, life science, and biotechnology company owned by the multinational chemical conglomerate Merck Group.

N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) is an organic compound consisting of a 5-membered lactam. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples can appear yellow. It is miscible with water and with most common organic solvents. It also belongs to the class of dipolar aprotic solvents such as dimethylformamide and dimethyl sulfoxide. It is used in the petrochemical, polymer and battery industries as a solvent, exploiting its nonvolatility and ability to dissolve diverse materials.

Chromyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO2Cl2. It is a reddish brown compound that is a volatile liquid at room temperature, which is unusual for transition metal compounds.

PyBOP is a peptide coupling reagent used in solid phase peptide synthesis. It is used as a substitute for the BOP reagent - avoiding the formation of the carcinogenic waste product HMPA.

1,3-Difluoro-2-propanol is a metabolic poison which disrupts the citric acid cycle and is used as a rodenticide, similar to sodium fluoroacetate. It is the main ingredient in the rodenticide product Gliftor which was widely used in the former USSR and still approved in China.

Ethyl iodoacetate is a chemical compound that is a derivative of ethyl acetate. Under normal conditions, the compound is a clear, light yellow to orange liquid.

Imiprothrin is a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide. It is an ingredient in some commercial and consumer insecticide products for indoor use. It has low acute toxicity to humans through the inhalation and dermal routes, but to insects it acts as a neurotoxin causing paralysis. It is effective against cockroaches, waterbugs, ants, silverfish, crickets and spiders, among others.

Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) is a toxin produced by cyanobacteria. It is the most toxic of the microcystins.

N,N-Diisopropylaminoethanol (DIPA) is a processor for production of various chemicals and also an intermediate in the production of the nerve agents VX and NX. It is a colorless liquid, although aged samples can appear yellow.

Thiocarbohydrazide is a toxic compound made by the reaction of carbon disulfide with hydrazine (hydrazinolysis). It is used in the silver proteinate specific staining of carbohydrates in electron microscopy.

Tetrachlorvinphos is an organophosphate insecticide used to kill fleas and ticks.

4-Aminophenylmercuric acetate (CH3CO2HgC6H4NH2, also known as 4-(Acetoxymercurio)aniline or APMA), is an organomercurial compound and thiol-blocking reagent used in experimental biology and chemistry to activate matrix metalloproteinases and collagenase proteolytic enzymes. The material is highly toxic.

1-Heptadecanol or heptadecyl alcohol is a saturated fatty alcohol with the CAS number 1454-85-9.
1-Nonadecanol is one of the constituents of supercritical carbon dioxide essential oil of freshly collected aerial parts of Heracleum thomsonii (Umbelliferae).