Related Research Articles
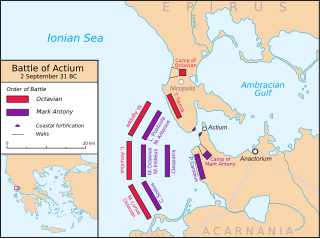
Year 31 BC was either a common year starting on Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday or a leap year starting on Tuesday or Wednesday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Tuesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Antonius and Caesar or as Caesar and Messalla. The denomination 31 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 23 BC was either a common year starting on Saturday or Sunday or a leap year starting on Friday, Saturday or Sunday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Friday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Varro. The denomination 23 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The 10s decade ran from January 1, AD 10, to December 31, AD 19.

The 20s decade ran from January 1, AD 20, to December 31, AD 29.

The 30s decade ran from January 1, AD 30, to December 31, AD 39.

The 1st century BC, also known as the last century BC and the last century BCE, started on the first day of 100 BC and ended on the last day of 1 BC. The AD/BC notation does not use a year zero; however, astronomical year numbering does use a zero, as well as a minus sign, so "2 BC" is equal to "year –1". 1st century AD follows.
This article concerns the period 39 BC – 30 BC.
AD 4 was a common year starting on Wednesday or a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar and a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Catus and Saturninus. The denomination "AD 4" for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
6 was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lepidus and Lucius Arruntius. The denomination "AD 6" for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 18 (XVIII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Caesar. The denomination AD 18 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 44 (XLIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Crispus and Taurus. The denomination AD 44 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 0s BC is the period between 9 BC and 1 BC, the last nine years of the before Christ era. It is one of two "0-to-9" decade-like timespans that contain nine years, along with the 0s.

100 (C) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar, the 100th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 100th year of the 1st millennium, the 100th and last year of the 1st century, and the 1st year of the 100s decade. As of the start of 100, the Gregorian calendar was 2 days behind the Julian calendar, which was the dominant calendar of the time.
This article concerns the period 19 BC – 10 BC.
This article concerns the period 29 BC – 20 BC.
Year 37 BC was either a common year starting on Monday, Tuesday or Wednesday or a leap year starting on Monday or Tuesday of the Julian calendar and a leap year starting on Monday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Agrippa and Gallus. The denomination 37 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 30 BC was either a common year starting on Wednesday, Thursday or Friday or a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Octavian and Crassus. The denomination 30 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Herod Antipas was a 1st-century ruler of Galilee and Perea. He bore the title of tetrarch and is referred to as both "Herod the Tetrarch" and "King Herod" in the New Testament. He was a son of Herod the Great and a grandson of Antipater the Idumaean. He is widely known today for accounts in the New Testament of his role in events that led to the executions of John the Baptist and Jesus of Nazareth.
AD 2 (II) or 2 AD was a common year starting on Sunday or Monday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Sunday of the proleptic Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vinicius and Varus, named after Roman consuls Publius Vinicius and Alfenus Varus, and less frequently, as year 755 AUC within the Roman Empire. The denomination "AD 2" for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The 0s began on January 1, AD 1 and ended on December 31, AD 9, covering the first nine years of the Common Era. It is one of two "0-to-9" decade-like timespans that contain nine years, along with the 0s BC.
References
- ↑ Evans, Craig A. (2004). Of Scribes and Sages: Ancient versions and traditions. A&C Black. pp. 137–140. ISBN 978-0-567-08083-7.
- ↑ "List of Rulers of Korea". www.metmuseum.org. Retrieved April 21, 2019.
- ↑ Dunn, James D.G. (2003). Jesus Remembered. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 344. ISBN 978-0-8028-3931-2.
- ↑ "Herod | Biography & Facts". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved April 7, 2019.