Related Research Articles

Year 27 BC was either a common year starting on Sunday, Monday or Tuesday or a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Sunday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Second Consulship of Octavian and Agrippa. The denomination 27 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
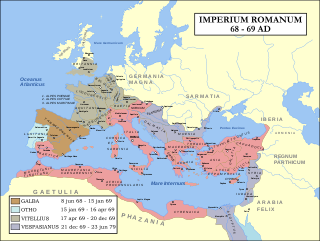
AD 69 (LXIX) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the consulship of Galba and Vinius. The denomination AD 69 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 25 (XXV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Agrippa. The denomination AD 25 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 106 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caepio and Serranus and the Fifth Year of Yuanfeng. The denomination 106 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 3 (III) or 3 AD was a common year starting on Monday or Tuesday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Monday of the proleptic Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was the Year of the Consulship of Lamia and Servilius. The denomination "AD 3" for this year has been used since the early medieval period when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 22 (XXII) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Agrippa and Galba. The denomination AD 22 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 0s BC is the period between 9 BC and 1 BC, the last nine years of the before Christ era. It is one of two "0-to-9" decade-like timespans that contain nine years, along with the 0s.
AD 57 (LVII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Piso. The denomination AD 57 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 245 (CCXLV) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Philippus and Titianus. The denomination 245 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 104 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marius and Fimbria and the First Year of Taichu. The denomination 104 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 14 BC was either a common year starting on Thursday or Friday or a leap year starting on Wednesday, Thursday or Friday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Tuesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Crassus and Lentulus. The denomination 14 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 1 BC was a common year starting on Friday or Saturday in the Julian calendar and a leap year starting on Thursday in the proleptic Julian calendar. It was also a leap year starting on Saturday in the Proleptic Gregorian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Piso. The denomination 1 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. The following year is AD 1 in the widely used Julian calendar and the proleptic Gregorian calendar, which both do not have a "year zero".
Year 7 BC was a common year starting on Saturday or Sunday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Thursday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. In the Roman world, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Tiberius and Piso. The denomination 7 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 8 BC was either a common year starting on Friday or Saturday or a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Censorinus and Gaius Asinius. The denomination 8 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 45 BC was either a common year starting on Thursday, Friday or Saturday or a leap year starting on Friday or Saturday and the first year of the Julian calendar and a leap year starting on Friday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar without Colleague. The denomination 45 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
108 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Galba and Hortensius/Scaurus and the Third Year of Yuanfeng. The denomination 108 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 33 BC was either a common year starting on Saturday, Sunday or Monday or a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar and a leap year starting on Saturday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Octavian and Tullus. The denomination 33 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 144 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Galba and Cotta. The denomination 144 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 200 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Maximus and Cotta. The denomination 200 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 2 (II) or 2 AD was a common year starting on Sunday or Monday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Sunday of the proleptic Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vinicius and Varus, named after Roman consuls Publius Vinicius and Alfenus Varus, and less frequently, as year 755 AUC within the Roman Empire. The denomination "AD 2" for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
References
- ↑ Charles A. Frazee (2002). Two Thousand years ago. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 133. ISBN 978-0-8028-4805-5.
- ↑ Julien Bridge. Avignon & Provence
- ↑ "Galba | Roman Emperor, Death of Nero, Murder | Britannica". www.britannica.com. August 3, 2023. Retrieved September 22, 2023.