This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2022) |

| Millennia |
|---|
| 1st millennium |
| Centuries |
| Decades |
| Years |
|
| Categories |
The 0s began on January 1, AD 1 and ended on December 31, AD 9, covering the first nine years of the Common Era.
Contents
- Calendar details
- Politics and wars
- Heads of state
- Wars
- Events
- Africa
- China
- Europe
- Korea
- Persia
- Roman Empire
- Demographics
- Significant people
- Births
- Deaths
- See also
- References
- External links
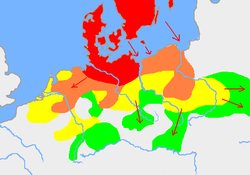
In Europe, the 0s saw the continuation of conflict between the Roman Empire and Germanic tribes in the Early Imperial campaigns in Germania. Vinicius, Tiberius and Varus led Roman forces in multiple punitive campaigns, before sustaining a major defeat at the hands of Arminius in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. Concurrently, the Roman Empire fought the Bellum Batonianum against a rebelling alliance of native peoples led by Bato the Daesitiate in Illyricum, which was suppressed in AD 9. A conflict also took place in Korea, where Daeso, King of Dongbuyeo invaded Goguryeo with a 50,000-man army in AD 6. He was forced to retreat when heavy snow began to fall, stopping the conflict until the next decade. In China, the last ruler of the Chinese Western Han dynasty (Ruzi Ying) was deposed, allowing Wang Mang to establish the Xin dynasty.
Literary works from the 0s include works from the ancient Roman poet Ovid; the Ars Amatoria , an instructional elegy series in three books, Metamorphoses, a poem which chronicles the history of the world from its creation to the deification of Julius Caesar within a loose mythico-historical framework, and Ibis, a curse poem written during his years in exile across the Black Sea for an offense against Augustus. Nicolaus of Damascus wrote the 15-volume History of the World.
Estimates for the world population by AD 1 range from 170 to 300 million. A census was concluded in China in AD 2: final numbers showed a population of nearly 60 million (59,594,978 people in slightly more than 12 million households). The census is one of the most accurate surveys in Chinese history. [2]