Related Research Articles

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.
Year 491 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augurinus and Atratinus. The denomination 491 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Xerxes I, commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC. He was the son of Darius the Great and Atossa, a daughter of Cyrus the Great. In Western history, Xerxes is best known for his invasion of Greece in 480 BC, which ended in Persian defeat. Xerxes was designated successor by Darius over his elder brother Artobazan and inherited a large, multi-ethnic empire upon his father's death. He consolidated his power by crushing revolts in Egypt and Babylon, and renewed his father's campaign to subjugate Greece and punish Athens and its allies for their interference in the Ionian Revolt. In 480 BC, Xerxes personally led a large army and crossed the Hellespont into Europe. He achieved victories at Thermopylae and Artemisium before capturing and razing Athens. His forces gained control of mainland Greece north of the Isthmus of Corinth until their defeat at the Battle of Salamis. Fearing that the Greeks might trap him in Europe, Xerxes retreated with the greater part of his army back to Asia, leaving behind Mardonius to continue his campaign. Mardonius was defeated at Plataea the following year, effectively ending the Persian invasion.
This article concerns the period 519 BC – 510 BC.
This article concerns the period 489 BC – 480 BC.
This article concerns the period 469 BC – 460 BC.

Year 486 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Viscellinus and Rutilus. The denomination 486 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
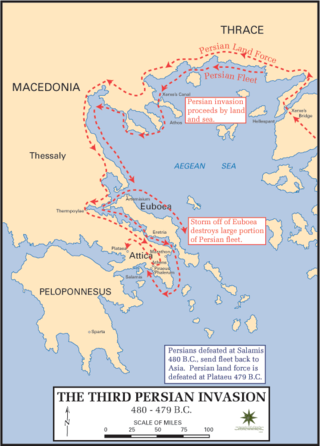
Year 480 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Cincinnatus. The denomination 480 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 483 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Potitus. The denomination 483 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 330 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Crassus and Venno. The denomination 330 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Ahasuerus is a name applied in the Hebrew Bible to three rulers of Ancient Persia and to a Babylonian official first appearing in the Tanakh in the Book of Esther and later in the Book of Tobit. It is a transliteration of either Xerxes I or Artaxerxes I; both are names of multiple Achaemenid dynasty Persian kings.
Year 465 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Barbatus. The denomination 465 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 519 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 235 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 519 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Persepolis was the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire. It is situated in the plains of Marvdasht, encircled by the southern Zagros mountains, Fars province of Iran. It is one of the key Iranian cultural heritage sites and a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1979.

Naqsh-e Rostam is an ancient archeological site and necropolis located about 13 km northwest of Persepolis, in Fars province, Iran. A collection of ancient Iranian rock reliefs are cut into the face of the mountain and the mountain contains the final resting place of four Achaemenid kings, notably king Darius the Great and his son, Xerxes. This site is of great significance to the history of Iran and to Iranians, as it contains various archeological sites carved into the rock wall through time for more than a millennium from the Elamites and Achaemenids to Sassanians. It lies a few hundred meters from Naqsh-e Rajab, with a further four Sassanid rock reliefs, three celebrating kings and one a high priest.

Apadana is a large hypostyle hall in Persepolis, Iran. It belongs to the oldest building phase of the city of Persepolis, in the first half of the 6th century BC, as part of the original design by Darius the Great. Its construction was completed by Xerxes I. Modern scholarship "demonstrates the metaphorical nature of the Apadana reliefs as idealised social orders".

Masistes was a Persian prince of the Achaemenid Dynasty, son of king Darius I and of his wife Atossa, and full brother of king Xerxes I. He was satrap (governor) of Bactria during his brother's reign, where he attempted to start a revolt in 478 BC.

The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire, was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of 5.5 million square kilometres. The empire spanned from the Balkans and Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Valley to the southeast.

The Tachara, or the Tachar Château, also referred to as the Palace of Darius the Great, was the exclusive building of Darius I at Persepolis, Iran. It is located 70 km northeast of the modern city of Shiraz in Fars province.

Doriscus was a settlement in ancient Thrace, on the northern shores of Aegean Sea, in a plain west of the river Hebrus. It was notable for remaining in Persian hands for many years after the Second Persian invasion of Greece, and remained thus known as the last Persian stronghold in Europe.