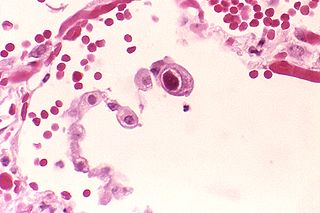
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Humans and other primates serve as natural hosts. The 11 species in this genus include human betaherpesvirus 5, which is the species that infects humans. Diseases associated with HHV-5 include mononucleosis and pneumonia, and congenital CMV in infants can lead to deafness and ambulatory problems.
White spot syndrome (WSS) is a viral infection of penaeid shrimp. The disease is highly lethal and contagious, killing shrimp quickly. Outbreaks of this disease have wiped out the entire populations of many shrimp farms within a few days, in places throughout the world.
Simplexvirus bovinealpha2, also known as Bovine alphaherpesvirus 2 (BoHV2) is a virus of the family Herpesviridae. It causes two diseases in cattle, bovine mammillitis and pseudo-lumpy skin disease.

Bovine malignant catarrhal fever (BMCF) is a fatal lymphoproliferative disease caused by a group of ruminant gamma herpes viruses including Alcelaphine gammaherpesvirus 1 (AlHV-1) and Ovine gammaherpesvirus 2 (OvHV-2) These viruses cause unapparent infection in their reservoir hosts, but are usually fatal in cattle and other ungulates such as deer, antelope, and buffalo. In Southern Africa the disease is known as snotsiekte, from the Afrikaans.
Infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV), is a negative-sense single-stranded, bullet-shaped RNA virus that is a member of the Rhabdoviridae family, and from the genus Novirhabdovirus. It causes the disease known as infectious hematopoietic necrosis in salmonid fish such as trout and salmon. The disease may be referred to by a number of other names such as Chinook salmon disease, Coleman disease, Columbia River sockeye disease, Cultus Lake virus disease, Oregon sockeye disease, Sacramento River Chinook disease and sockeye salmon viral disease. IHNV is commonly found in the Pacific Coast of Canada and the United States, and has also been found in Europe and Japan. The first reported epidemics of IHNV occurred in the United States at the Washington and the Oregon fish hatcheries during the 1950s. IHNV is transmitted following shedding of the virus in the feces, urine, sexual fluids, and external mucus and by direct contact or close contact with the surrounding water. The virus gains entry into fish at the base of the fins.
Malacoherpesviridae is a family of DNA viruses in the order Herpesvirales. Molluscs serve as natural hosts, making members of this family the only known herpesviruses to infect invertebrates. There are currently only two species recognised in this family, both classified into separate genera. Disease associated with this family includes sporadic episodes of high mortality among larvae and juveniles. The family name Malacoherpesviridae is derived from Greek word 'μαλακός (malacos) meaning 'soft' and from Greek word 'μαλάκιον (malakion) meaning 'mollusc'.

Alloherpesviridae is a family of viruses in the order Herpesvirales. This family includes the species that infect fish and amphibians. Phylogenetic studies have confirmed the validity of this family and suggest that it may be divided into two clades: one consisting of viruses from cyprinid and anguillid hosts and the other of viruses from ictalurid, salmonid, acipenserid, and ranid hosts. There are currently 13 species in this family, divided among four genera. A disease associated with this family includes channel catfish disease.

Betanodavirus, or nervous necrosis virus (NNV), is a genus of nonenveloped positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Nodaviridae. Member viruses infect fish and cause viral nervous necrosis (VNN) and viral encephalopathy and retinopathy (VER). The genus contains four species.
Ostreavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, and one of only two genera in the family Malacoherpesviridae. Molluscs serve as natural hosts. There is only one species described in this genus, Ostreid herpesvirus 1 (OsHV-1), commonly known as oyster herpesvirus. A disease associated with this genus is sporadic episodes of high mortality among larvae and juveniles.
Aurivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, and one of only two genera the family Malacoherpesviridae. Haliotid molluscs serve as natural hosts. There is only one species described in this genus, Haliotid herpesvirus 1 (AbHV-1), commonly known as abalone herpesvirus. A disease associated with this virus is acute ganglioneuritis.
Batravirus ranidallo1, also known as Ranid herpesvirus 1 (RaHV-1), is a double-stranded DNA virus within the order Herpesvirales. The virus was initially observed within renal tumors in 1934 by Baldwin Lucké, and more recently has become identifiable through the use of PCR in samples isolated from frog tumors. RaHV-1 causes renal tumors within the northern leopard frog, Rana pipiens. The virus has not yet been isolated in vitro within cell lines, meaning that while its existence and symptoms are fairly evident, its methods of transmission, cell infection, and reproduction are largely unknown.
Macropodid alphaherpesvirus 1 (MaHV-1) is a species of herpesvirus in the genus Simplexvirus. It was officially accepted as a valid species by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses in 2004.
Batravirus ranidallo2, also known as Ranid herpesvirus 2 (RaHV-2) is a species of virus in the genus Batrachovirus, family Alloherpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Cyvirus anguillidallo1, also known as Anguillid herpesvirus 1 (AngHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus Cyprinivirus, family Alloherpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Cyvirus cyprinidallo2, also known as Cyprinid herpesvirus 2 (CyHV-2) is a species of virus in the genus Cyprinivirus, family Alloherpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Ictalurid herpesvirus 1 (IcHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus Ictalurivirus, family Alloherpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales. It causes disease in channel catfish and blue catfish, and can cause significant economic loss in catfish farms. The disease is endemic in the USA and there are reports of the virus in Honduras and Russia.
Ictalurid herpesvirus 2 (IcHV-2) is a species of virus in the genus Ictalurivirus, family Alloherpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Salmovirus salmonidallo1, also known as Salmonid herpesvirus 1 (SalHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus Salmonivirus, and family Alloherpesviridae.
Salmonid herpesvirus 2 (SalHV-2) is a species of virus in the genus Salmonivirus, family Alloherpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Salmonid herpesvirus 3 (SalHV-3) is a species of virus in the genus Salmonivirus, family Alloherpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.



