
Aluminium is a chemical element; it has symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, forming a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, nonmagnetic, and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the twelfth-most common element in the universe. The radioactivity of 26Al, a more unstable isotope, leads to it being used in radiometric dating.

Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21. It is a silvery-white metallic d-block element. Historically, it has been classified as a rare-earth element, together with yttrium and the lanthanides. It was discovered in 1879 by spectral analysis of the minerals euxenite and gadolinite from Scandinavia.

Phosphoric acid is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula H3PO4. It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, which is a colourless, odourless, and non-volatile syrupy liquid. It is a major industrial chemical, being a component of many fertilizers.
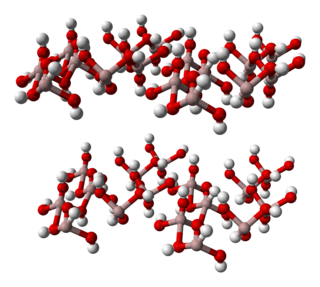
Aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3, is found in nature as the mineral gibbsite and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyleite, and nordstrandite. Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric, i.e., it has both basic and acidic properties. Closely related are aluminium oxide hydroxide, AlO(OH), and aluminium oxide or alumina, the latter of which is also amphoteric. These compounds together are the major components of the aluminium ore bauxite. Aluminium hydroxide also forms a gelatinous precipitate in water.
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behavior begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.
A deodorant is a substance applied to the body to prevent or mask body odor caused by bacterial breakdown of perspiration, for example in the armpits, groin, or feet. A subclass of deodorants, called antiperspirants, prevents sweating itself, typically by blocking sweat glands. Antiperspirants are used on a wider range of body parts, at any place where sweat would be inconvenient or unsafe, since unwanted sweating can interfere with comfort, vision, and grip. Other types of deodorant allow sweating but prevent bacterial action on sweat, since human sweat only has a noticeable smell when it is decomposed by bacteria.

Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li[AlH4] or LiAlH4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, especially for the reduction of esters, carboxylic acids, and amides. The solid is dangerously reactive toward water, releasing gaseous hydrogen (H2). Some related derivatives have been discussed for hydrogen storage.

Anodizing is an electrolytic passivation process used to increase the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the surface of metal parts.

Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula AlCl3. It forms a hexahydrate with the formula [Al(H2O)6]Cl3, containing six water molecules of hydration. Both the anhydrous form and the hexahydrate are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving them a yellow colour.

Aluminium sulfate is a salt with the formula Al2(SO4)3. It is soluble in water and is mainly used as a coagulating agent (promoting particle collision by neutralizing charge) in the purification of drinking water and wastewater treatment plants, and also in paper manufacturing.
Sodium aluminosilicate refers to compounds which contain sodium, aluminium, silicon and oxygen, and which may also contain water. These include synthetic amorphous sodium aluminosilicate, a few naturally occurring minerals and synthetic zeolites. Synthetic amorphous sodium aluminosilicate is widely used as a food additive, E 554.

Aluminium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula AlF3. It forms hydrates AlF3·xH2O. Anhydrous AlF3 and its hydrates are all colorless solids. Anhydrous AlF3 is used in the production of aluminium. Several occur as minerals.
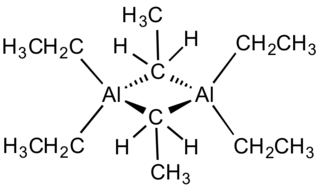
Triethylaluminium is one of the simplest examples of an organoaluminium compound. Despite its name the compound has the formula Al2(C2H5)6 (abbreviated as Al2Et6 or TEA). This colorless liquid is pyrophoric. It is an industrially important compound, closely related to trimethylaluminium.
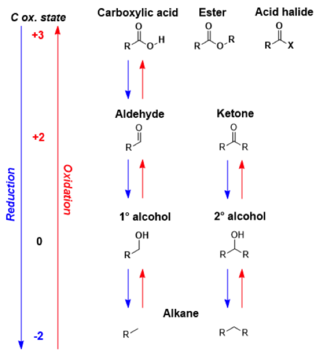
In organic chemistry, carbonyl reduction is the conversion of any carbonyl group, usually to an alcohol. It is a common transformation that is practiced in many ways. Ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, and acid halides - some of the most pervasive functional groups, -comprise carbonyl compounds. Carboxylic acids, esters, and acid halides can be reduced to either aldehydes or a step further to primary alcohols, depending on the strength of the reducing agent. Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced respectively to primary and secondary alcohols. In deoxygenation, the alcohol group can be further reduced and removed altogether by replacement with H.
Aluminium triacetate, formally named aluminium acetate, is a chemical compound with composition Al(CH
3CO
2)
3. Under standard conditions it appears as a white, water-soluble solid that decomposes on heating at around 200 °C. The triacetate hydrolyses to a mixture of basic hydroxide / acetate salts, and multiple species co-exist in chemical equilibrium, particularly in aqueous solutions of the acetate ion; the name aluminium acetate is commonly used for this mixed system.

Aluminium (British and IUPAC spellings) or aluminum (North American spelling) combines characteristics of pre- and post-transition metals. Since it has few available electrons for metallic bonding, like its heavier group 13 congeners, it has the characteristic physical properties of a post-transition metal, with longer-than-expected interatomic distances. Furthermore, as Al3+ is a small and highly charged cation, it is strongly polarizing and aluminium compounds tend towards covalency; this behaviour is similar to that of beryllium (Be2+), an example of a diagonal relationship. However, unlike all other post-transition metals, the underlying core under aluminium's valence shell is that of the preceding noble gas, whereas for gallium and indium it is that of the preceding noble gas plus a filled d-subshell, and for thallium and nihonium it is that of the preceding noble gas plus filled d- and f-subshells. Hence, aluminium does not suffer the effects of incomplete shielding of valence electrons by inner electrons from the nucleus that its heavier congeners do. Aluminium's electropositive behavior, high affinity for oxygen, and highly negative standard electrode potential are all more similar to those of scandium, yttrium, lanthanum, and actinium, which have ds2 configurations of three valence electrons outside a noble gas core: aluminium is the most electropositive metal in its group. Aluminium also bears minor similarities to the metalloid boron in the same group; AlX3 compounds are valence isoelectronic to BX3 compounds (they have the same valence electronic structure), and both behave as Lewis acids and readily form adducts. Additionally, one of the main motifs of boron chemistry is regular icosahedral structures, and aluminium forms an important part of many icosahedral quasicrystal alloys, including the Al–Zn–Mg class.
Copper(II) laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula Cu(C
11H
23COO)
2. It is a light blue solid that does not dissolve in water. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. It is structurally related to copper(II) acetate.
Zinc laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
46ZnO
4. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Magnesium laurate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
46MgO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Potassium laurate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
12H
23KO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.











