
A daylily, day lily or ditch-lily is a flowering plant in the genus Hemerocallis, a member of the family Asphodelaceae, subfamily Hemerocallidoideae, native to Asia. Despite the common name, it is not, in fact, a lily, nor does it specifically grow in ditches. Gardening enthusiasts and horticulturists have long bred Hemerocallis species for their attractive flowers; a select few species of the genus have edible petals, while some are extremely toxic. Thousands of cultivars have been registered by the American Daylily Society, the only internationally recognized registrant according to the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (ICNCP).. The plants are perennial, bulbous plants, whose common name alludes to its flowers, which typically last about a day.

Acorus is a genus of monocot flowering plants. This genus was once placed within the family Araceae (aroids), but more recent classifications place it in its own family Acoraceae and order Acorales, of which it is the sole genus of the oldest surviving line of monocots. Some older studies indicated that it was placed in a lineage, that also includes aroids (Araceae), Tofieldiaceae, and several families of aquatic monocots. However, modern phylogenetic studies demonstrate that Acorus is sister to all other monocots. Common names include calamus and sweet flag.

Asplenium platyneuron, commonly known as ebony spleenwort or brownstem spleenwort, is a fern native to North America east of the Rocky Mountains. It takes its common name from its dark, reddish-brown, glossy stipe and rachis, which support a once-divided, pinnate leaf. The fertile fronds, which die off in the winter, are darker green and stand upright, while the sterile fronds are evergreen and lie flat on the ground. An auricle at the base of each pinna points towards the tip of the frond. The dimorphic fronds and alternate, rather than opposite, pinnae distinguish it from the similar black-stemmed spleenwort.

Hepatica is a genus of herbaceous perennials in the buttercup family, native to central and northern Europe, Asia and eastern North America. Some botanists include Hepatica within a wider interpretation of Anemone.

Pyrus pyrifolia is a species of pear tree native to southern China and northern Indochina that has been introduced to Korea, Japan and other parts of the world. The tree's edible fruit is known by many names, including Asian pear, Persian pear, Japanese pear, Chinese pear, Korean pear, Taiwanese pear, apple pear, zodiac pear, three-halves pear, papple, naspati and sand pear. Along with cultivars of P. × bretschneideri and P. ussuriensis, the fruit is also called the nashi pear. Cultivars derived from Pyrus pyrifolia are grown throughout East Asia, and in other countries such as India, Pakistan, Nepal, Australia, New Zealand, and the United States. Traditionally in East Asia the tree's flowers are a popular symbol of early spring, and it is a common sight in gardens and the countryside.

Lespedeza is a genus of some 45 species of flowering plants in the pea family (Fabaceae), commonly known as bush clovers or Japanese clovers (hagi). The genus is native to warm temperate to subtropical regions of eastern North America, eastern and southern Asia and Australasia.

Arisaema is a large and diverse genus of the flowering plant family Araceae. The largest concentration of species is in China and Japan, with other species native to other parts of southern Asia as well as eastern and central Africa, Mexico and eastern North America. Asiatic species are often called cobra lilies, while western species are often called jack-in-the-pulpit; both names refer to the distinctive appearance of the flower, which consists of an erect central spadix rising from a spathe.

Arisaema triphyllum, the Jack-in-the-pulpit, is a species of flowering plant in the arum family Araceae. It is a member of the Arisaema triphyllum complex, a group of four or five closely related taxa in eastern North America. The specific name triphyllum means "three-leaved", a characteristic feature of the species, which is also referred to as Indian turnip, bog onion, and brown dragon.

Anemone hepatica, the common hepatica, liverwort, liverleaf, kidneywort, or pennywort, is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae, native to woodland in temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. This herbaceous perennial grows from a rhizome.

Arisaema dracontium, the dragon-root or green dragon, is a herbaceous perennial plant in the genus Arisaema and the family Araceae. It is native to North America from Quebec through Minnesota south through Florida and Texas, where it is found growing in damp woods. It has also been reported from northeastern Mexico Plants grow 20–50 centimetres (7.9–19.7 in) tall when in bloom and after flowering reach 100 centimetres (39 in), and each grows from a corm. Normally, a plant produces one leaf with a long petiole, its leaf is composed of 7 to 13 leaflets, with its central leaflet being the largest one and with leaflets becoming smaller as they are produced distally, the leaflets are held out horizontally over the plant. During flowering in spring, a single slender, green spathe 3–6 centimetres (1.2–2.4 in) long is produced; it covers a tapering, long thin spadix. The tail-like spadix grows out around the top of its spathe. After flowering, up to 150 berries are produced in a club-shaped column. In late summer, the green berries turn orange-red, each berry produces 1 to 3 seeds. It is listed as a vulnerable species in Canada.

Dracontomelon is a genus of flowering plants in the family Anacardiaceae, growing mostly in SE Asia and the Pacific islands. The fruit may be used in local cuisine, especially as souring agents.

Arisaema flavum is a species of flowering plant widespread across north-eastern Africa and southern Asia. It is native to Ethiopia, Somalia, the Arabian Peninsula, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Nepal, Assam, Himalayas, Tibet, Yunnan, and Sichuan. The species epithet flavum is Latin for yellow and indicates its flower colour.

Arisaema thunbergii subsp. urashima is a herbaceous perennial plant. It is widespread through the woodlands of Japan, especially near the coast. The plant has a very curious inflorescence, and is popular in horticulture. As with all arisaemas, the inflorescence consists of a spathe tube enclosing a spadix appendix. In the case of A. thunbergi subsp. urashima, the spadix appendix is elongated into a free hanging thread of 45 to 60 cm. The underground tuber often produces offsets, which can be removed and grown on. The foliage dies down by summer, leaving the fruiting spike to ripen in autumn. The red berries contain high amounts of oxalic acid, and can cause painful irritation to the skin. All parts of the plant should be considered poisonous.
Hiroyoshi Ohashi is a botanist formerly at the University of Tokyo and Tohoku University. He began publishing on Japanese Arisaema in the early 1960s. He published a couple of miscellaneous notes on Arisaema in 1963 and 1964 and these were followed by a revision of the genus for Japan jointly published in 1980 with J. Murata, and by the Araceae treatment for the Wildflowers of Japan.
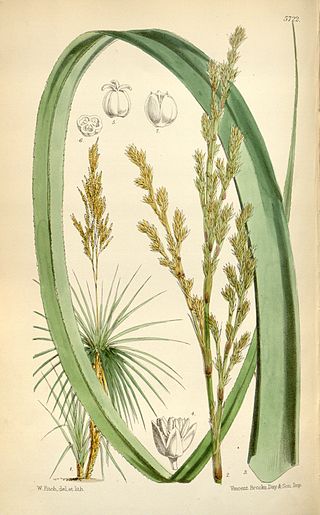
Prionium serratum, the palmiet, is a robust, evergreen, semiaquatic, rhizomatous flowering plant growing to 2 m in height. It is the only species in the genus Prionium, and is endemic to South Africa. Some authors have separated Prionium from the Thurniaceae, putting it instead in its own family, the Prioniaceae.

Arisaema quinatum is a species of flowering plant in the arum family Araceae. It is a member of the Arisaema triphyllum complex, a group of closely related taxa in eastern North America. The specific name quinatum means "divided into five lobes", a reference to its characteristic leaves. It is commonly known as the southern Jack-in-the-pulpit but some refer to it as Preacher John.
Arisaema pusillum is a species of flowering plant in the arum family Araceae. It is a member of the Arisaema triphyllum complex, a group of closely related taxa in eastern North America. The specific name pusillum, which means "very small, slender", describes the overall size of the plant relative to that of the more common Arisaema triphyllum. It is commonly known as the small Jack-in-the-pulpit. It is sometimes referred to as the swamp Jack, not to be confused with Arisaema stewardsonii, which is also known by that name.
Arisaema acuminatum is a species of flowering plant in the arum family Araceae. It is a member of the Arisaema triphyllum complex, a group of closely related taxa in eastern North America. The specific name acuminatum means "with a long, narrow and pointed tip", which describes the shape of the spathe hood. The species is commonly known as the Florida Jack-in-the-pulpit.

Eriocapitella japonica is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae. The specific epithet japonica means "from Japan", which is a misnomer since the species is introduced in Japan. It is native to China, Taiwan, and Vietnam.

Gleditsia japonica, the Japanese locust, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to the eastern Himalayas, central and southern China, Manchuria, Korea, and central and southern Japan. It is used as a street tree in a number of cities in China and Europe.
















