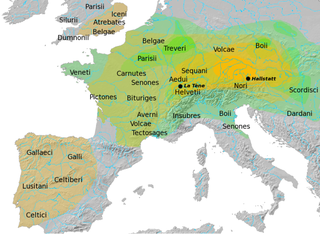
The La Tène culture was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age, succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscans, and the Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences.

A torc, also spelled torq or torque, is a large rigid or stiff neck ring in metal, made either as a single piece or from strands twisted together. The great majority are open at the front, although some have hook and ring closures and a few have mortice and tenon locking catches to close them. Many seem designed for near-permanent wear and would have been difficult to remove.

The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC and followed in much of its area by the La Tène culture. It is commonly associated with Proto-Celtic speaking populations.
The Arras culture is an archaeological culture of the Middle Iron Age in East Yorkshire, England. It takes its name from the cemetery site of Arras, at Arras Farm, (53.86°N 0.59°W) near Market Weighton, which was discovered in the 19th century. The site spans three fields, bisected by the main east-west road between Market Weighton and Beverley, and is arable farmland; little to no remains are visible above ground. The extent of the Arras culture is loosely associated with the Parisi tribe of pre-Roman Britain.

Celtic art is associated with the peoples known as Celts; those who spoke the Celtic languages in Europe from pre-history through to the modern period, as well as the art of ancient peoples whose language is uncertain, but have cultural and stylistic similarities with speakers of Celtic languages.

Champlevé is an enamelling technique in the decorative arts, or an object made by that process, in which troughs or cells are carved, etched, die struck, or cast into the surface of a metal object, and filled with vitreous enamel. The piece is then fired until the enamel fuses, and when cooled the surface of the object is polished. The uncarved portions of the original surface remain visible as a frame for the enamel designs; typically they are gilded in medieval work. The name comes from the French for "raised field", "field" meaning background, though the technique in practice lowers the area to be enamelled rather than raising the rest of the surface.

Fiskerton is a village and civil parish in the West Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. The population of the civil parish at the 2011 census was 1,209. It is situated approximately 6 miles (10 km) east from the city and county town of Lincoln, and on the north side of the River Witham.
The Witham Shield is an Iron Age decorative bronze shield facing of La Tène style, dating from about the 4th century BC. The shield was discovered in the River Witham in the vicinity of Washingborough and Fiskerton in Lincolnshire, England in 1826. Further excavations at a nearby site have revealed posts interpreted as the foundation for a causeway, as well as artefacts including a sword, spears and part of a human skull with a sword fragment lodged within. The shield is now in the British Museum.

A fibula is a brooch or pin for fastening garments, typically at the right shoulder. The fibula developed in a variety of shapes, but all were based on the safety-pin principle. Unlike most modern brooches, fibulae were not only decorative; they originally served a practical function: to fasten clothing for both sexes, such as dresses and cloaks.

Hanging bowls are a distinctive type of artefact of the period between the end of Roman rule in Britain in c. 410 AD and the emergence of the Christian Anglo-Saxon kingdoms during the 7th century, continuing rather later. The surviving examples have mostly been found in Anglo-Saxon graves, but there is general agreement that they reflect Celtic traditions of decoration.
Miranda Jane Aldhouse-Green, is a British archaeologist and academic, known for her research on the Iron Age and the Celts. She was Professor of Archaeology at Cardiff University from 2006 to 2013. Until about 2000 she published as Miranda Green or Miranda J. Green.

The Waterloo Helmet is a pre-Roman Celtic bronze ceremonial horned helmet with repoussé decoration in the La Tène style, dating to circa 150–50 BC, that was found in 1868 in the River Thames by Waterloo Bridge in London, England. It is now on display at the British Museum in London.

The Meyrick Helmet is an Iron Age bronze peaked helmet, with La Tène style decoration, that is held at the British Museum in London. It is one of only four Iron Age helmets to have been discovered in Britain, the other three being the more famous Waterloo Helmet, the Canterbury Helmet and the North Bersted Warrior helmet. Unlike the Waterloo Helmet, which bears two cone-shaped horns, the Meyrick Helmet is hornless and appears to be based on a Roman model. Vincent Megaw, emeritus professor of archaeology at the University of Leicester, has conjectured that the helmet may have belonged to a British auxiliary fighting in the Roman army during the campaigns against the Brigantes in AD 71–74.

The Wandsworth Shield is a circular bronze Iron Age shield boss or mount decorated in La Tène style which was found in the River Thames at Wandsworth in London sometime before 1849. Another incomplete bronze shield mount, sometimes called the Wandsworth Mask Shield was found at the same time. Both shield mounts are now held at the British Museum. The bold repoussé decoration on the Wandsworth Shield, comprising two birds with outstretched wings and long trailing tail feathers, has led Barry Cunliffe, Emeritus Professor of European Archaeology at the University of Oxford, to consider the shield to be "among the masterpieces of British Celtic art".

The Torrs Horns and Torrs Pony-cap are Iron Age bronze pieces now in the National Museum of Scotland, which were found together, but whose relationship is one of many questions about these "famous and controversial" objects that continue to be debated by scholars. Most scholars agree that horns were added to the pony-cap at a later date, but whether they were originally made for this purpose is unclear; one theory sees them as mounts for drinking-horns, either totally or initially unconnected to the cap. The three pieces are decorated in a late stage of La Tène style, as Iron Age Celtic art is called by archaeologists. The dates ascribed to the elements vary, but are typically around 200 BC; it is generally agreed that the horns are somewhat later than the cap, and in a rather different style.

The Basse Yutz Flagons are a pair of Iron Age ceremonial drinking vessels that date from the mid 5th century BCE. Since their discovery in ill-documented circumstances in the 1920s and their subsequent purchase by the British Museum, they have been described as "great masterpieces" that "combine most of the key features of early Celtic Art". They are in many respects very similar to the Dürrnberg Flagon found in Austria.

The Keltenmuseum in Hallein near Salzburg contains major discoveries from the La Tene period of the Iron Age which come from burials in the area surrounding the nearby Hallein Salt Mine, at Dürrnberg. The Museum was founded in 1882 and was housed in the Bürgerspital. In 1930 it was moved into the Rathaus and from 1952 occupied a gateway of the town or stadt's fortifications. In 1970 the name was changed to Keltenmuseum and the museum was moved into the former Salt Offices on the Pflegerplatz, which fronts the river Salzach. In 1980 the Museum staged a major exhibition "Die Kelten in Mitteleuropa", which demonstrated the wealth of discoveries that were being made at the Hallein. In 1993-4 the Austrian architect Heinz Tesar drew up plans for the conversion and extension of the Museum and on 1 January 2012 the Museum became a constituent part of Salzburg Museum.

The Agris Helmet is a ceremonial Celtic helmet from c. 350 BC that was found in a cave near Agris, Charente, France, in 1981. It is a masterpiece of Celtic art, and would probably have been used for display rather than worn in battle. The helmet consists of an iron cap completely covered with bands of bronze. The bronze is in turn covered with unusually pure gold leaf, with embedded coral decorations attached using silver rivets. One of the cheek guards was also found and has similar materials and designs. The helmet is mostly decorated in early Celtic patterns but there are later Celtic motifs and signs of Etruscan or Greek influence. The quality of the gold indicates that the helmet may well have been made locally in the Atlantic region.

The Fiskerton log boat is an Iron Age log boat, found during excavations in 2001 on the banks of the River Witham near Fiskerton, Lincolnshire.

Llyn Cerrig Bach Plaque is a bronze plaque that dates from 200BC to AD100 in the Iron Age, found at Llyn Cerrig Bach.

















