
Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is transmitted by arthropod vectors. The term arbovirus is a portmanteau word. Tibovirus is sometimes used to more specifically describe viruses transmitted by ticks, a superorder within the arthropods. Arboviruses can affect both animals and plants. In humans, symptoms of arbovirus infection generally occur 3–15 days after exposure to the virus and last three or four days. The most common clinical features of infection are fever, headache, and malaise, but encephalitis and viral hemorrhagic fever may also occur.
Bolivian hemorrhagic fever (BHF), also known as black typhus or Ordog Fever, is a hemorrhagic fever and zoonotic infectious disease originating in Bolivia after infection by Machupo mammarenavirus.

Bunyavirales is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses with mainly tripartite genomes. Member viruses infect arthropods, plants, protozoans, and vertebrates. It is the only order in the class Ellioviricetes. The name Bunyavirales derives from Bunyamwera, where the original type species Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus was first discovered. Ellioviricetes is named in honor of late virologist Richard M. Elliott for his early work on bunyaviruses.

Lassa mammarenavirus (LASV) is an arenavirus that causes Lassa hemorrhagic fever, a type of viral hemorrhagic fever (VHF), in humans and other primates. Lassa mammarenavirus is an emerging virus and a select agent, requiring Biosafety Level 4-equivalent containment. It is endemic in West African countries, especially Sierra Leone, the Republic of Guinea, Nigeria, and Liberia, where the annual incidence of infection is between 300,000 and 500,000 cases, resulting in 5,000 deaths per year.

An arenavirus is a bisegmented ambisense RNA virus that is a member of the family Arenaviridae. These viruses infect rodents and occasionally humans. A class of novel, highly divergent arenaviruses, properly known as reptarenaviruses, have also been discovered which infect snakes to produce inclusion body disease. At least eight arenaviruses are known to cause human disease. The diseases derived from arenaviruses range in severity. Aseptic meningitis, a severe human disease that causes inflammation covering the brain and spinal cord, can arise from the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Hemorrhagic fever syndromes, including Lassa fever, are derived from infections such as Guanarito virus, Junin virus, Lassa virus, Lujo virus, Machupo virus, Sabia virus, or Whitewater Arroyo virus. Because of the epidemiological association with rodents, some arenaviruses and bunyaviruses are designated as roboviruses.
Venezuelan hemorrhagic fever (VHF) is a zoonotic human illness first identified in 1989. The disease is most prevalent in several rural areas of central Venezuela and is caused by Guanarito mammarenavirus (GTOV) which belongs to the Arenaviridae family. The short-tailed cane mouse is the main host for GTOV which is spread mostly by inhalation of aerosolized droplets of saliva, respiratory secretions, urine, or blood from infected rodents. Person-to-person spread is possible, but uncommon.
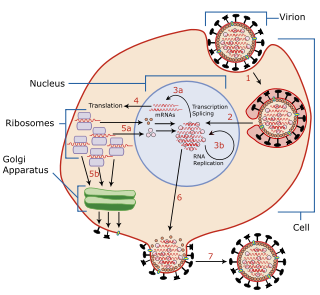
Viral entry is the earliest stage of infection in the viral life cycle, as the virus comes into contact with the host cell and introduces viral material into the cell. The major steps involved in viral entry are shown below. Despite the variation among viruses, there are several shared generalities concerning viral entry.
Oligoryzomys microtis, also known as the small-eared colilargo or small-eared pygmy rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Oligoryzomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in western Brazil, eastern Peru, Bolivia, and northern Paraguay.

Argentinian mammarenavirus, better known as the Junin virus or Junín virus (JUNV), is an arenavirus in the Mammarenavirus genus that causes Argentine hemorrhagic fever (AHF). The virus took its original name from the city of Junín, around which the first cases of infection were reported, in 1958.

The big-eared woodrat is a nocturnal rodent of the woodrat genus Neotoma, in the family Cricetidae. Closely related to, and formerly included in the species Neotoma fuscipes, it is endemic to western North America and occurs west and south of the Salinas Valley from the California Coast Ranges south of Monterey Bay to northern Baja California, as well as in the Sierra Nevada, extending north to the South Fork American River.
Brazilian hemorrhagic fever (BzHF) is an infectious disease caused by Brazilian mammarenavirus, an arenavirus. Brazilian mammarenavirus is one of the arenaviruses from South America to cause hemorrhagic fever. It shares a common progenitor with Argentinian mammarenavirus, Machupo mammarenavirus, Tacaribe mammarenavirus, and Guanarito mammarenavirus. It is an enveloped RNA virus and is highly infectious and lethal. Very little is known about this disease, but it is thought to be transmitted by the excreta of rodents. This virus has also been implicated as a means for bioterrorism, as it can be spread through aerosols.
Caño Delgadito orthohantavirus (CADV) is a hantavirus present in Venezuela. Its natural reservoir is Alston's cotton rat. Transmission among cotton rats appears to be horizontal. While human disease caused by CADV has not yet been identified, it has been isolated from oropharyngeal swabs and urine of infected cotton rats, indicating that it may be infectious to humans in the same manner as other hantaviruses, via inhalation of aerosolized droplets of saliva, respiratory secretions, or urine. CADV was discovered in the 1990s from rodent species in the Llanos in Venezuela.
Catacamas virus is a single-stranded, enveloped novel RNA virus in the genus Orthohantavirus of the order Bunyavirales isolated in Oryzomys couesi near the town of Catacamas in eastern Honduras. It is a member virus of Bayou orthohantavirus.
Choclo orthohantavirus (CHOV) is a single-stranded, negative-sense RNA zoonotic New World hantavirus. It was first isolated in 1999 in western Panama. The finding marked the first time Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) was found in Central America.
Oyewale Tomori is a Nigerian professor of virology, educational administrator, and former vice chancellor of Redeemer's University.
Syrian hamsters are one of several rodents used in animal testing. Syrian hamsters are used to model human medical conditions including various cancers, metabolic diseases, non-cancer respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, infectious diseases, and general health concerns. In 2014, Syrian hamsters accounted for 14.6% of the total animal research participants in the United States covered by the Animal Welfare Act.

Mammarenavirus is a genus of viruses in the family Arenaviridae. The name is a portmanteau of mammal and the former name Arenavirus, and differentiates it from the reptile-associated Reptarenavirus. Arenavirus comes from the Latin arena (sand) for the sandy appearance of the virions.
Whitewater Arroyo mammarenavirus (WWAV) is a zoonotic Arenavirus associated with hemorrhagic fever with liver failure.
Mopeia mammarenavirus (MOPV) is a species of virus in the genus Mammarenavirus. It was initially isolated from the Mastomys natalensis mouse in the East African country of Mozambique in 1977. It is of the "Old World" Arenavirus lineage and is closely related to Lassa mammarenavirus, sharing 75% of its amino acid sequence.
Anne Moscona is an American virologist and pediatrician. She is best known for identifying cell entry mechanisms for enveloped respiratory viruses, elucidating general infection mechanisms that apply to parainfluenza virus, Nipah virus, measles virus, and other viruses, and for applying this knowledge to identify antiviral strategies to prevent infection by viruses including SARS-CoV-2. She is frequently consulted as a medical expert during viral outbreaks, including epidemic and pandemic influenza. Since 2016, she has served as the Sherie L. Morrison Professor Microbiology & Immunology, Professor of Pediatrics, and Professor of Physiology & Cellular Biophysics at Columbia University Medical Center in New York City, where she directs the Center for Host Pathogen Interaction. In 2022, Moscona was elected as president of the American Society for Virology, the nation's leading virology research organization, and will lead the organization starting in July 2023. For the last two years she has served the American Society for Virology as Councilor for Medical Virology.







