The Bern People's Party (German : Bernische Volkspartei, BVP; French : Parti populaire bernois, PPB) was a Protestant conservative political party in Switzerland.
| This article is part of a series on the |
 |
|---|
The Bern People's Party (German : Bernische Volkspartei, BVP; French : Parti populaire bernois, PPB) was a Protestant conservative political party in Switzerland.
The BVP was established in 1882. [1] It ran eight candidates in the Bern-Oberaargau and Bern-Seeland constituencies in the 1884 federal elections, but failed to win a seat. However, Johannes Schär the BVP's first member of the National Council after winning a by-election in Bern-Oberaargau on 9 May 1886.
In the 1887 elections the party put forward nine candidates in the Bern-Emmental and Bern-Oberaargau constituencies. Schär was re-elected in Oberaargau, alongside Emil Elsässer and Ulrich Burkhalter; Schär and Elsässer were elected in the first round of voting and Burkhalter in the second. In the 1890 elections the party only contested Bern-Oberaargau; four candidates were nominated, including Burkhalter and Schär, but only Burkhalter was re-elected.
The same four candidates contested the 1893 elections in Bern-Oberaargau, and although Burkhalter was re-elected again, he joined the Liberal group after the elections. In the 1896 elections party founder Ulrich Dürrenmatt was its only candidate, again running in Bern-Oberaargau and failing to win a seat. The 1899 elections saw BVP candidates Dürrenmatt and Johann Egger contest Bern-Oberaargau, again failing to win a seat.
Although Dürrenmatt was its only candidate in the 1902 elections, he was elected in Bern-Oberaargau in the first round of voting. He was re-elected in the 1905 elections (as the party's sole candidate) in the second round of voting; he died in 1908, a few months before the 1908 elections. Hugo Dürrenmatt was the party's only candidate in the 1908 elections, but failed to win a seat. The party did not contest the 1911 elections.

The Federal Council is the federal cabinet of the Swiss Confederation. Its seven members also serve as the collective head of state and government of Switzerland. Since after World War II, the Federal Council is by convention a permanent grand coalition government composed of representatives of the country's major parties and language regions.

The 2002 Irish general election to the 29th Dáil was held on Friday, 17 May, just over three weeks after the dissolution of the 28th Dáil on Thursday, 25 April by President Mary McAleese, at the request of the Taoiseach, Bertie Ahern. The general election took place in 42 Dáil constituencies throughout Ireland for 166 seats in Dáil Éireann, the house of representatives of the Oireachtas, with a revision of constituencies since the last election under the Electoral (Amendment) Act 1998.

Kevin Lamoureux is a politician in Manitoba, Canada. On November 29, 2010, he was elected to the House of Commons of Canada for the constituency of Winnipeg North in a by-election. He was re-elected during the 2011 election by a margin of just 44 votes and being the only Liberal flip this election. Lamoureux previously served in the Legislative Assembly of Manitoba from 1988 to 1999 and from 2003 to 2010, and he twice sought the leadership of the Manitoba Liberal Party. He serves in the House of Commons as a member of the Liberal Party of Canada.

The United National Independence Party (UNIP) is a political party in Zambia. It governed the country from 1964 to 1991 under the socialist presidency of Kenneth Kaunda, and was the sole legal party in the country between 1973 and 1990. On 4 April 2021, Bishop Trevor Mwamba was elected President of UNIP.

Elections in Benin take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a presidential system. Both the President and the National Assembly are directly elected by voters, with elections organised by the Autonomous National Electoral Commission (CENA).
Elections in Hungary are held at two levels: general elections to elect the members of the National Assembly and local elections to elect local authorities. European Parliament elections are also held every 5 years.

General elections were held in Singapore on 21 September 1963, five days after Singapore became part of Malaysia. Voters elected all 51 members of the Legislative Assembly. The elections were the only ones to date with no boundary changes to any existing constituencies prior to the elections. The result was a victory for the People's Action Party (PAP), which won 37 of the 51 seats, while the majority of the remaining seats were won by Barisan Sosialis (BS).

Legislative elections were held in France on 10 June and 17 June 2007 to elect the 13th National Assembly of the Fifth Republic, a few weeks after the presidential election run-off on 6 May. 7,639 candidates stood for 577 seats, including France's overseas possessions. Early first-round results projected a large majority for President Nicolas Sarkozy's Union for a Popular Movement (UMP) and its allies; however, second-round results showed a closer race and a stronger left. Nevertheless, the right retained its majority from 2002 despite losing some 40 seats to the Socialists.
The Executive Council is the executive of the Swiss canton of Bern.
On December 12, 2007, all seven members of the Federal Council, the government of Switzerland, were elected by the joint chambers of the Federal Assembly for the 2008–2012 term of office. Councillors are elected individually by an absolute majority of votes, with the incumbent councillors defending their seats in descending order of seniority.
A by-election to the Swiss Federal Council was held in Switzerland on 16 September 2009, after incumbent Federal Councillor Pascal Couchepin announced his intention to retire on 31 October 2009.

An electoral or voting system is a set of rules used to determine the results of an election. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, non-profit organisations and informal organisations. These rules govern all aspects of the voting process: when elections occur, who is allowed to vote, who can stand as a candidate, how ballots are marked and cast, how the ballots are counted, how votes translate into the election outcome, limits on campaign spending, and other factors that can affect the result. Political electoral systems are defined by constitutions and electoral laws, are typically conducted by election commissions, and can use multiple types of elections for different offices.
An election for all seven members of the Federal Council, the government of Switzerland, was held on 14 December 2011, following the federal election on 23 October 2011. Micheline Calmy-Rey announced she would not run for re-election to the council. According to a traditional informal convention, the successor has to come from the French-speaking or Italian-speaking part of Switzerland. The candidates for her post announced by their respective cantonal sections are Alain Berset (Fribourg), Pierre-Yves Maillard (Vaud), Stéphane Rossini (Valais), and Marina Carobbio (Ticino).

Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 18 October 2015 for the National Council and the first round of elections to the Council of States, with runoff elections to the Council of States being held in various cantons until 22 November.
The 2007 Zürich cantonal elections were held on 15 April 2007, to elect the seven members of the cantonal Executive Council and the 180 members of the Cantonal Council.

Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 27 October 1872. The Radical Left remained the largest group in the National Council.

The Malay Union was a political party in Singapore from 1926 to 1960.

An election for all seven members of the Federal Council, the Government of Switzerland, was held on 9 December 2015, following the federal election on 19 October 2015, for the 2016–2020 term.
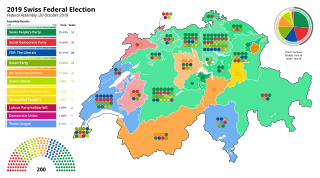
Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 20 October 2019 to elect all members of both houses of the Federal Assembly. This was followed by the 2019 election to the Swiss Federal Council, the federal executive, by the United Federal Assembly.

A by-election to the Swiss Federal Council was held on 20 September 2017, after federal councillor Didier Burkhalter (FDP-NE) announced he would leave the Council effective 31 October 2017. The by-election resulted in the election of Ignazio Cassis (FDP-TI), resulting in no change in the partisan composition of the council.