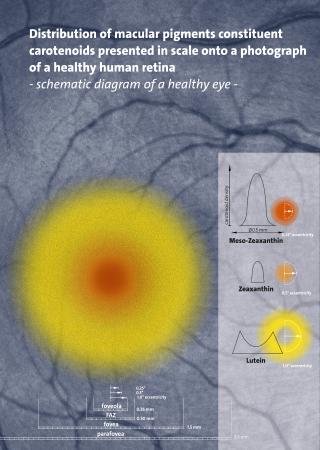
Carotenoids are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Over 1,100 identified carotenoids can be further categorized into two classes – xanthophylls and carotenes.

Canthaxanthin is a keto-carotenoid pigment widely distributed in nature. Carotenoids belong to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenoids. The chemical formula of canthaxanthin is C40H52O2. It was first isolated in edible mushrooms. It has also been found in green algae, bacteria, crustaceans, and bioaccumulates in fish such as carp, golden grey mullet, seabream and trush wrasse.
Nitrate reductase (NAD(P)H) (EC 1.7.1.2, assimilatory nitrate reductase, assimilatory NAD(P)H-nitrate reductase, NAD(P)H bispecific nitrate reductase, nitrate reductase (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (phosphate)), nitrate reductase NAD(P)H, NAD(P)H-nitrate reductase, nitrate reductase [NAD(P)H2], NAD(P)H2:nitrate oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name nitrite:NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalises the following chemical reaction
Nitrate reductase (NADH) (EC 1.7.1.1, assimilatory nitrate reductase, NADH-nitrate reductase, NADH-dependent nitrate reductase, assimilatory NADH: nitrate reductase, nitrate reductase (NADH2), NADH2:nitrate oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name nitrite:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyzes the following chemical reaction
Pentachlorophenol monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.50, pentachlorophenol dechlorinase, pentachlorophenol dehalogenase, pentachlorophenol 4-monooxygenase, PCP hydroxylase, pentachlorophenol hydroxylase, PcpB, PCB 4-monooxygenase, PCB4MO) is an enzyme with systematic name pentachlorophenol,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (hydroxylating, dechlorinating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Spheroidene monooxygenase (EC 1.14.15.9, CrtA, acyclic carotenoid 2-ketolase, spirilloxantin monooxygenase, 2-oxo-spirilloxanthin monooxygenase) is an enzyme with systematic name spheroidene, reduced-ferredoxin:oxygen oxidoreductase (spheroiden-2-one-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction


