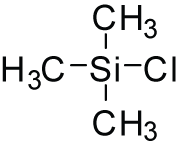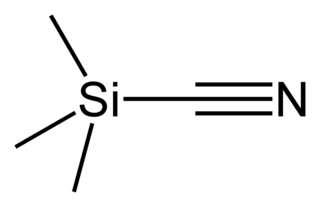Dimethylmercury is an extremely toxic organomercury compound with the formula (CH3)2Hg. A volatile, flammable, dense and colorless liquid, dimethylmercury is one of the strongest known neurotoxins. Less than 0.1 mL is capable of inducing severe mercury poisoning resulting in death.

A trimethylsilyl group (abbreviated TMS) is a functional group in organic chemistry. This group consists of three methyl groups bonded to a silicon atom [−Si(CH3)3], which is in turn bonded to the rest of a molecule. This structural group is characterized by chemical inertness and a large molecular volume, which makes it useful in a number of applications.
In inorganic chemistry, chlorosilanes are a group of reactive, chlorine-containing chemical compounds, related to silane and used in many chemical processes. Each such chemical has at least one silicon-chlorine bond. Trichlorosilane is produced on the largest scale. The parent chlorosilane is silicon tetrachloride.
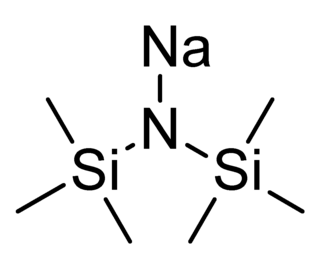
Sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide is the organosilicon compound with the formula NaN(Si 3)2. This species, usually called NaHMDS, is a strong base used for deprotonation reactions or base-catalyzed reactions. Its advantages are that it is commercially available as a solid and it is soluble not only in ethers, such as THF or diethyl ether, but also in aromatic solvents, like benzene and toluene by virtue of the lipophilic TMS groups.
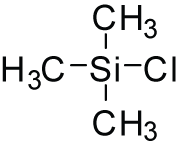
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound, with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry.

Sodium phosphide is the inorganic compound with the formula Na3P. It is a black solid. It is often described as Na+ salt of the P3− anion. Na3P is a source of the highly reactive phosphide anion. It should not be confused with sodium phosphate, Na3PO4.

Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an inorganic compound.
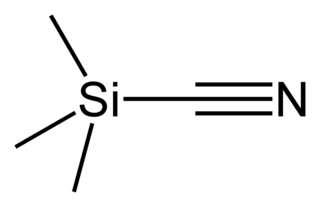
Trimethylsilyl cyanide is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3SiCN. This volatile liquid consists of a cyanide group, that is CN, attached to a trimethylsilyl group. The molecule is used in organic synthesis as the equivalent of hydrogen cyanide. It is prepared by the reaction of lithium cyanide and trimethylsilyl chloride:
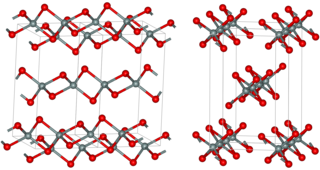
Silicon disulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula SiS2. Like silicon dioxide, this material is polymeric, but it adopts a 1-dimensional structure quite different from the usual forms of SiO2.
Bis(trimethylsilyl)amine (also known as hexamethyldisilazane and HMDS) is an organosilicon compound with the molecular formula [(CH3)3Si]2NH. The molecule is a derivative of ammonia with trimethylsilyl groups in place of two hydrogen atoms. An electron diffraction study shows that silicon-nitrogen bond length (173.5 pm) and Si-N-Si bond angle (125.5°) to be similar to disilazane (in which methyl groups are replaced by hydrogen atoms) suggesting that steric factors are not a factor in regulating angles in this case. This colorless liquid is a reagent and a precursor to bases that are popular in organic synthesis and organometallic chemistry. Additionally, HMDS is also increasingly used as molecular precursor in chemical vapor deposition techniques to deposit silicon carbonitride thin films or coatings.

Hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO or MM) is an organosilicon compound with the formula O[Si(CH3)3]2. This volatile colourless liquid is used as a solvent and as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the hydrolysis of trimethylsilyl chloride. The molecule is the protypical disiloxane and resembles a subunit of polydimethylsiloxane.
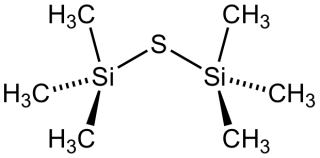
Bis(trimethylsilyl) sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula ((CH3)3Si)2S. Often abbreviated (tms)2S, this colourless, vile-smelling liquid is a useful aprotic source of "S2−" in chemical synthesis.
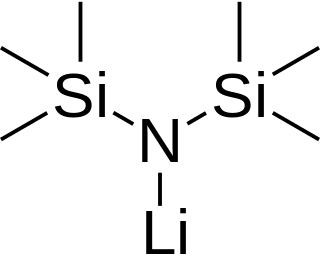
Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide is a lithiated organosilicon compound with the formula LiN(Si(CH3)3)2. It is commonly abbreviated as LiHMDS or Li(HMDS) (lithium hexamethyldisilazide - a reference to its conjugate acid HMDS) and is primarily used as a strong non-nucleophilic base and as a ligand. Like many lithium reagents, it has a tendency to aggregate and will form a cyclic trimer in the absence of coordinating species.
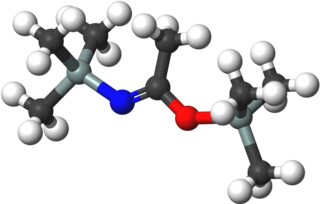
Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide (BSA) is an organosilicon compound with the formula MeC(OSiMe3)NSiMe3 (Me = CH3). It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in diverse organic solvents, but reacts rapidly with moisture and solvents containing OH and NH groups. It is used in analytical chemistry to increase the volatility of analytes, e.g., for gas chromatography. It is also used to introduce the trimethylsilyl protecting group in organic synthesis. A related reagent is N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA).
Silylation is the introduction of one or more (usually) substituted silyl groups (R3Si) to a molecule. Silylations are core methods for production of organosilicon chemistry. Silanization involves similar methods but usually refers to attachment of silyl groups to solids.
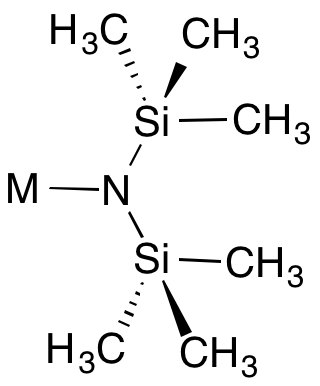
Metal bis(trimethylsilyl)amides are coordination complexes composed of a cationic metal M with anionic bis(trimethylsilyl)amide ligands (the −N 2 monovalent anion, or −N 2 monovalent group, and are part of a broader category of metal amides.

Trimethylsilyl cyclopentadiene is an organosilicon compound with the chemical formula C5H5Si(CH3)3. It exists as a colorless liquid. It is used in the synthesis of some metal cyclopentadienyl complexes and has attracted interest for its fluxional structure.

Tris(trimethylsilyl)amine is the simplest tris(trialkylsilyl)amine which are having the general formula (R3Si)3N, in which all three hydrogen atoms of the ammonia are replaced by trimethylsilyl groups (-Si(CH3)3). Tris(trimethylsilyl)amine has been for years in the center of scientific interest as a stable intermediate in chemical nitrogen fixation (i. e. the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen N2 into organic substrates under normal conditions).
Bis(trimethylsilyl)sulfur diimide is the organosulfur compound with the formula S(NSiMe3)2 (Me = CH3). A colorless liquid, it is a diaza analogue of sulfur dioxide, i.e., a sulfur diimide. It is a reagent in the synthesis of sulfur nitrides. For example, it is a precursor to C2(N2S)2.

(Trimethylsilyl)methyllithium is classified both as an organolithium compound and an organosilicon compound. It has the empirical formula LiCH2Si(CH3)3, often abbreviated LiCH2tms. It crystallizes as the hexagonal prismatic hexamer [LiCH2tms]6, akin to some polymorphs of methyllithium. Many adducts have been characterized including the diethyl ether complexed cubane [Li4(μ3-CH2tms)4(Et2O)2] and [Li2(μ-CH2tms)2(tmeda)2].