
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle.
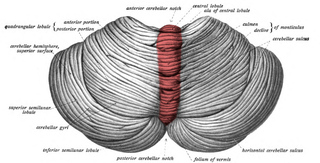
The cerebellar vermis is located in the medial, cortico-nuclear zone of the cerebellum, which is in the posterior fossa of the cranium. The primary fissure in the vermis curves ventrolaterally to the superior surface of the cerebellum, dividing it into anterior and posterior lobes. Functionally, the vermis is associated with bodily posture and locomotion. The vermis is included within the spinocerebellum and receives somatic sensory input from the head and proximal body parts via ascending spinal pathways.

In biological morphology and anatomy, a sulcus is a furrow or fissure. It may be a groove, natural division, deep furrow, elongated cleft, or tear in the surface of a limb or an organ, most notably on the surface of the brain, but also in the lungs, certain muscles, as well as in bones, and elsewhere. Many sulci are the product of a surface fold or junction, such as in the gums, where they fold around the neck of the tooth.

The lobes of the brain are the major identifiable zones of the human cerebral cortex, and they comprise the surface of each hemisphere of the cerebrum. The two hemispheres are roughly symmetrical in structure, and are connected by the corpus callosum. They traditionally have been divided into four lobes, but are today considered as having six lobes each. The lobes are large areas that are anatomically distinguishable, and are also functionally distinct to some degree. Each lobe of the brain has numerous ridges, or gyri, and furrows, the sulci that constitute further subzones of the cortex. The expression "lobes of the brain" usually refers only to those of the cerebrum, not to the distinct areas of the cerebellum.

The posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) is the largest branch of the vertebral artery. It is one of the three main arteries that supply blood to the cerebellum, a part of the brain. Blockage of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery can result in a type of stroke called lateral medullary syndrome.

The inferior parietal lobule lies below the horizontal portion of the intraparietal sulcus, and behind the lower part of the postcentral sulcus. Also known as Geschwind's territory after Norman Geschwind, an American neurologist, who in the early 1960s recognised its importance. It is a part of the parietal lobe.

The largest and deepest fissure in the cerebellum is named the horizontal fissure.

The lesser wings of the sphenoid or orbito-sphenoids are two thin triangular plates, which arise from the upper and anterior parts of the body, and, projecting lateralward, end in sharp points [Fig. 1].

The porta hepatis or transverse fissure of the liver is a short but deep fissure, about 5 cm long, extending transversely beneath the left portion of the right lobe of the liver, nearer its posterior surface than its anterior border.

The middle cerebellar peduncle is a paired structure of the brain. It connects the pons to the cerebellum, with fibres originating from the pontine nucleus and travelling to the opposite hemisphere of the cerebellar cortex. It is supplied by the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) and branches from the basilar artery. It conveys information from the cerebrum and the pons to the cerebellum.

In anatomy, a lobe is a clear anatomical division or extension of an organ that can be determined without the use of a microscope at the gross anatomy level. This is in contrast to the much smaller lobule, which is a clear division only visible under the microscope.

The cerebellar tonsil is a rounded lobule on the undersurface of each cerebellar hemisphere, continuous medially with the uvula of the cerebellar vermis and superiorly by the flocculonodular lobe. Synonyms include: tonsilla cerebelli, amygdala cerebelli, the latter of which is not to be confused with the cerebral tonsils or amygdala nuclei located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex.

The nodule, or anterior end of the inferior vermis, abuts against the roof of the fourth ventricle, and can only be distinctly seen after the cerebellum has been separated from the medulla oblongata and pons.

The tuber of vermis, the most posterior division of the inferior vermis, is of small size, and laterally spreads out into the large inferior semilunar lobules, which comprise at least two-thirds of the inferior surface of the hemisphere.
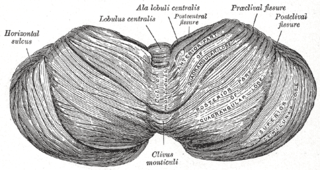
The folium vermis is a short, narrow, concealed band at the posterior extremity of the vermis, consisting apparently of a single folium, but in reality marked on its upper and under surfaces by secondary fissures.

The central lobule is a small square lobule, situated in the anterior cerebellar notch. It overlaps the lingula, from which it is separated by the precentral fissure; laterally, it extends along the upper and anterior part of each hemisphere, where it forms a wing-like prolongation (ala), on each side, as the alae of the central lobule or alae lobuli centralis.

The monticulus of the cerebellum is divided by the primary fissure into an anterior, raised part, the culmen or summit, and a posterior sloped part, the clivus; the quadrangular lobule is similarly divided.

The culmen is the portion of the anterior vermis adjacent to the primary fissure of cerebellum.

The uvula forms a considerable portion of the inferior vermis; it is separated on either side from the tonsil by the sulcus vallecula, at the bottom of which it is connected to the tonsil by a ridge of gray matter, indented on its surface by shallow furrows, and hence called the furrowed band.

The anatomy of the cerebellum can be viewed at three levels. At the level of gross anatomy, the cerebellum consists of a tightly folded and crumpled layer of cortex, with white matter underneath, several deep nuclei embedded in the white matter, and a fluid-filled ventricle in the middle. At the intermediate level, the cerebellum and its auxiliary structures can be broken down into several hundred or thousand independently functioning modules or compartments known as microzones. At the microscopic level, each module consists of the same small set of neuronal elements, laid out with a highly stereotyped geometry.



















