The cerebellum is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, and motor learning in humans.

The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle.

The brainstem is the stalk-like part of the brain that interconnects the cerebrum and diencephalon with the spinal cord. In the human brain, the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch.
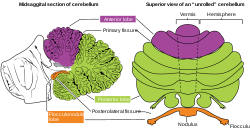
The cerebellar vermis is located in the medial, cortico-nuclear zone of the cerebellum, which is in the posterior fossa of the cranium. The primary fissure in the vermis curves ventrolaterally to the superior surface of the cerebellum, dividing it into anterior and posterior lobes. Functionally, the vermis is associated with bodily posture and locomotion. The vermis is included within the spinocerebellum and receives somatic sensory input from the head and proximal body parts via ascending spinal pathways.

The anterior lobe of cerebellum is the portion of the cerebellum responsible for mediating unconscious proprioception. Inputs into the anterior lobe of the cerebellum are mainly from the spinal cord. It is sometimes equated to the "paleocerebellum".

The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum.

The dentate nucleus is a cluster of neurons, or nerve cells, in the central nervous system that has a dentate – tooth-like or serrated – edge. It is located within the deep white matter of each cerebellar hemisphere, and it is the largest single structure linking the cerebellum to the rest of the brain. It is the largest and most lateral, or farthest from the midline, of the four pairs of deep cerebellar nuclei, the others being the globose and emboliform nuclei, which together are referred to as the interposed nucleus, and the fastigial nucleus. The dentate nucleus is responsible for the planning, initiation and control of voluntary movements. The dorsal region of the dentate nucleus contains output channels involved in motor function, which is the movement of skeletal muscle, while the ventral region contains output channels involved in nonmotor function, such as conscious thought and visuospatial function.

The globose nucleus is one of the deep cerebellar nuclei. It is located medial to the emboliform nucleus, and lateral to the fastigial nucleus. The globose nucleus and emboliform nucleus are known collectively as the interposed nuclei.
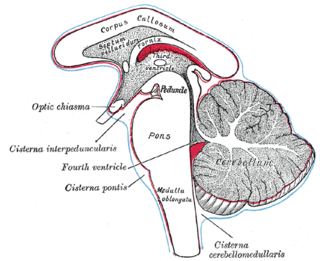
The subarachnoid cisterns are spaces formed by openings in the subarachnoid space, an anatomic space in the meninges of the brain. The space is situated between the two meninges, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. These cisterns are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

The flocculus is a small lobe of the cerebellum at the posterior border of the middle cerebellar peduncle anterior to the biventer lobule. Like other parts of the cerebellum, the flocculus is involved in motor control. It is an essential part of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, and aids in the learning of basic motor skills in the brain.

The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior cranial fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.

The middle cerebellar peduncle is a paired structure of the brain. It connects the pons to the cerebellum, with fibres originating from the pontine nucleus and travelling to the opposite hemisphere of the cerebellar cortex. It is supplied by the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) and branches from the basilar artery. It conveys information from the cerebrum and the pons to the cerebellum.

The tela choroidea is a region of meningeal pia mater that adheres to the underlying ependyma, and gives rise to the choroid plexus in each of the brain’s four ventricles. Tela is Latin for woven and is used to describe a web-like membrane or layer. The tela choroidea is a very thin part of the loose connective tissue of pia mater overlying and closely adhering to the ependyma. It has a rich blood supply. The ependyma and vascular pia mater – the tela choroidea, form regions of minute projections known as a choroid plexus that projects into each ventricle. The choroid plexus produces most of the cerebrospinal fluid of the central nervous system that circulates through the ventricles of the brain, the central canal of the spinal cord, and the subarachnoid space. The tela choroidea in the ventricles forms from different parts of the roof plate in the development of the embryo.

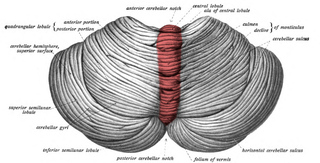
The cerebellar tonsil is a rounded lobule on the undersurface of each cerebellar hemisphere, continuous medially with the uvula of the cerebellar vermis and superiorly by the flocculonodular lobe. Synonyms include: tonsilla cerebelli, amygdala cerebelli, the latter of which is not to be confused with the cerebral tonsils or amygdala nuclei located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex.

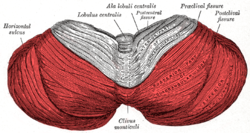
The central lobule is a small square lobule, situated in the anterior cerebellar notch. It overlaps the lingula, from which it is separated by the precentral fissure; laterally, it extends along the upper and anterior part of each hemisphere, where it forms a wing-like prolongation (ala), on each side, as the alae of the central lobule or alae lobuli centralis.

The monticulus of the cerebellum is divided by the primary fissure into an anterior, raised part, the culmen or summit, and a posterior sloped part, the clivus; the quadrangular lobule is similarly divided.
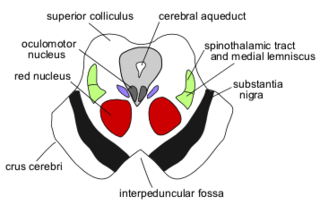
The central tegmental tract is a structure in the midbrain and pons.
The cerebellothalamic tract or the tractus cerebellothalamicus, is part of the superior cerebellar peduncle. It originates in the cerebellar nuclei, crosses completely in the decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle, bypasses the red nucleus, and terminates in posterior division of ventral lateral nucleus of thalamus. The ventrolateral nucleus has different divisions and distinct connections, mostly with frontal and parietal lobes. The primary motor cortex and premotor cortex get information from the ventrolateral nucleus projections originating in the interposed nucleus and dentate nuclei. Other dentate nucleus projections via thalamic pathway transmit information to prefrontal cortex and posterior parietal cortex. The cerebellum sends thalamocortical projections and in addition may also send connections from the thalamus to association areas serving cognitive and affective functions.

The anatomy of the cerebellum can be viewed at three levels. At the level of gross anatomy, the cerebellum consists of a tightly folded and crumpled layer of cortex, with white matter underneath, several deep nuclei embedded in the white matter, and a fluid-filled ventricle in the middle. At the intermediate level, the cerebellum and its auxiliary structures can be broken down into several hundred or thousand independently functioning modules or compartments known as microzones. At the microscopic level, each module consists of the same small set of neuronal elements, laid out with a highly stereotyped geometry.
Cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome (CCAS), also called Schmahmann's syndrome is a condition that follows from lesions (damage) to the cerebellum of the brain. It refers to a constellation of deficits in the cognitive domains of executive function, spatial cognition, language, and affect resulting from damage to the cerebellum. Impairments of executive function include problems with planning, set-shifting, abstract reasoning, verbal fluency, and working memory, and there is often perseveration, distractibility and inattention. Language problems include dysprosodia, agrammatism and mild anomia. Deficits in spatial cognition produce visual–spatial disorganization and impaired visual–spatial memory. Personality changes manifest as blunting of affect or disinhibited and inappropriate behavior. These cognitive impairments result in an overall lowering of intellectual function. CCAS challenges the traditional view of the cerebellum being responsible solely for regulation of motor functions. It is now thought that the cerebellum is responsible for monitoring both motor and nonmotor functions. The nonmotor deficits described in CCAS are believed to be caused by dysfunction in cerebellar connections to the cerebral cortex and limbic system.