The Marchantiophyta are a division of non-vascular land plants commonly referred to as hepatics or liverworts. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of genetic information.

Marchantiales is an order of thallose liverworts that includes species like Marchantia polymorpha, a widespread plant often found beside rivers, and Lunularia cruciata, a common and often troublesome weed in moist, temperate gardens and greenhouses.

Marchantiopsida is a class of liverworts within the phylum Marchantiophyta. The species in this class are known as complex thalloid liverworts. The species in this class are widely distributed and can be found worldwide.

Marchantiaceae is a family of liverworts in order Marchantiales. It contains a single genus Marchantia.

Jungermanniales is the largest order of liverworts. They are distinctive among the liverworts for having thin leaf-like flaps on either side of the stem. Most other liverworts are thalloid, with no leaves. Due to their dorsiventral organization and scale-like, overlapping leaves, the Jungermanniales are sometimes called "scale-mosses".

Metzgeriales is an order of liverworts. The group is sometimes called the simple thalloid liverworts: "thalloid" because the members lack structures resembling stems or leaves, and "simple" because their tissues are thin and relatively undifferentiated. All species in the order have a small gametophyte stage and a smaller, relatively short-lived, spore-bearing stage. Although these plants are almost entirely restricted to regions with high humidity or readily available moisture, the group as a whole is widely distributed, and occurs on every continent except Antarctica.

Jungermanniopsida is the largest of three classes within the division Marchantiophyta (liverworts).

Cavicularia densa is the only species in the liverwort genus Cavicularia. The species was first described in 1897 by Franz Stephani, and is endemic to Japan, where it grows on fine moist soil.

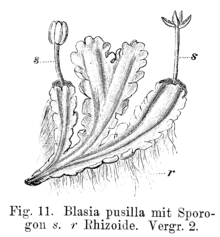
Blasiaceae is a family of liverworts with only two species: Blasia pusilla and Cavicularia densa. The family has traditionally been classified among the Metzgeriales, but molecular cladistics suggests a placement at the base of the Marchantiopsida.

Treubiaceae is a family of liverworts in the order Treubiales. Species are large and leafy, and were previously classified among the Metzgeriales.

Haplomitriopsida is a newly recognized class of liverworts comprising fifteen species in three genera. Recent cladistic analyses of nuclear, mitochondrial, and plastid gene sequences place this monophyletic group as the basal sister group to all other liverworts. The group thus provides a unique insight into the early evolution of liverworts in particular and of land plants in general.
Apotreubia is a genus of liverworts in the family Treubiaceae. There are four species, including: Apotreubia nana, which is found in subalpine New Guinea, and Apotreubia pusilla, which has a disjunct distribution between eastern Asia and British Columbia.

Treubia is a genus of liverworts in the family Treubiaceae. There are seven species, all of which are restricted to the southern hemisphere. Five of the species occur in Australasia and the other occurs in Chile. All species are dioicous, with separate male and female gametophytes.
Makinoa crispata is the only species of liverwort in the genus Makinoa and family Makinoaceae. The genus Verdoornia was formerly included in this family, but has been transferred to the family Aneuraceae on the basis of recent cladistic analysis of genetic sequences.

Ptilidium is a genus of liverwort, and is the only genus in family Ptilidiaceae. It includes only three species: Ptilidium californicum, Ptilidium ciliare, and Ptilidium pulcherrimum. The genus is distributed throughout the arctic and subarctic, with disjunct populations in New Zealand and Tierra del Fuego. Molecular analysis suggests that the genus has few close relatives and diverged from other leafy liverworts early in their evolution.

Solenostomataceae is a family of liverworts in the order Jungermanniales.
Neotrichocoleaceae is a family of liverworts in order Ptilidiales. It is closely related to the genera Ptilidium and Herzogianthus.

Riella is a genus in the liverwort family Riellaceae, and includes about eighteen species. Plants in the genus are small and grow submerged in shallow temporary pools. Although the genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisphere, locating populations is often difficult. Its occurrence is sporadic and local, and the tiny plants are ephemeral. The ornamented spores remain viable for several years, allowing the plants to survive annual drying of their habitat. The plants are easily grown in laboratory cultures.

Haplomitrium is a genus of liverworts.

Monoclea forsteri is one of the two species in the thallose liverwort family Monocleaceae. It is dioicous with the capsule dehiscing with a single longitudinal slit. Endemic and widely distributed throughout New Zealand, it is also the country's largest thalloid liverwort. Hooker described the species in 1820. The holotype is in the British Museum.