
Barkerville was the main town of the Cariboo Gold Rush in British Columbia, Canada, and is preserved as a historic town. It is located on the north slope of the Cariboo Plateau near the Cariboo Mountains 80 kilometres (50 mi) east of Quesnel. BC Highway 26, which follows the route of the Cariboo Wagon Road, the original access to Barkerville, goes through it.

Quesnel is a city located in the Cariboo Regional District of British Columbia, Canada. Located nearly evenly between the cities of Prince George and Williams Lake, it is on the main route to northern British Columbia and the Yukon. Quesnel is located at the confluence of the Fraser River and Quesnel River. As of 2021, Quesnel's metropolitan area had a population of 23,113 making it one of the largest urban centres between Prince George and Kamloops.

Events from the year 1862 in Canada.
Highway 97 is a major highway in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is the longest continuously numbered route in the province, running 2,081 km (1,293 mi) and is the only route that runs the entire north–south length of British Columbia, connecting the Canada–United States border near Osoyoos in the south to the British Columbia–Yukon boundary in the north at Watson Lake, Yukon.
Highway 2, known locally as the Tupper Highway, is one of the two short connections from Dawson Creek to the border between British Columbia and Alberta.
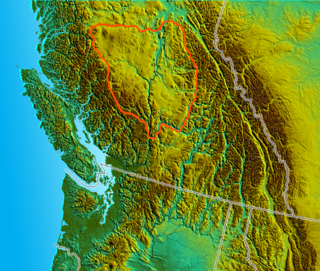
The Cariboo is an intermontane region of British Columbia, Canada, centered on a plateau stretching from Fraser Canyon to the Cariboo Mountains. The name is a reference to the caribou that were once abundant in the region.

Yale is an unincorporated town in the Canadian province of British Columbia, which grew in importance during the Fraser Canyon Gold Rush.

The Cariboo Road was a project initiated in 1860 by the Governor of the Colony of British Columbia, James Douglas. It was built in response to the Cariboo Gold Rush to facilitate settlement of the area by miners. It involved a feat of engineering stretching from Fort Yale to Barkerville, B.C. through extremely hazardous canyon territory in the Interior of British Columbia.

The Cariboo Gold Rush was a gold rush in the Colony of British Columbia, which later became the Canadian province of British Columbia. The first gold discovery was made at Hills Bar in 1858, followed by more strikes in 1859 on the Horsefly River, and on Keithley Creek and Antler Creek in 1860. The actual rush did not begin until 1861, when these discoveries were widely publicized. By 1865, following the strikes along Williams Creek, the rush was in full swing.

Bowron Lake Provincial Park is a wilderness provincial park located in east-central British Columbia, Canada, near the border with Alberta. It is 117 km (73 mi) east of the city of Quesnel. Other nearby towns include Wells and the historic destination of Barkerville. Once a popular hunting and fishing destination, today the park is protected and known for its abundant wildlife, rugged glaciated mountains, and freshwater lakes.
Cariboo was one of the twelve original electoral districts created when British Columbia became a Canadian province in 1871. Roughly corresponding to the old colonial electoral administrative district of the same name, it was a three-member riding until the 1894 election, when it was reduced through reapportionment and became a two-member riding until the 1916 election, after which it has been a single-member riding. It produced many notable Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs), including George Anthony Boomer Walkem, third and fifth holder of the office of Premier of British Columbia and who was one of the first representatives elected from the riding; John Robson, ninth Premier of British Columbia; and Robert Bonner, a powerful minister in the W.A.C. Bennett cabinet, and later CEO of MacMillan Bloedel and BC Hydro.
Wells is a small mining and tourist town in the Cariboo District of central British Columbia, located on BC Highway 26, 74 km (46 mi) from Quesnel and 8 km (5 mi) before the highway's terminus at Barkerville. It gains much of its revenue and jobs from tourists who pass through on their way to the Bowron Lake Provincial Park and to the historic museum town of Barkerville.

Clinton is a village in British Columbia, Canada, located approximately 40 km (25 mi) northwest of Cache Creek and 30 km south of 70 Mile House.

Stanley was a gold rush town in the Cariboo region of British Columbia that began during the Cariboo Gold Rush.
The Old Cariboo Road is a reference to the original wagon road to the Cariboo gold fields in what is now the Canadian province of British Columbia. It should not be confused with the Cariboo Road, which was built slightly later and used a different route.

The Enterprise was a passenger and freight sternwheeler that was built for service on the Soda Creek to Quesnel route on the upper Fraser River in British Columbia. It was built at Four Mile Creek near Alexandria by pioneer shipbuilder James Trahey of Victoria for Gustavus Blin Wright and Captain Thomas Wright and was put into service in the spring of 1863. Her captain was JW Doane. The Enterprise was the first of twelve sternwheelers that would work on this section of the Fraser from 1863 to 1921. Though she was not large, she was a wonderful example of the early craft of shipbuilding. All of the lumber she was built from was cut by hand and her boiler and engines had been brought to the building site at Four Mile packed by mule via the wagon road from Port Douglas, 300 miles away.
Cottonwood River is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. Rising at the confluence of the Swift River and Lightning Creek at Coldspring House in the Cariboo goldfields of the northern Cariboo Plateau, it flows northwest and then turns southwest to join the Fraser just north of the city of Quesnel, which is at the confluence of the Quesnel River with the Fraser.

Cottonwood, including the Cottonwood Ranch and Cottonwood House, is an unincorporated settlement in the North Cariboo region of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. Originally a ranch, it is located in the northern Cariboo Plateau, just 8 km northwest of Coldspring House, which is at the confluence of the Swift River and Lightning Creek, which is the beginning of the Cottonwood River. Lightning Creek was one of the more famous of the gold-bearing creeks of the Cariboo Gold Rush.
Coldspring House is an unincorporated locality and former roadhouse on the Cariboo Wagon Road in the Cariboo Country of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. Located just east of the confluence of Lightning Creek and the Swift River between Quesnel and Barkerville along that route. Only 8 km east along that road from Cottonwood House, another roadhouse still operating as a store and campground today, as well as a provincial heritage property with a small museum. Just farther along the route, which is today's BC Highway 26, is Beaver Pass House. All date from the era of the Cariboo Gold Rush and were busy stopping places for travellers going to and from the goldfields.
Pinegrove is an unincorporated locality on BC Highway 26 in the Cariboo Country of the Central Interior of British Columbia, located between Coldspring House (SW) and Beaver Pass House (NE), southwest of Four Mile Lake. It is the location of the Troll Ski Resort.













