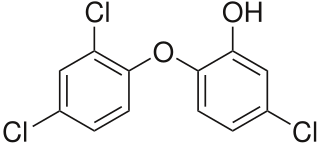
Triclosan is an antibacterial and antifungal agent present in some consumer products, including toothpaste, soaps, detergents, toys, and surgical cleaning treatments. It is similar in its uses and mechanism of action to triclocarban. Its efficacy as an antimicrobial agent, the risk of antimicrobial resistance, and its possible role in disrupted hormonal development remains controversial. Additional research seeks to understand its potential effects on organisms and environmental health.

In the animal rights movement, cruelty-free is a label for products or activities that do not harm or kill animals anywhere in the world. Products tested on animals or made from animals are not considered cruelty-free, since these tests are often painful and cause the suffering and death of millions of animals every year.
Aluminium chlorohydrate is a group of water-soluble, specific aluminium salts having the general formula AlnCl3n−m(OH)m. It is used in cosmetics as an antiperspirant and as a coagulant in water purification.

Parabens are chemicals that are commonly used as preservatives in cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. Chemically, they are a series of parahydroxybenzoates or esters of parahydroxybenzoic acid. Research is being conducted to evaluate the potential health implications of paraben usage.

Nail polish is a lacquer that can be applied to the human fingernail or toenails to decorate and protect the nail plates. The formula has been revised repeatedly to enhance its decorative properties, to be safer for the consumer to use, and to suppress cracking or peeling. Nail polish consists of a mix of an organic polymer and several other components that give it colors and textures. Nail polishes come in all color shades and play a significant part in manicures and pedicures.

Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) is a European Union regulation dating from 18 December 2006. REACH addresses the production and use of chemical substances, and their potential impacts on both human health and the environment. Its 849 pages took seven years to pass, and it has been described as the most complex legislation in the Union's history and the most important in 20 years. It is the strictest law to date regulating chemical substances and will affect industries throughout the world. REACH entered into force on 1 June 2007, with a phased implementation over the next decade. The regulation also established the European Chemicals Agency, which manages the technical, scientific and administrative aspects of REACH.

The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) is a United States law, passed by the 94th United States Congress in 1976 and administered by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), that regulates chemicals not regulated by other U.S. federal statutes, including chemicals already in commerce and the introduction of new chemicals. When the TSCA was put into place, all existing chemicals were considered to be safe for use and subsequently grandfathered in. Its three main objectives are to assess and regulate new commercial chemicals before they enter the market, to regulate chemicals already existing in 1976 that posed an "unreasonable risk of injury to health or the environment", as for example PCBs, lead, mercury and radon, and to regulate these chemicals' distribution and use.
Samuel Seymour Epstein was a physician and, at the time of his death, professor emeritus of environmental and occupational health at the School of Public Health of the University of Illinois at Chicago. He is known for his contributions on avoidable causes of cancer, for which he was given the Right Livelihood Award in 1998. His papers are held at the National Library of Medicine in Bethesda, Maryland.

Permanent makeup, also known as permanent cosmetics, derma-pigmentation, micro-pigmentation, and cosmetic tattooing, is a cosmetic technique which employs tattoos as a means of producing designs that resemble makeup, such as eye-lining and other permanent enhancing colors to the skin of the face, lips, and eyelids. It is also used to produce artificial eyebrows, particularly in people who have lost them as a consequence of old age, disease, such as alopecia totalis, chemotherapy, or a genetic disturbance, and to disguise scars and hypopigmentation in the skin such as in vitiligo. It is also used to restore or enhance the breast's areola, such as after breast surgery.
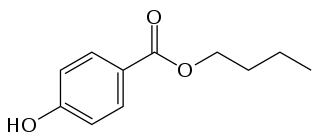
Butylparaben, or butyl p-hydroxybenzoate, is an organic compound with the formula C
4H
9O
2CC
6H
4OH. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It has proven to be a highly successful antimicrobial preservative in cosmetics. It is also used in medication suspensions, and as a flavoring additive in food.

Breast Cancer Action (BCAction) is a U.S.-based grassroots education and activist organization driven by and supporting people living with breast cancer. It was founded in 1990 by Elenore Pred, Susan Claymon, and Linda Reyes. Based in San Francisco, BCAction is known for understanding breast cancer not as an individual crisis, but a public health emergency, and for their commitment to social justice. The organization's mission is to achieve health justice for all women at risk of and living with breast cancer. BCAction is known for its Think Before You Pink campaign, launched in 2002, which encourages consumers to ask critical questions before buying pink ribbon products and holds corporations accountable for pinkwashing.
The Personal Care Products Council (PCPC) is an American trade association. The PCPC was founded in 1894 as the Manufacturing Perfumers' Association, renamed the American Manufacturers of Toilet Articles (AMTA) in 1922, and renamed again as the Cosmetic, Toiletry, and Fragrance Association (CTFA) in 1970. The current name was adopted in November 2007.

A nail salon or nail bar is a specialty beauty salon establishment that primarily offers nail care services such as manicures, pedicures, and nail enhancements. Often, nail salons also offer skin care services. Manicures are also offered by general beauty salons, spas, and hotels. People who work at nail salons are usually called nail technicians, manicurists, or nailists.

Triclocarban is an antibacterial chemical once common in, but now phased out of, personal care products like soaps and lotions. It was originally developed for the medical field. Although the mode of action is unknown, TCC can be effective in fighting infections by targeting the growth of bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. Additional research seeks to understand its potential for causing antibacterial resistance and its effects on organismal and environmental health.
A soap substitute is a natural or synthetic cleaning product used in place of soap or other detergents, typically to reduce environmental impact or health harms or provide other benefits.
The California Green Chemistry Initiative (CGCI) is a six-part initiative to reduce public and environmental exposure to toxins through improved knowledge and regulation of chemicals; two parts became statute in 2008. The other four parts were not passed, but are still on the agenda of the California Department of Toxic Substances Control green ribbon science panel discussions. The two parts of the California Green Chemistry Initiative that were passed are known as AB 1879 : Hazardous Materials and Toxic Substances Evaluation and Regulation and SB 509 : Toxic Information Clearinghouse. Implementation of CGCI has been delayed indefinitely beyond the January 1, 2011.
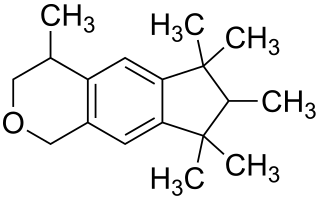
Galaxolide is a synthetic musk with a clean sweet musky floral woody odor used in fragrances. It is one of the musk components that perfume and cologne manufacturers use to add a musk odor to their products. Galaxolide was first synthesized in 1965, and used in the late 1960s in some fabric softeners and detergents. High concentrations were also incorporated in fine fragrances.

The cosmetic industry describes the industry that manufactures and distributes cosmetic products. These include colour cosmetics, like foundation and mascara, skincare such as moisturisers and cleansers, haircare such as shampoos, conditioners and hair colours, and toiletries such as bubble bath and soap. The manufacturing industry is dominated by a small number of multinational corporations that originated in the early 20th century, but the distribution and sale of cosmetics is spread among a wide range of different businesses. Cosmetics must be safe when customers use them in accordance with the label's instructions or in the conventional or expected manner. One measure a producer may take to guarantee the safety of a cosmetic product is product testing. FDA occasionally does testing as part of its research program or when looking into potential safety issues with a product. Both the cosmetics business and consumers can benefit from the FDA's resources on product testing.
Silent Spring Institute is a nonprofit organization dedicated to studying and reporting primarily on breast cancer prevention, although its research covers other health-related topics as well.
Women's Voices for the Earth (WVE) is a feminist, women-led, North American environmental organization that specializes in research and advocacy regarding toxic chemicals used in products that disproportionately impact women's health, including cosmetics, menstrual care products, professional salon and cleaning products. WVE is a non-profit organization whose mission is to amplify women's voices to eliminate toxics that harm communities and health. With its inclusive vision of environmental work WVE has become a hub for visionary feminist environmentalism that recognizes the systemic connections between health, class, race, and the environment. Addressing the inter-connectivity of these various channels of exposure to toxic chemicals has been key to WVE's approach which is multi-scalar: targeting consumer behaviors, corporate practices, and government policies.












