
Carex is a vast genus of over 2,000 species of grass-like plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges. Other members of the family Cyperaceae are also called sedges, however those of genus Carex may be called true sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of Carex is known as caricology.

Carex limosa is a species of sedge known as bog-sedge, mud sedge, and shore sedge.

Carex pauciflora, the few-flowered sedge, is a perennial species of sedge in the family Cyperaceae native to bogs and fens in cool temperate, subarctic, and mountainous regions of the Northern Hemisphere. The specific epithet pauciflora refers to the Latin term for 'few flowered'.
Carex amplifolia is a species of sedge known by the common name bigleaf sedge. It is native to western North America from British Columbia to Montana to California, where it grows in wet and seasonally wet areas in coniferous forests.

Carex buxbaumii is a species of sedge known as Buxbaum's sedge or club sedge. It is native to much of the northern Northern Hemisphere, from Alaska to Greenland to Eurasia, and including most of Canada and the United States. It grows in wet habitat, such as marshes and fens. This sedge grows in clumps from long rhizomes. The stems are 75–100 cm (30–39 in) in maximum height. The leaves are narrow and small. The inflorescence has a bract which is sometimes longer than the spikes. The fruits have dark-colored bracts and a sac called a perigynium or utricle which is gray-green and rough in texture.

Carex comosa is a species of sedge known as longhair sedge and bristly sedge. It is native to North America, where it grows in western and eastern regions of Canada and the United States, and parts of Mexico. It grows in wet places, including meadows and many types of wetlands. Tolerates deeper water than most common species and is good for retention basins. This sedge produces clumps of triangular stems up to 100 or 120 centimeters tall from short rhizomes. The inflorescence is up to 35 centimeters long and has a long bract which is longer than the spikes. It is a cluster of several cylindrical spikes. The scales over the fruits taper into long, thin awns.

Carex diandra is a species of sedge known by the common names lesser tussock-sedge and lesser panicled sedge.

Carex leporina is a species of sedge known in the British Isles as oval sedge and in North America as eggbract sedge. It is native to Eurasia and eastern and western North America, where it grows in seasonally wet habitat, such as meadows and fields. This sedge produces many thin stems and narrow leaves. The inflorescence is an open cluster of several flower spikes. The pistillate flower has a reddish or brownish bract with a gold center and white tip.

Carex vesicaria is an essentially Holarctic species of sedge known as bladder sedge, inflated sedge, and blister sedge. It has been used to insulate footwear in Norway, Sweden and among the Sami people, and for basketry in North America.

Carex disticha is a Eurasian species of sedge known as the brown sedge or, in North America, tworank sedge.

Carex lutea is a rare species of sedge known by the common names golden sedge and sulphur sedge. It is endemic to North Carolina, where it is known only from Pender and Onslow Counties in the Cape Fear River watershed. There are nine populations. The plant was discovered in 1991 and described to science as a new species in 1994, and it has not been thoroughly studied nor completely surveyed yet. Its rarity was obvious by 2002, however, when it was federally listed as an endangered species.

Carex riparia, the greater pond sedge, is a species of sedge found across Europe and Asia. It grows in a variety of wet habitats, and can be a dominant species in some swamps. It is Britain's largest Carex, growing up to 130 cm tall, with glaucous leaves up to 160 cm long. It hybridises with a number of other Carex species, including the closely related Carex acutiformis – the lesser pond sedge. A variegated cultivar is grown as an ornamental grass.

Carex binervis, the green-ribbed sedge, is a European species of sedge with an Atlantic distribution. It is found from Fennoscandia to the Iberian Peninsula, and occurs in heaths, moorland and other damp, acidic environments. It typically grows to a height of 15–120 cm (6–50 in), and has inflorescences comprising one male and several female spikes, each up to 45 mm (1.8 in) long. The utricles have two conspicuous green veins, which give rise to both the scientific name and the common name of the species. In the vegetative state, it closely resembles C. bigelowii, a species that usually grows at higher altitude. C. binervis was first described by James Edward Smith in 1800, and is classified in Carex sect. Spirostachyae; several hybrids with other Carex species are known.

Carex bigelowii is a species of sedge known by the common names Bigelow's sedge, Gwanmo sedge, and stiff sedge. It has an Arctic–alpine distribution in Eurasia and North America, and grows up to 50 centimetres (20 in) tall in a variety of habitats.
Fox sedge is a common name for several plants and may refer to:

Carex simpliciuscula is a species of sedge known by the common names false sedge, simple bog sedge and simple kobresia. It has a circumpolar distribution, occurring throughout the northern latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere.

Carex otrubae, the false fox-sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae.
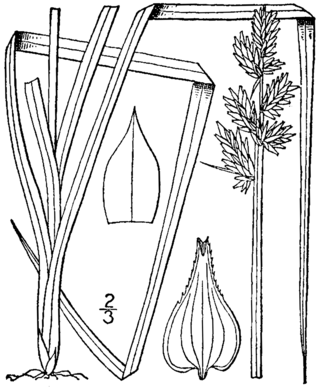
Carex conjuncta, known as soft fox sedge, is a species of sedge that was first formally named by Francis Boott in 1862. It is endemic to the central and eastern United States.
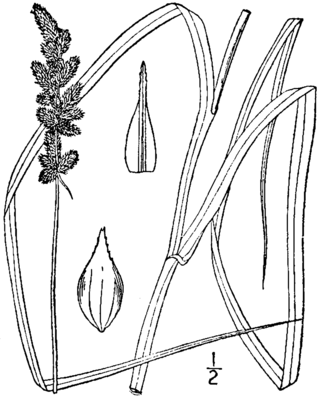
Carex annectens, sometimes called yellow-fruited fox sedge, is a species of sedge native to most of the eastern United States and southeastern Canada. It is common in prairies and high-water table fallow fields. In the Chicago area, its coefficient of conservatism is 3, and in Michigan, it is only 1, indicating its relatively low fidelity to high quality habitats.

Carex bicolor, the bicoloured sedge, is a species of sedge native to North America, Northern Europe and Northern Asia. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed the plant's conservation status as being of least concern because it has a widespread distribution and faces no particular threats.



















