Microcephaly is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it may develop in the first few years of life. Brain development is often affected; people with this disorder often have an intellectual disability, poor motor function, poor speech, abnormal facial features, seizures and dwarfism.

X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is a rare genetic disorder discovered in 1952 that affects the body's ability to fight infection. As the form of agammaglobulinemia that is X-linked, it is much more common in males. In people with XLA, the white blood cell formation process does not generate mature B cells, which manifests as a complete or near-complete lack of proteins called gamma globulins, including antibodies, in their bloodstream. B cells are part of the immune system and normally manufacture antibodies, which defend the body from infections by sustaining a humoral immunity response. Patients with untreated XLA are prone to develop serious and even fatal infections. A mutation occurs at the Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) gene that leads to a severe block in B cell development and a reduced immunoglobulin production in the serum. Btk is particularly responsible for mediating B cell development and maturation through a signaling effect on the B cell receptor BCR. Patients typically present in early childhood with recurrent infections, in particular with extracellular, encapsulated bacteria. XLA is deemed to have a relatively low incidence of disease, with an occurrence rate of approximately 1 in 200,000 live births and a frequency of about 1 in 100,000 male newborns. It has no ethnic predisposition. XLA is treated by infusion of human antibody. Treatment with pooled gamma globulin cannot restore a functional population of B cells, but it is sufficient to reduce the severity and number of infections due to the passive immunity granted by the exogenous antibodies.
Hypogammaglobulinemia is an immune system disorder in which not enough gamma globulins are produced in the blood. This results in a lower antibody count, which impairs the immune system, increasing risk of infection. Hypogammaglobulinemia may result from a variety of primary genetic immune system defects, such as common variable immunodeficiency, or it may be caused by secondary effects such as medication, blood cancer, or poor nutrition, or loss of gamma globulins in urine, as in nonselective glomerular proteinuria. Patients with hypogammaglobulinemia have reduced immune function; important considerations include avoiding use of live vaccines, and take precautionary measures when traveling to regions with endemic disease or poor sanitation such as receiving immunizations, taking antibiotics abroad, drinking only safe or boiled water, arranging appropriate medical cover in advance of travel, and ensuring continuation of any immunoglobulin infusions needed.

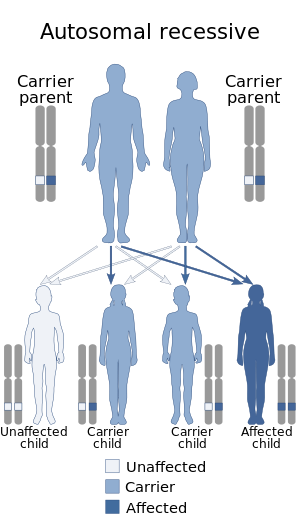
Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS) is a rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder causing chromosomal instability, probably as a result of a defect in the double Holliday junction DNA repair mechanism and/or the synthesis dependent strand annealing mechanism for repairing double strand breaks in DNA.

ZAP70 deficiency, or ZAP70 deficient SCID, is a rare autosomal recessive form of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) resulting in a lack of CD8+ T cells. People with this disease lack the capability to fight infections, and it is fatal if untreated.

Short-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency (SCADD) is an autosomal recessive fatty acid oxidation disorder which affects enzymes required to break down a certain group of fats called short chain fatty acids.

Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by the appearance of succinylaminoimidazolecarboxamide riboside and succinyladenosine (S-Ado) in cerebrospinal fluid, urine. These two succinylpurines are the dephosphorylated derivatives of SAICA ribotide (SAICAR) and adenylosuccinate (S-AMP), the two substrates of adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL), which catalyzes an important reaction in the de novo pathway of purine biosynthesis. ADSL catalyzes two distinct reactions in the synthesis of purine nucleotides, both of which involve the β-elimination of fumarate to produce aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide (AICAR) from SAICAR or adenosine monophosphate (AMP) from S-AMP.

Bare lymphocyte syndrome type II is a rare recessive genetic condition in which a group of genes called major histocompatibility complex class II are not expressed. The result is that the immune system is severely compromised and cannot effectively fight infection.
Hyper IgM syndrome is a rare primary immune deficiency disorders characterized by low or absent levels of serum IgG, IgA, IgE and normal or increased levels of serum IgM.

Hyper IgM Syndrome Type 2 is a rare disease. Unlike other hyper-IgM syndromes, Type 2 patients identified thus far did not present with a history of opportunistic infections. One would expect opportunistic infections in any immunodeficiency syndrome. The responsible genetic lesion is in the AICDA gene found at 12p13.

The fifth type of hyper-IgM syndrome has been characterized in three patients from France and Japan. The symptoms are similar to hyper IgM syndrome type 2, but the AICDA gene is intact.
Non-homologous end-joining factor 1 (NHEJ1), also known as Cernunnos or XRCC4-like factor (XLF), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NHEJ1 gene. XLF was originally discovered as the protein mutated in five patients with growth retardation, microcephaly, and immunodeficiency. The protein is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair. Patients with XLF mutations also have immunodeficiency due to a defect in V(D)J recombination, which uses NHEJ to generate diversity in the antibody repertoire of the immune system. XLF interacts with DNA ligase IV and XRCC4 and is thought to be involved in the end-bridging or ligation steps of NHEJ. The yeast homolog of XLF is Nej1.

Hyper-IgM syndrome type 3 is a form of hyper IgM syndrome characterized by mutations of the CD40 gene. In this type, Immature B cells cannot receive signal 2 from helper T cells which is necessary to mature into mature B cells.

Hyper-IgM syndrome type 4 is a form of Hyper IgM syndrome which is a defect in class switch recombination downstream of the AICDA gene that does not impair somatic hypermutation.

Deficiency of the interleukin-1–receptor antagonist (DIRA) is an autosomal recessive, genetic autoinflammatory syndrome resulting from mutations in IL1RN, the gene encoding the interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. The mutations result in an abnormal protein that is not secreted, exposing the cells to unopposed interleukin 1 activity. This results in sterile multifocal osteomyelitis, periostitis, and pustulosis due to skin inflammation from birth.
JAK3 deficiency is a dysfunction in cytokine receptor signalling and their production of cytokines.

DOCK8 deficiency, also called DOCK8 immunodeficiency syndrome, is the autosomal recessive form of hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome, a genetic disorder characterized by elevated immunoglobulin E levels, eosinophilia, and recurrent infections with staphylococcus and viruses. It is caused by a mutation in the DOCK8 gene.
STAT3 GOF is a rare genetic disorder of the immune system. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a transcription factor which is encoded by the STAT3 gene in humans. Germline gain-of-function (GOF) mutations in the gene STAT3 causes this early-onset autoimmune disease characterized by lymphadenopathy, autoimmune cytopenias, multiorgan autoimmunity, infections, eczema, and short stature. Investigations conducted by Sarah E Flanagan and Mark Russell from the Institute of Biomedical and Clinical Science, University of Exeter Medical School, Emma Haapaniemi from the Institute of Biomedical and Clinical Science, University of Exeter Medical Schoolby, and Joshua Milner from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, National Institutes of Health have described this condition in 19 patients.
Fryns-Aftimos syndrome is a rare chromosomal condition and is associated with pachygyria, severe mental retardation, epilepsy and characteristic facial features. This syndrome is a malformation syndrome, characterized by numerous facial dysmorphias not limited to hypertelorism, iris or retinal coloboma, cleft lip, and congenital heart defects. This syndrome has been seen in 30 unrelated people. Characterized by a de novo mutation located on chromosome 7p22, there is typically no family history prior to onset. The severity of the disorder can be determined by the size of the deletion on 7p22, enveloping the ACTB gene and surrounding genes, which is consistent with a contiguous gene deletion syndrome. Confirming a diagnosis of Fryns-Aftimos syndrome typically consists of serial single-gene testing or multigene panel of genes of interest or exome sequencing.
Filippi syndrome, also known as Syndactyly Type I with Microcephaly and Mental Retardation, is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic disease. Only a very limited number of cases have been reported to date. Filippi Syndrome is associated with diverse symptoms of varying severity across affected individuals, for example malformation of digits, craniofacial abnormalities, intellectual disability, and growth retardation. The diagnosis of Filippi Syndrome can be done through clinical observation, radiography, and genetic testing. Filippi Syndrome cannot be cured directly as of 2022, hence the main focus of treatments is on tackling the symptoms observed on affected individuals. It was first reported in 1985.